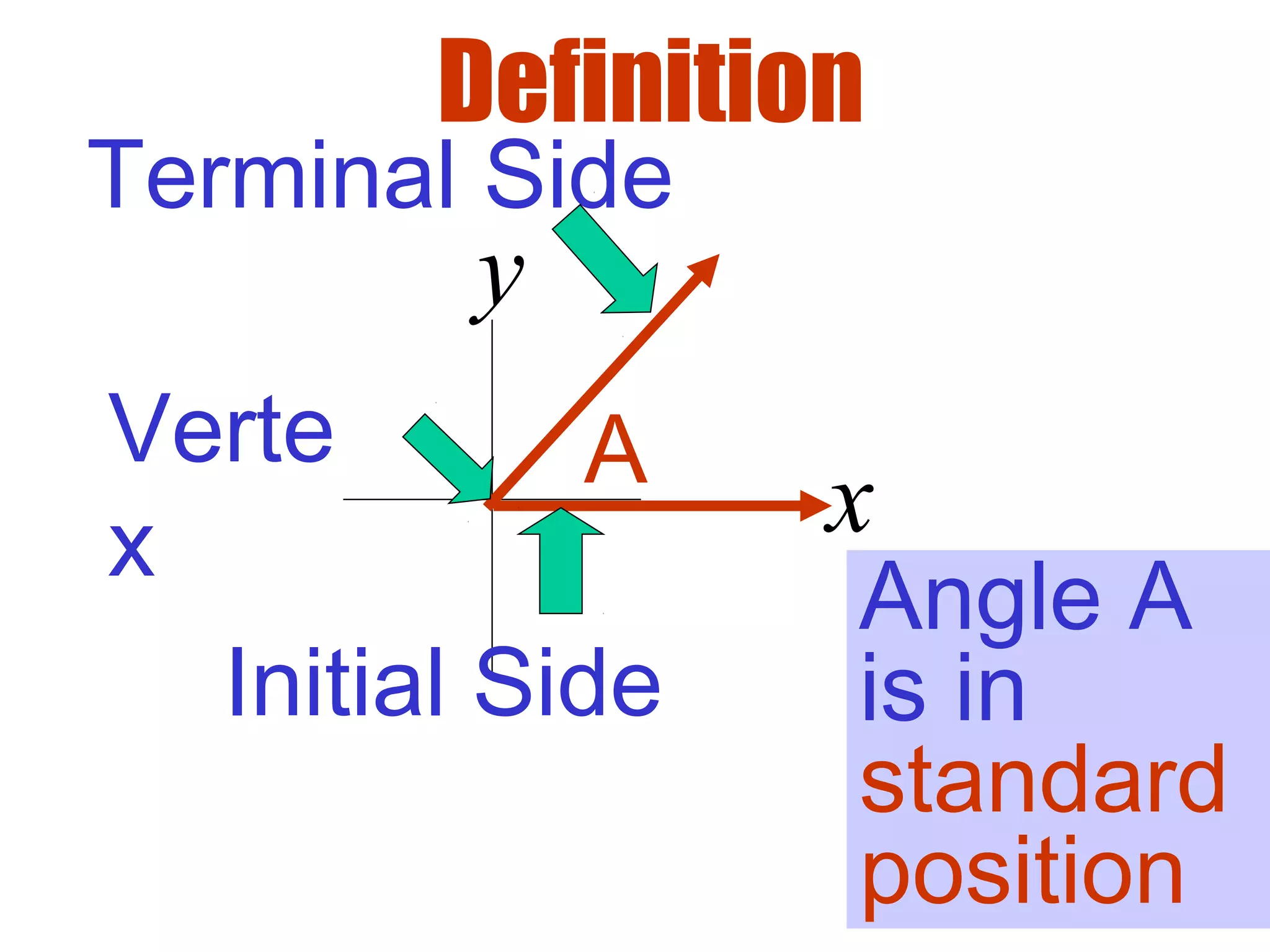
