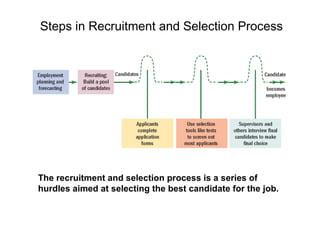
The document outlines the recruitment and selection process, which includes determining personnel needs through planning and forecasting, recruiting candidates from internal and external sources, screening candidates through interviews and assessments, and making offers to the best candidates. It provides details on factors to consider in personnel forecasting, effective recruitment strategies, and ensuring diversity in the hiring process. The goal of the process is to select the most qualified candidates to fill open positions.