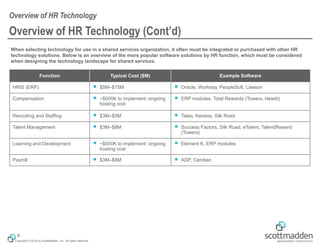
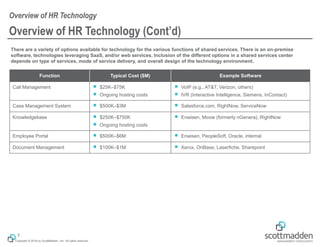
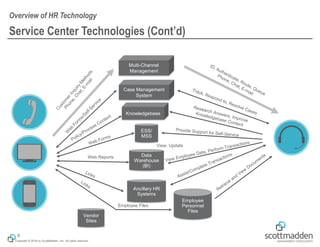
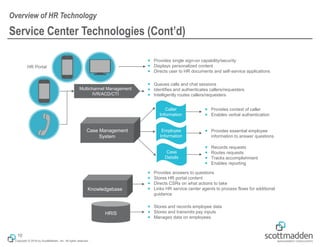
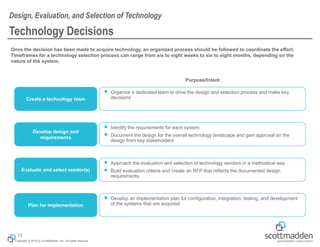
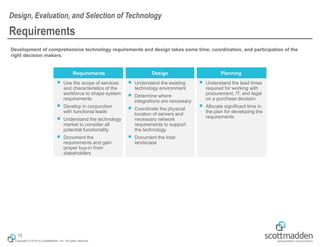
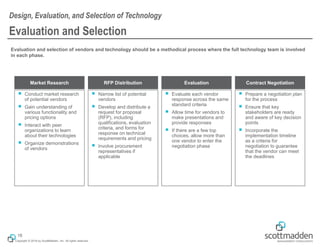
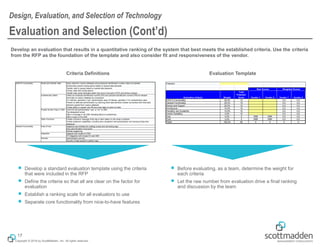
The document discusses key concepts in HR shared services technology, focusing on the design, evaluation, and selection of technology for HR functions. It outlines various categories of HR technology, trends in the field, and a structured approach for technology decision-making, including forming a dedicated technology team and conducting thorough evaluations. Additionally, it highlights lessons learned from past implementations to ensure successful adoption of technology solutions.