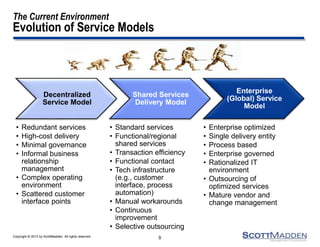
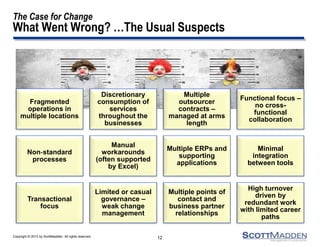
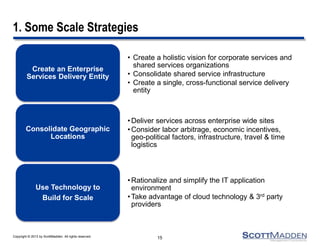
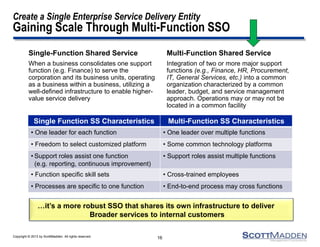
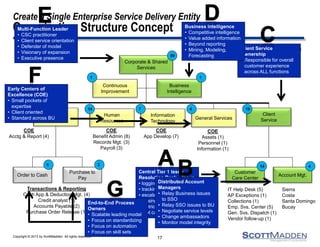
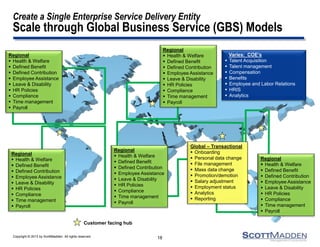
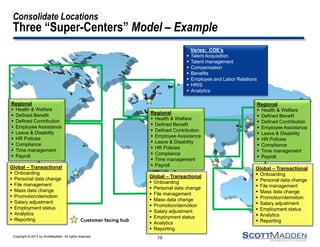
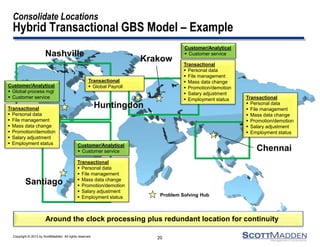
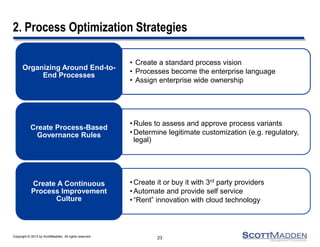
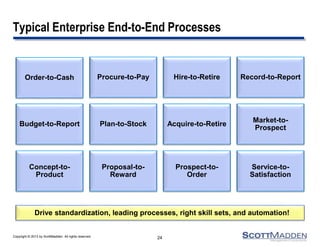
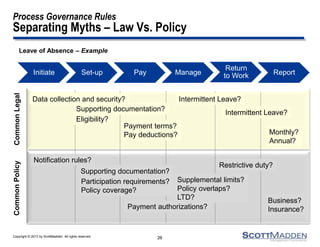
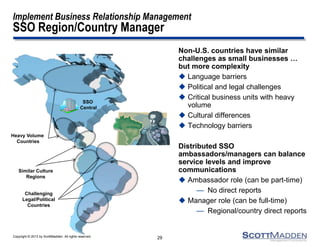
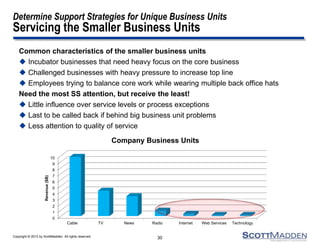
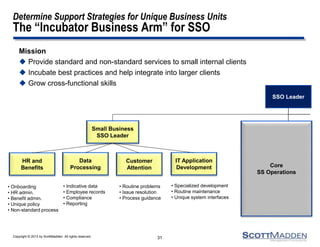
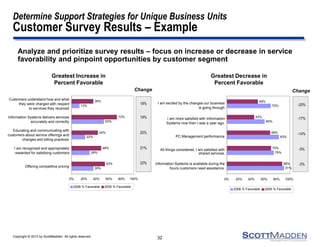
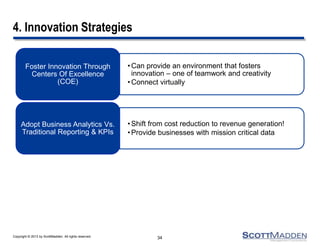
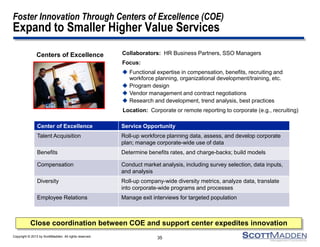
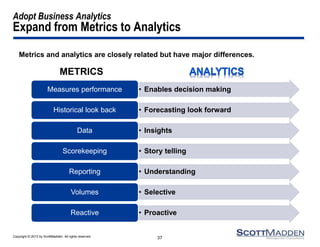
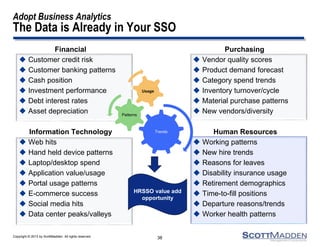
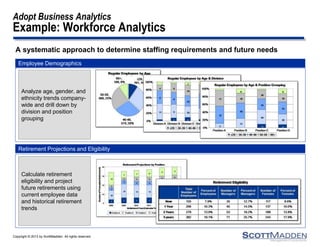
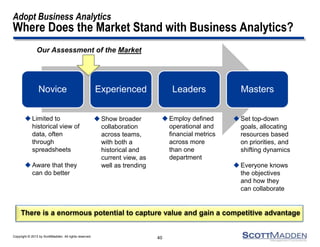
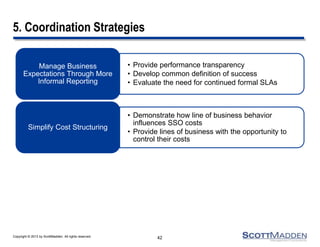
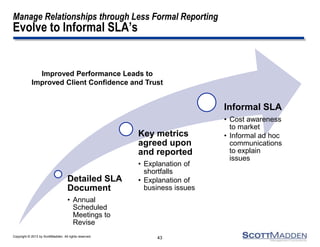
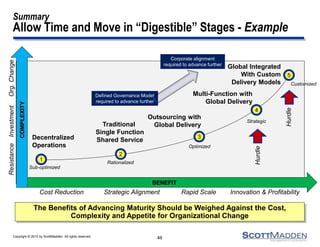
The document discusses a webinar on the evolution and transformation of shared services centers, emphasizing the shift from cost-saving models to more strategic, flexible, and technology-driven frameworks. It outlines the current state of shared services, the challenges organizations face, and the guiding principles for creating more efficient, multi-functional service delivery models. The presentation includes insights into process optimization, business responsiveness, and the importance of alignment with broader corporate objectives.