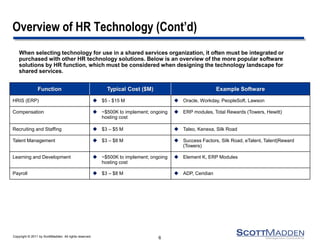
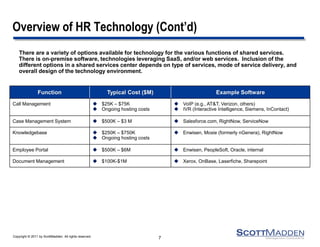
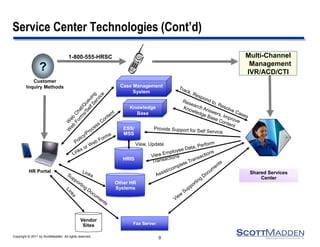
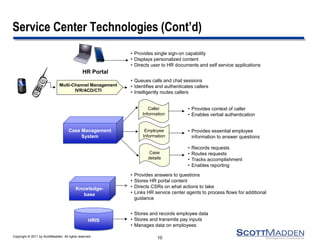
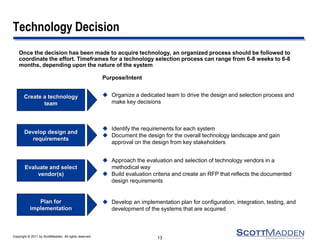
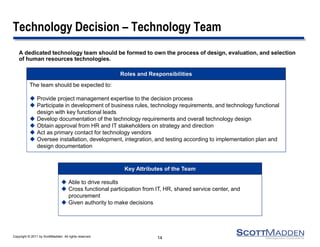
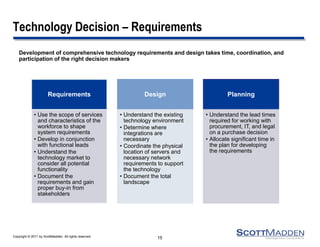
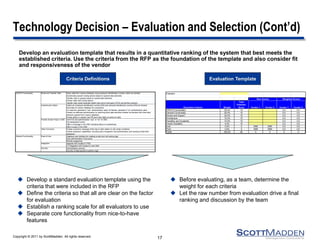
The document discusses key concepts and considerations in selecting technology for HR shared services, focusing on different types of HR technologies, their costs, and integration options. It highlights the importance of a structured decision-making process, involving a dedicated technology team, comprehensive requirements development, and careful evaluation of vendors. The document also outlines lessons learned from previous implementations to inform better decision-making in HR technology design and selection.