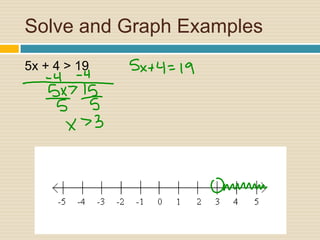
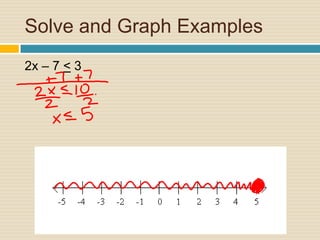
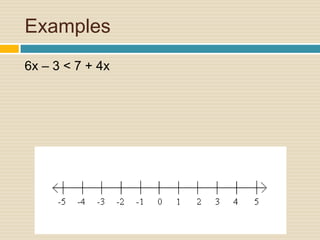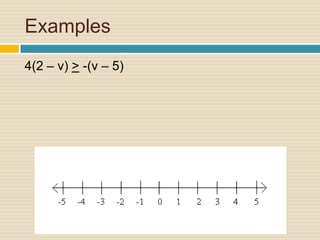This document provides information and examples about solving inequalities:
1) It gives examples of solving linear equations with one variable and two variables.
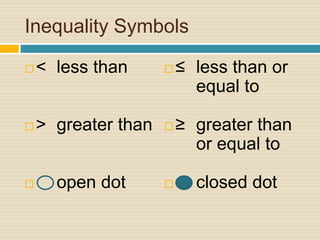
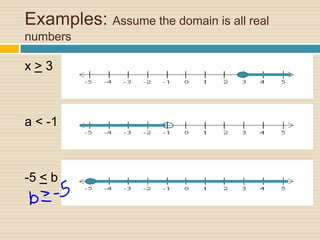
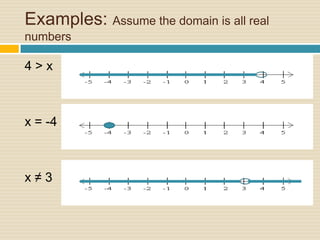
2) It explains the symbols used for different inequality types and how to graph them, including shading the correct side of the inequality.
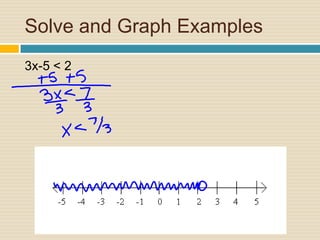
3) It provides rules for solving inequalities, such as reversing the inequality sign when multiplying or dividing both sides by a negative number.
4) Multiple examples are worked through step-by-step of solving and graphing various inequalities with one variable and multiple variables.