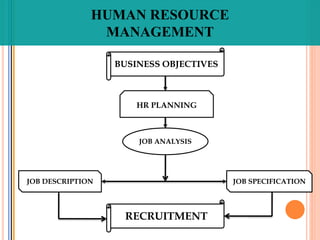
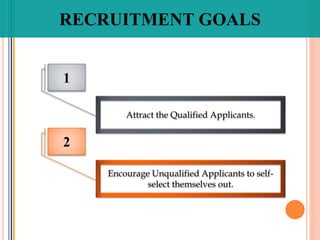
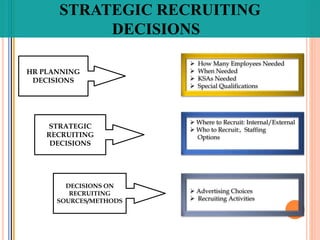
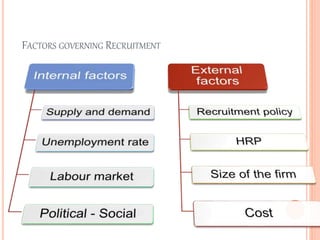
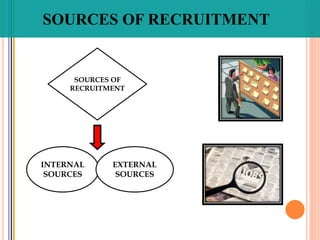
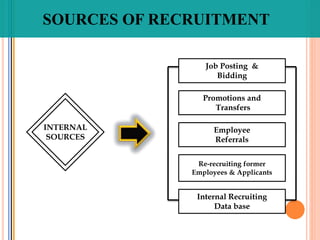
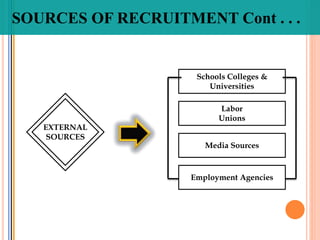
The document discusses recruitment and the recruitment process. It defines recruitment as the process of attracting job applicants and encouraging them to apply for open positions within an organization. The document outlines internal and external sources for recruitment, including current employees, former employees, schools and job sites. It also discusses different recruitment methods such as job postings, employee referrals, advertising, and the use of employment agencies. The goal of recruitment is to attract qualified candidates and encourage unqualified ones to self-select out of the application process.