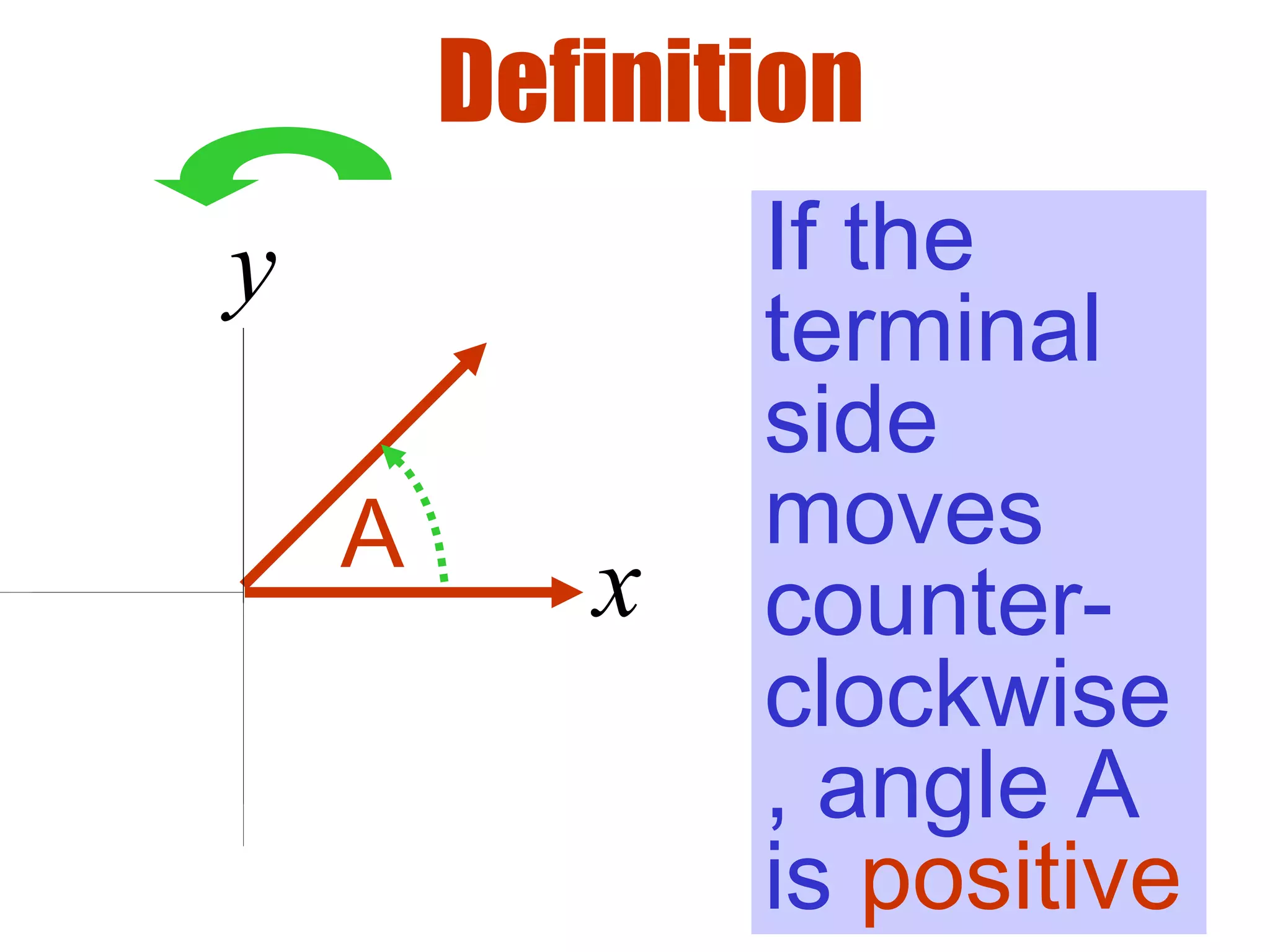
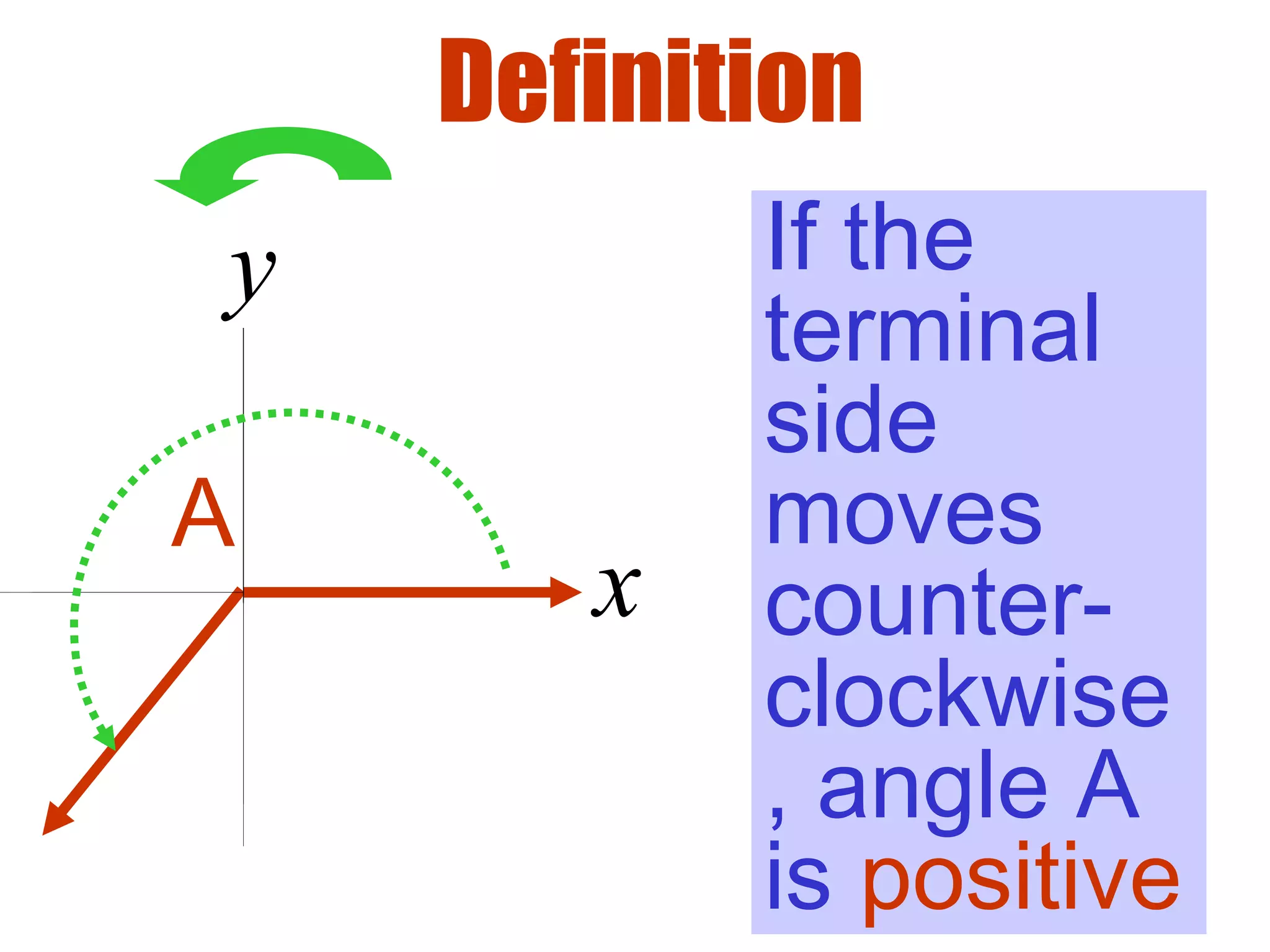
