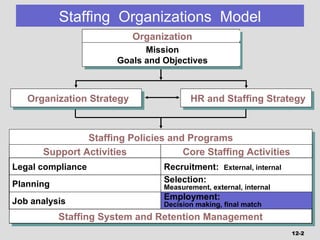
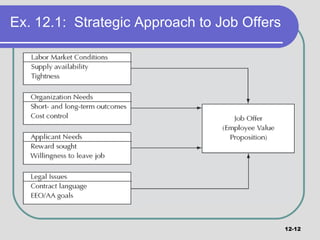
The document discusses various aspects of staffing activities, including finalizing employment matches. It covers requirements for enforceable employment contracts, such as having clear parties, consideration, and form. Job offers should be formulated strategically based on labor market factors and applicant preferences. The job offer content, process of formulation, and presentation are explained. New employee orientation and socialization programs are also reviewed. Legal compliance with issues like eligibility verification must also be considered.