This document provides an overview of solving inequalities, including:
1) The principles for solving inequalities are similar to equations but the direction of the inequality changes when multiplying or dividing by a negative number.
2) Interval notation is used to represent the solutions of inequalities on the number line.
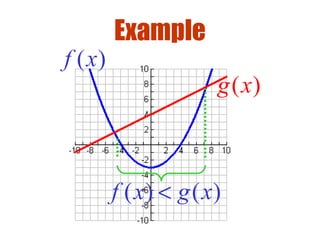
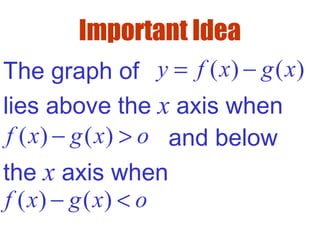
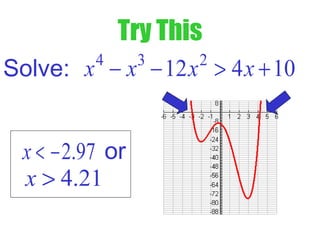
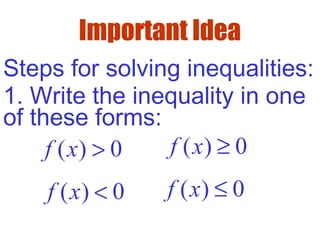
3) To solve inequalities, determine the zeros of the function and where the graph is above or below the x-axis to identify the intervals of solutions.


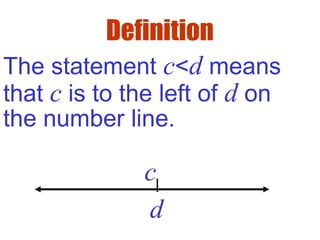
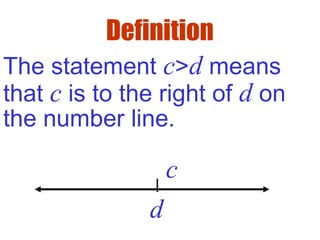


![Definition
( ),c d c x d⇔ < <
( ],c d c x d⇔ < ≤
Interval Notation:Let x,c & d
be real numbers with c<d:
[ ],c d c x d⇔ ≤ ≤
[ ),c d c x d⇔ ≤ <](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hprec2-5-130803105549-phpapp01/85/Hprec2-5-7-320.jpg)

![Try This
Write the following using
interval notation:
3 8x< ≤
( ]3,8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hprec2-5-130803105549-phpapp01/85/Hprec2-5-9-320.jpg)





![Try This
5 2 1 7x x− ≤ − ≤ +
[ ]2,8−
Solve. Write your answer
using interval notation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hprec2-5-130803105549-phpapp01/85/Hprec2-5-15-320.jpg)