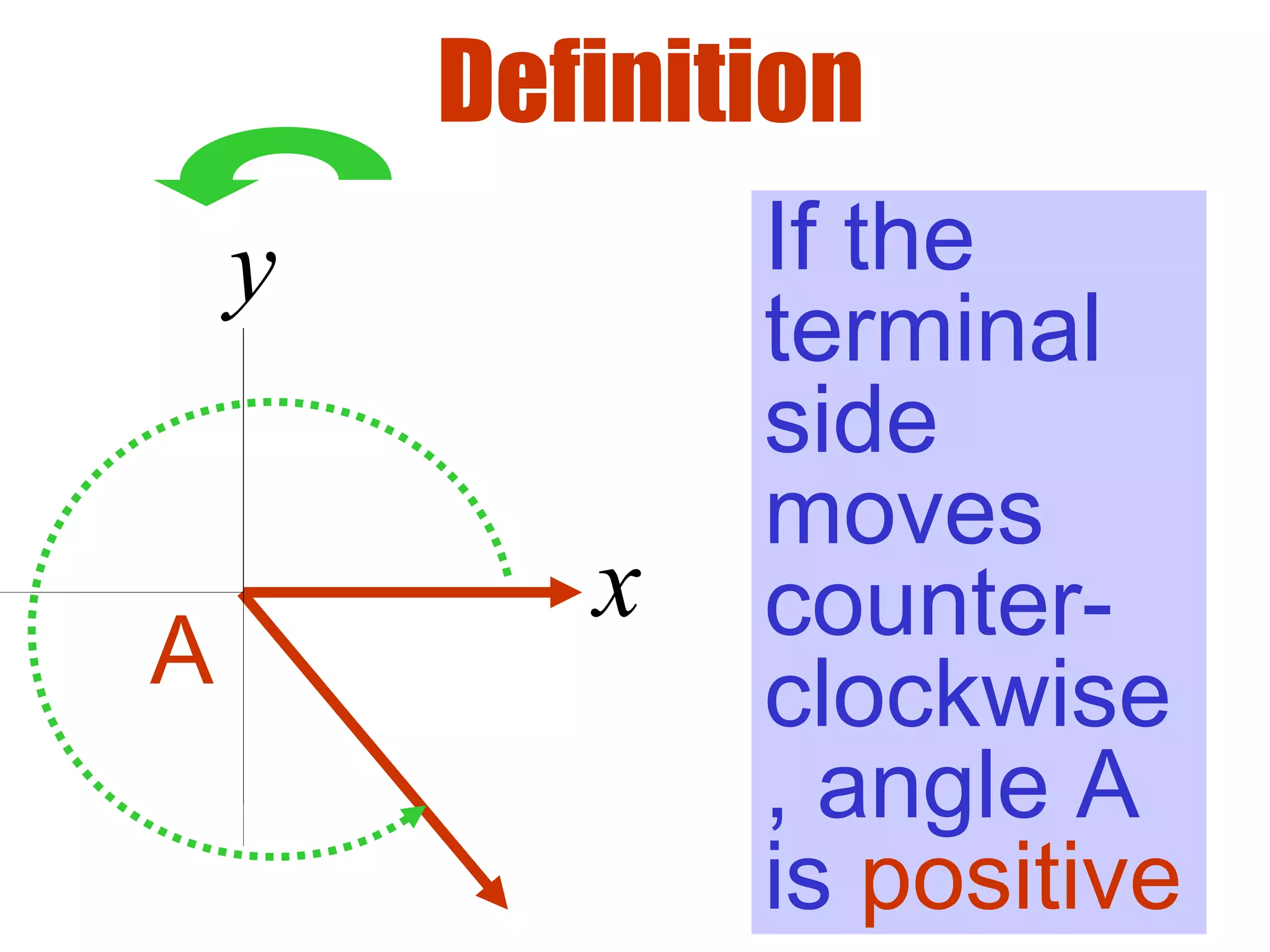
