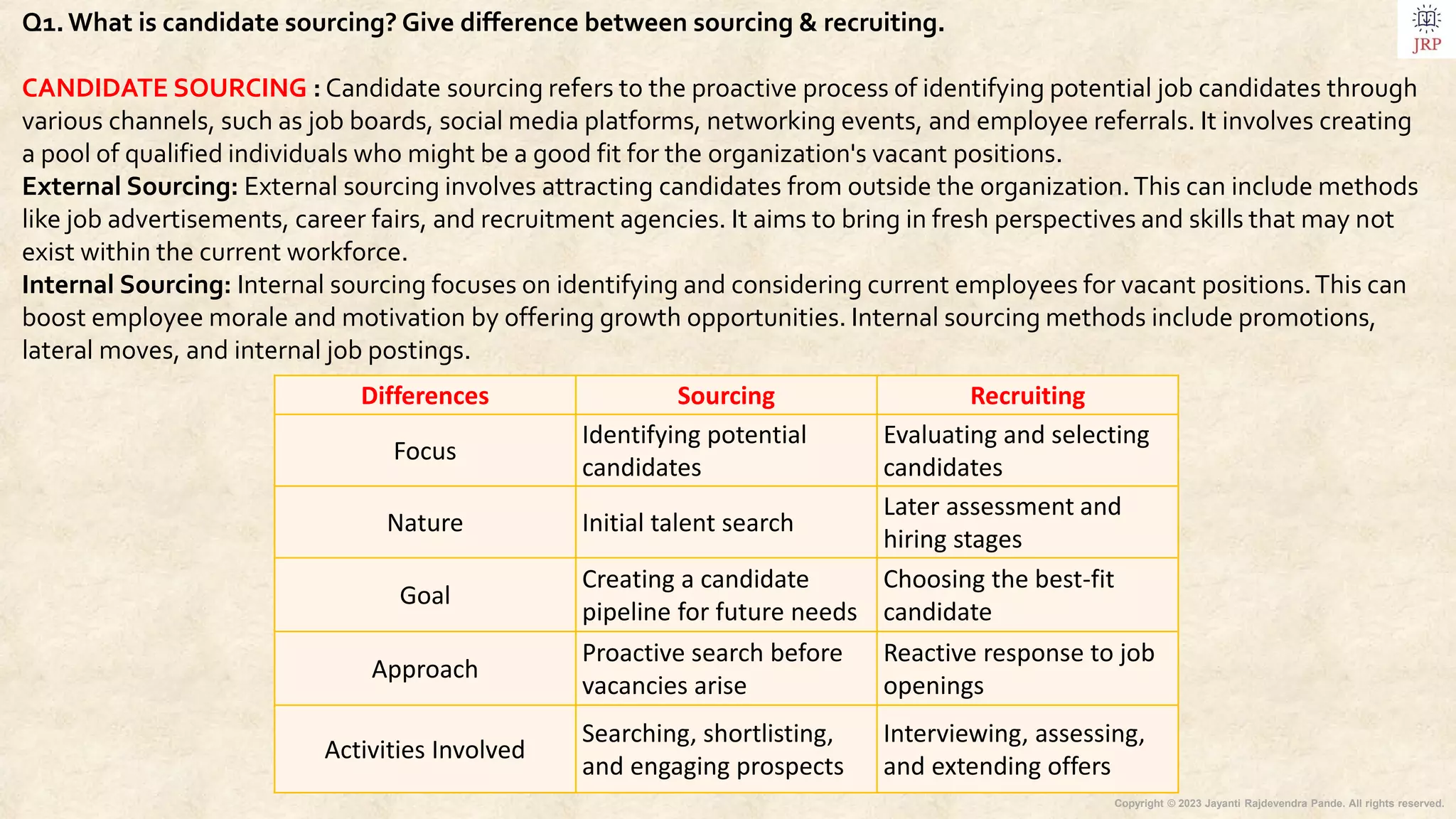
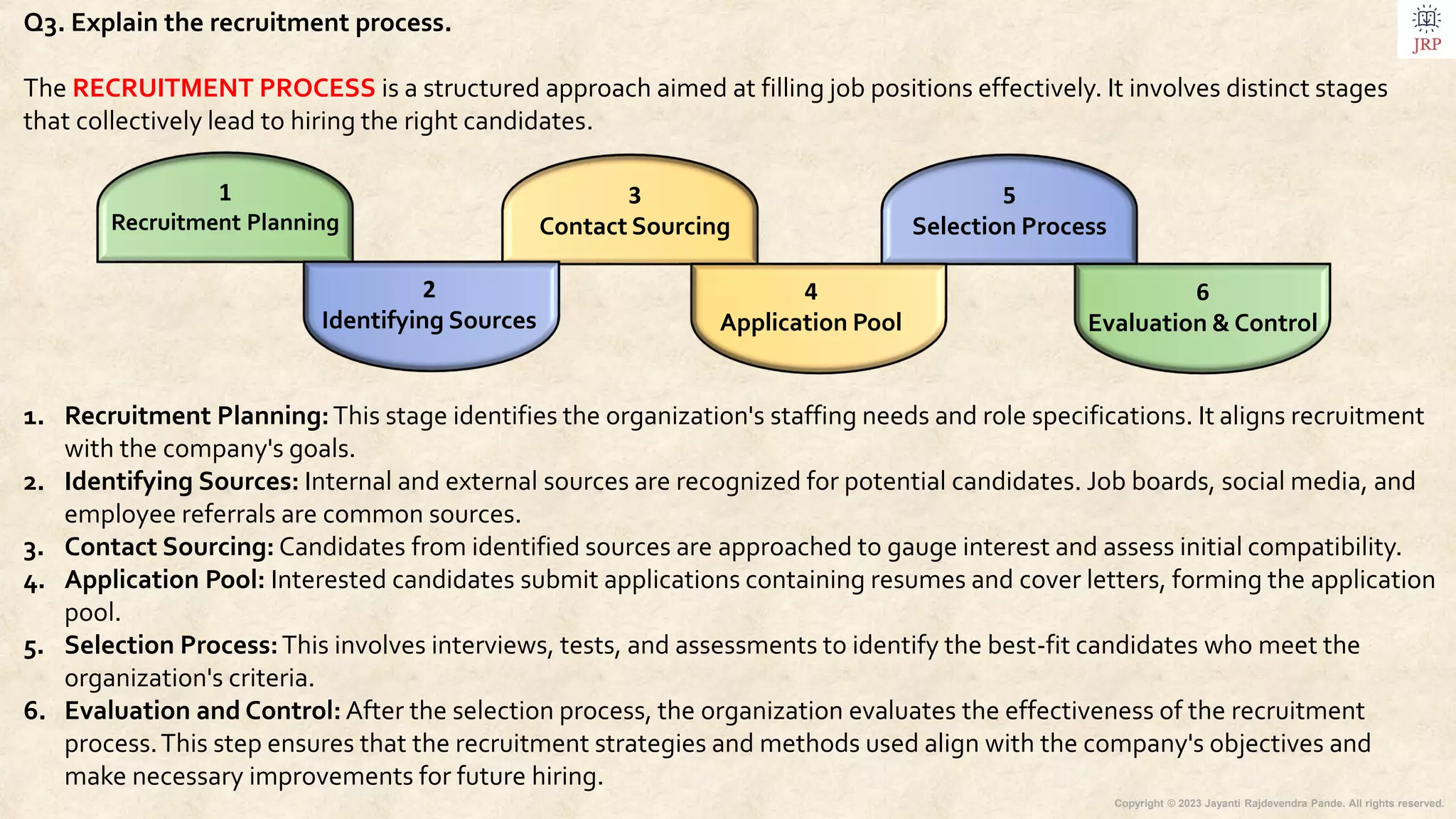
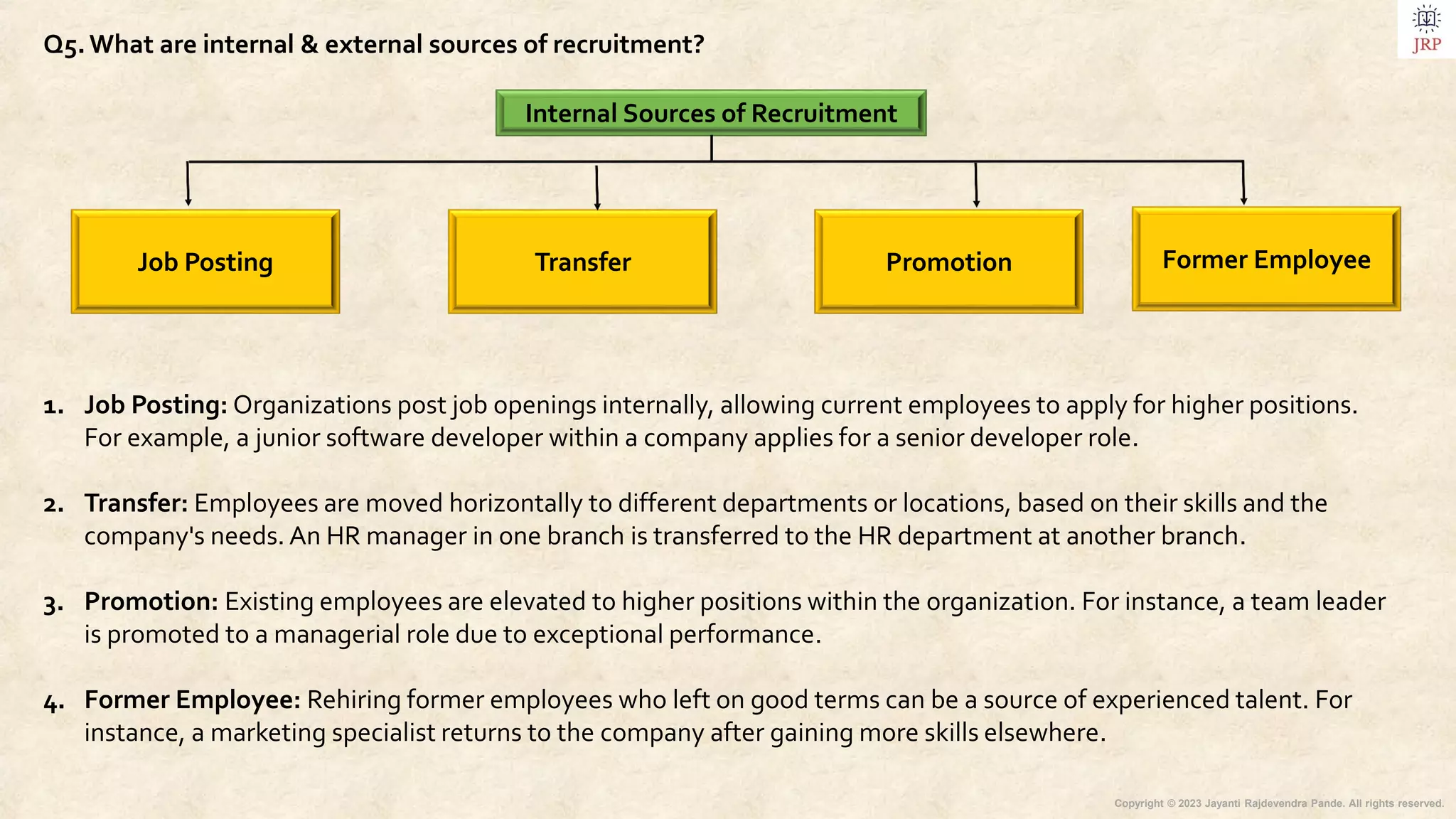
The document outlines the process of recruiting and selecting human resources, detailing candidate sourcing, recruitment features, and the structured stages involved in recruitment, such as planning and selection. It highlights internal and external sourcing methods, strategic approaches, centralized and decentralized recruitment, and modern recruitment techniques including e-recruitment and social media engagement. Additionally, it differentiates between recruitment and selection, emphasizes the importance of evaluation in recruitment programs, and discusses recent trends and barriers in the selection process.