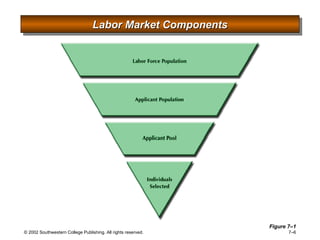
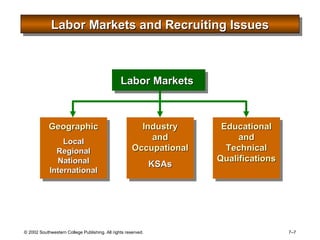
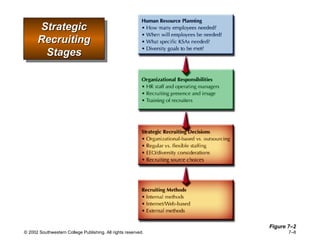
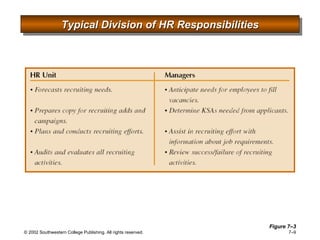
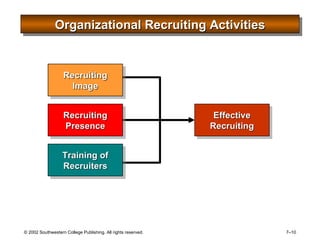
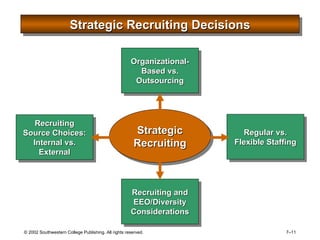
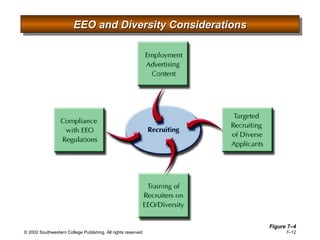
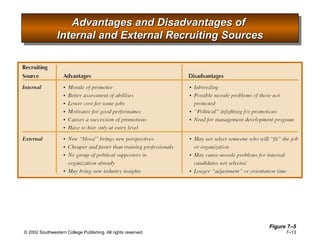
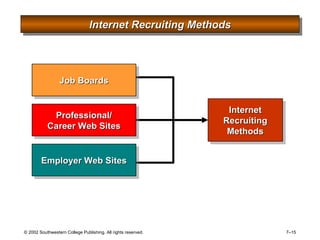
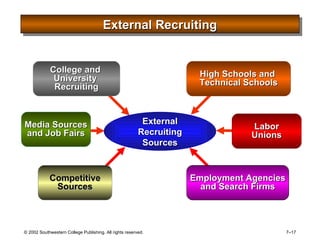
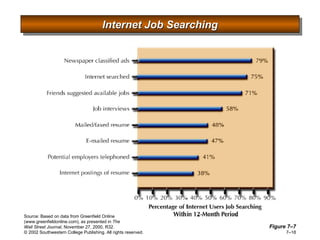
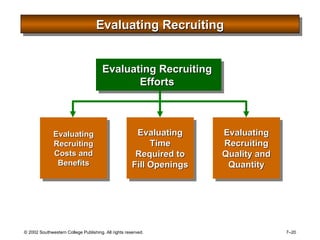
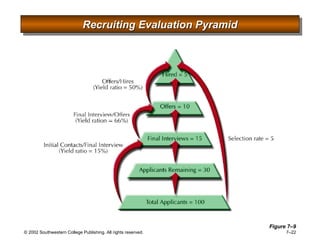
This document is a PowerPoint presentation focused on staffing and recruiting in human resource management. It outlines key concepts of recruiting within labor markets, strategic recruiting phases, and the pros and cons of internal versus external recruiting sources. The document also discusses the importance of internet recruiting and provides insights into evaluating recruiting efforts, including metrics and methods for assessing applicant quality and recruitment effectiveness.