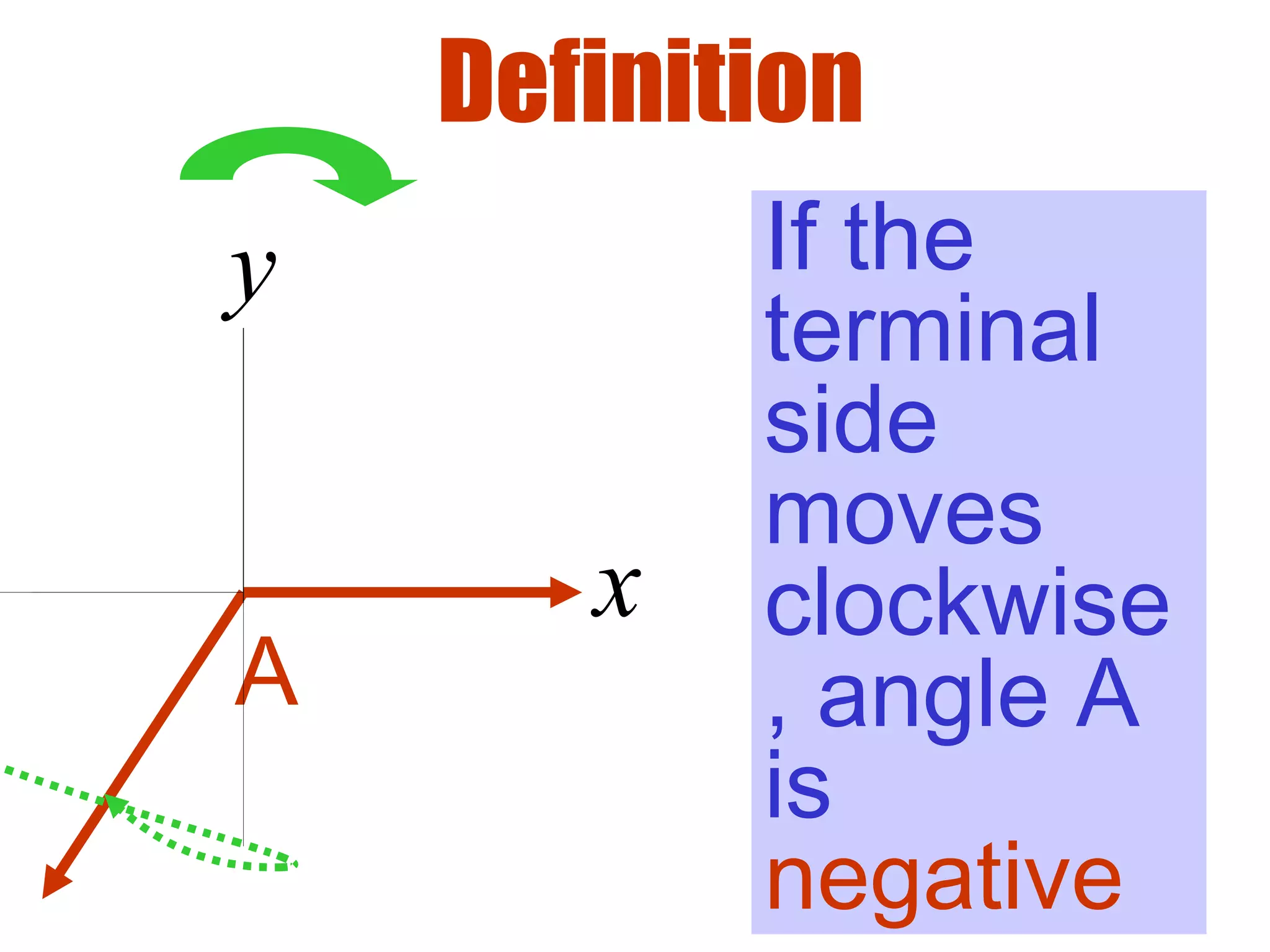
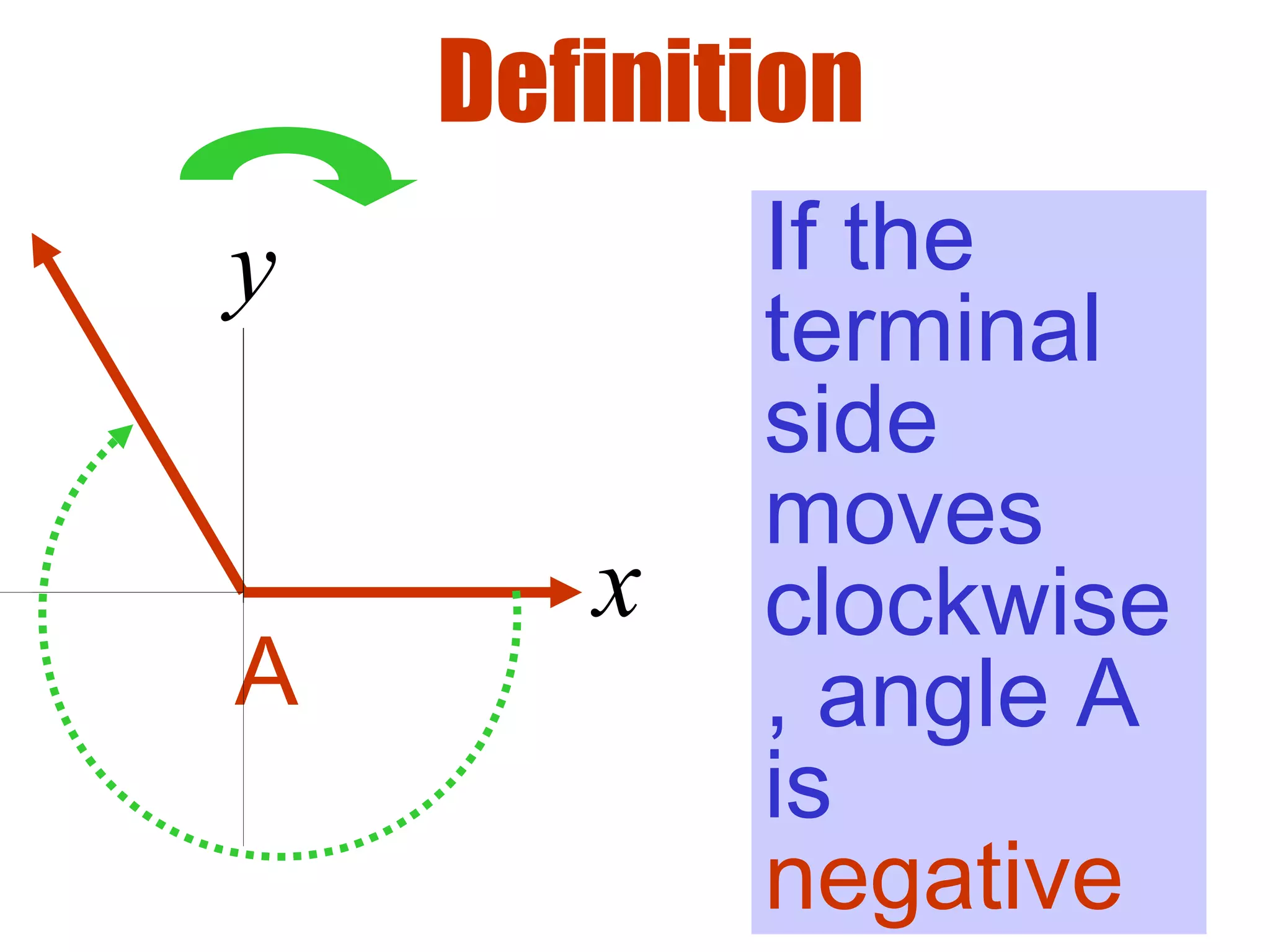
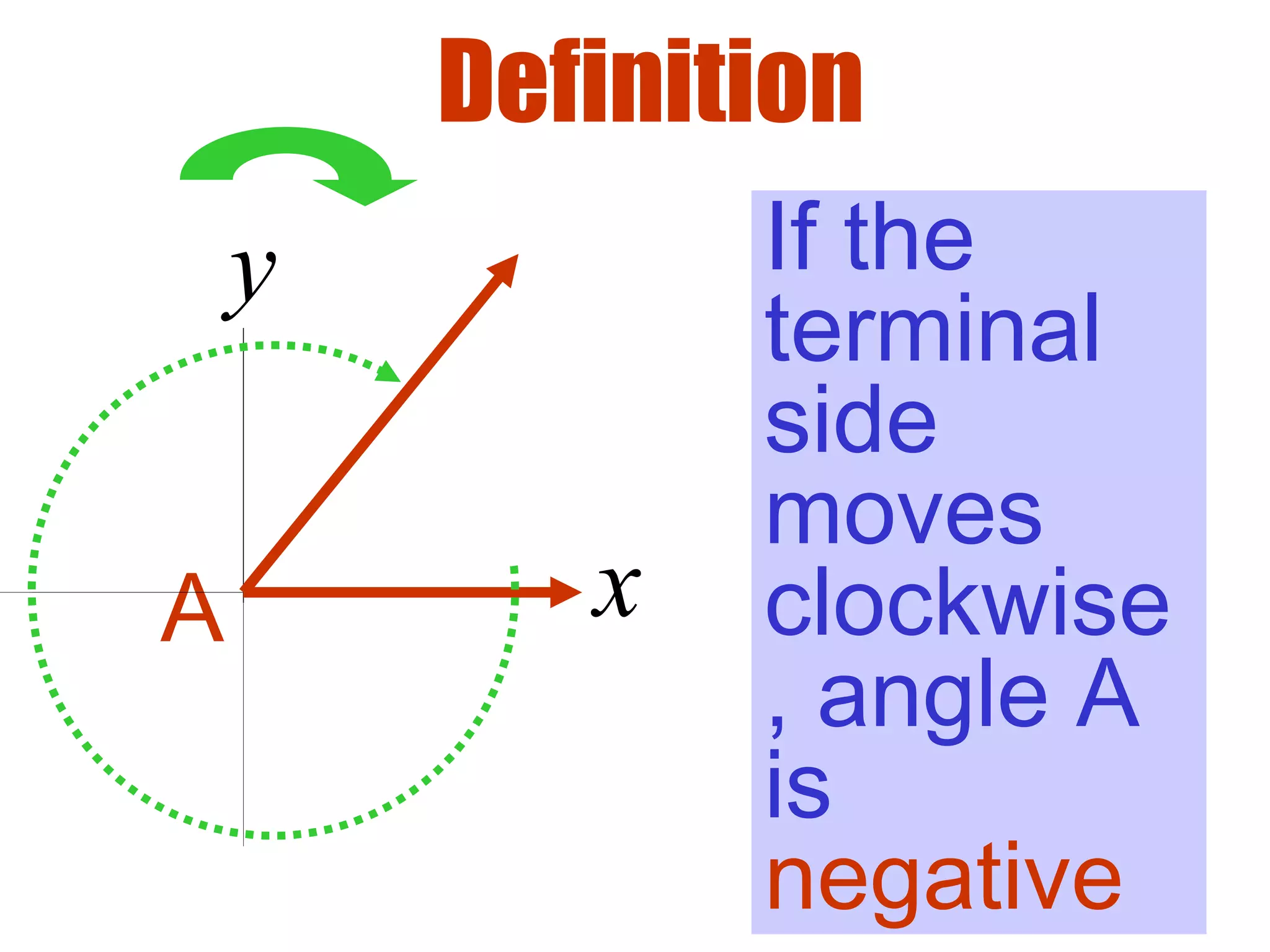
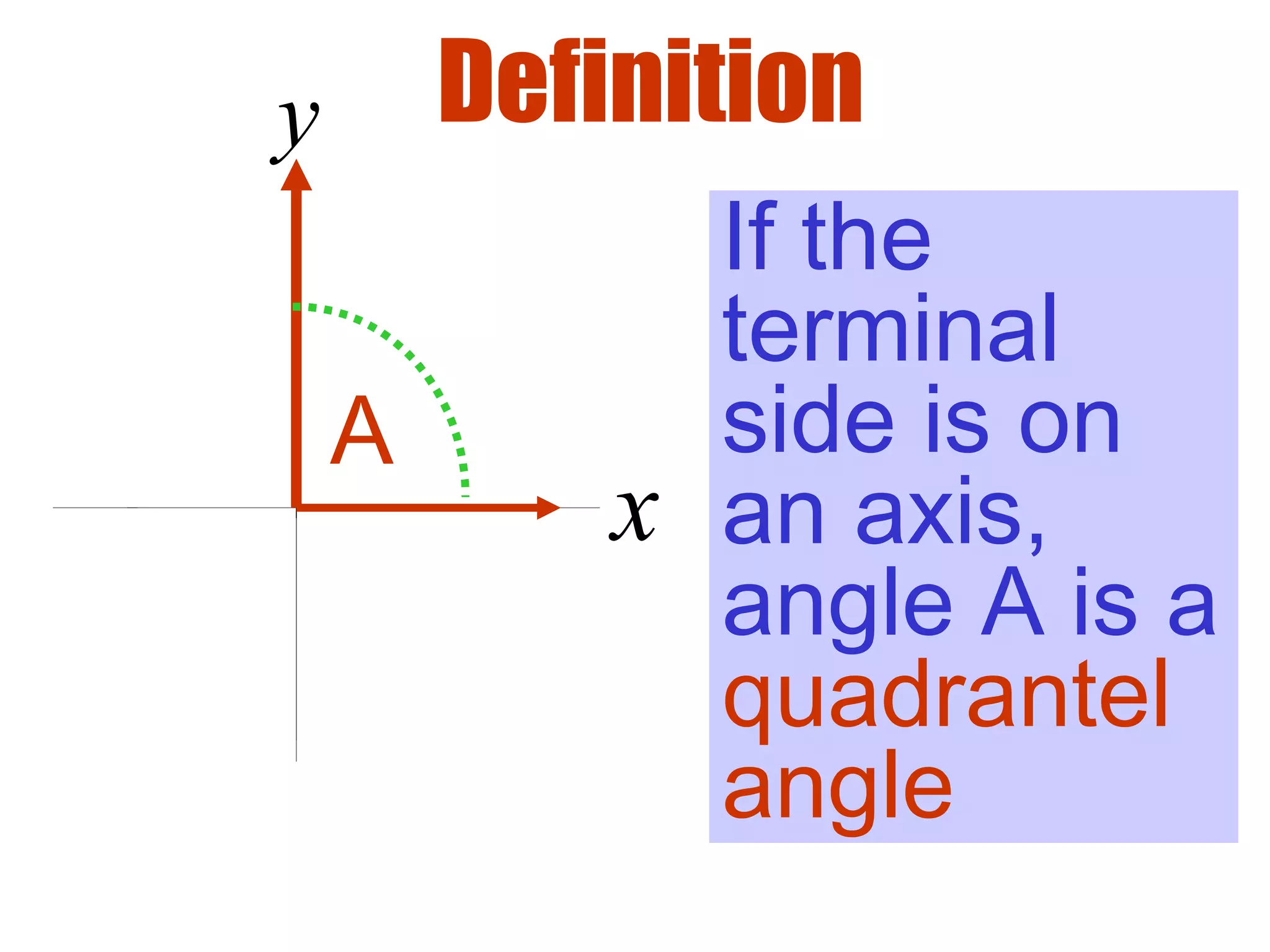
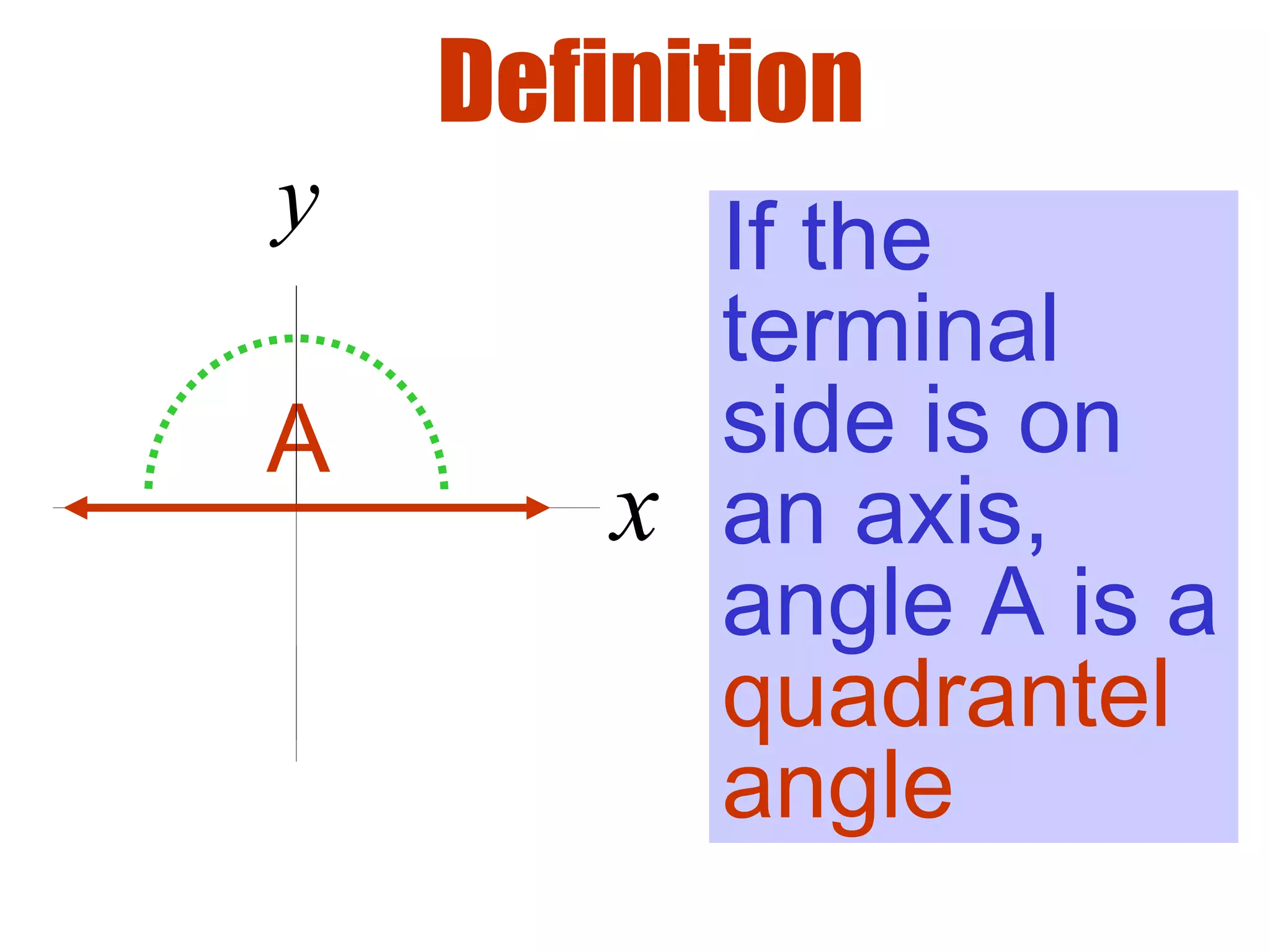
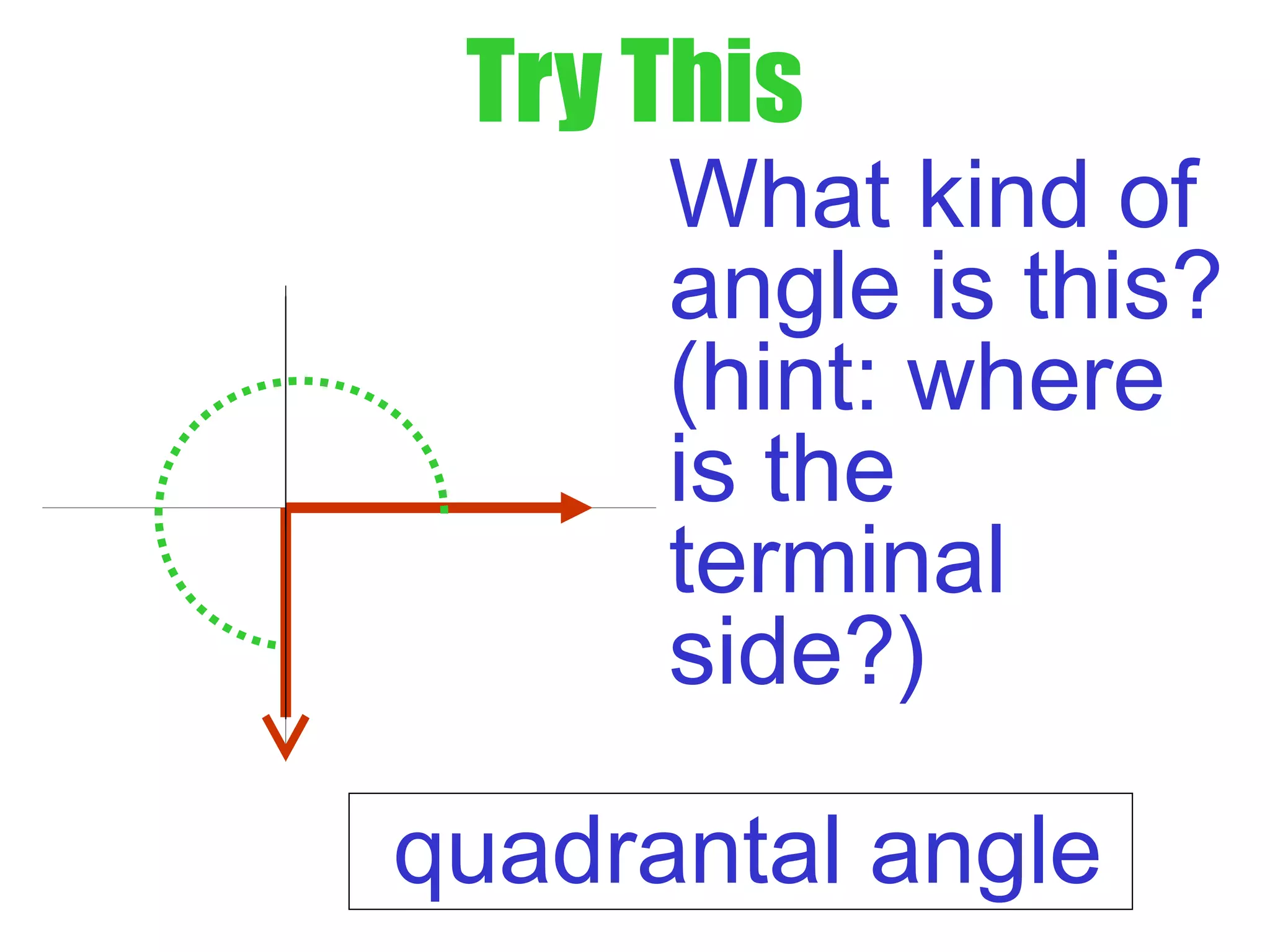
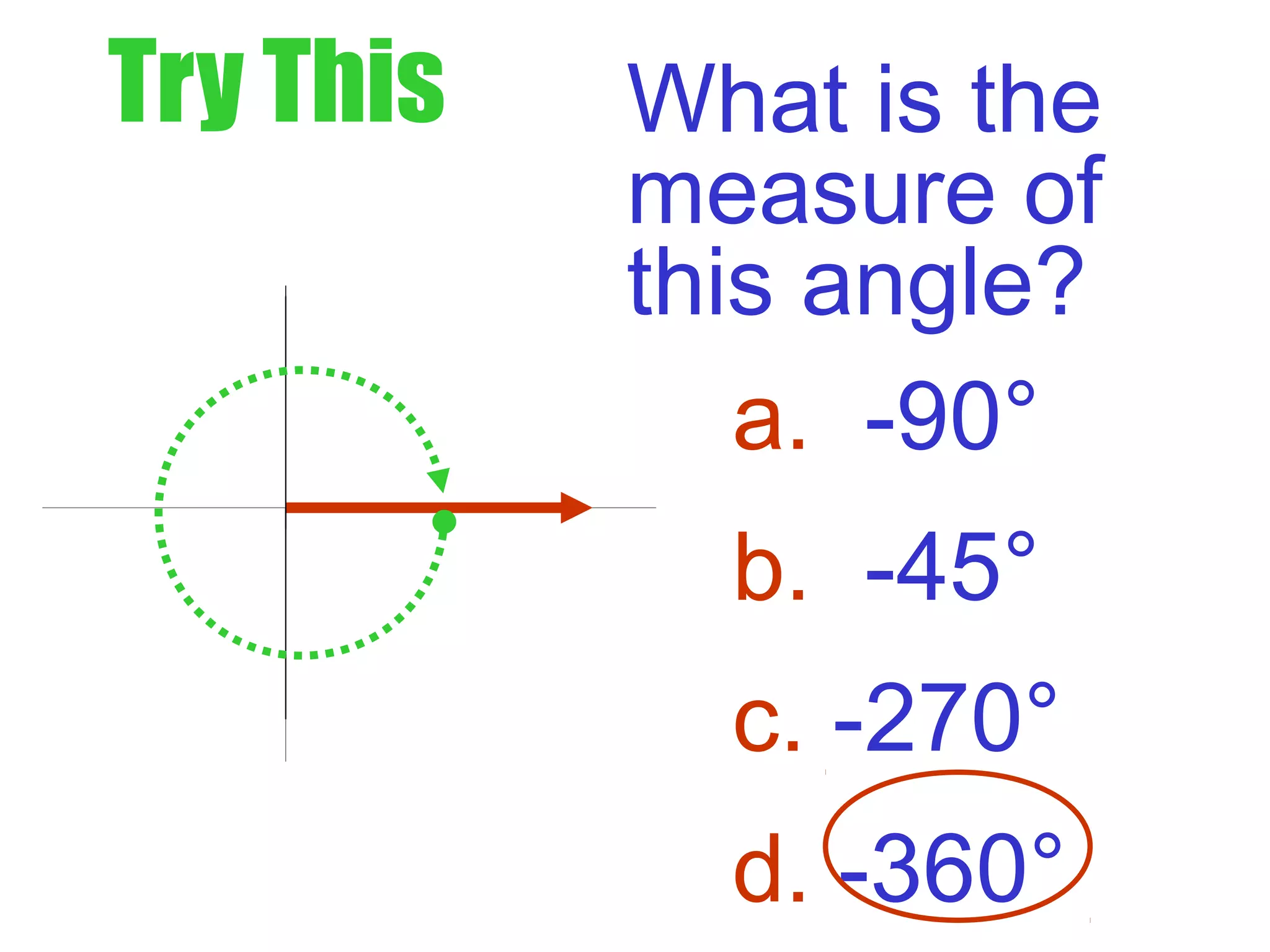
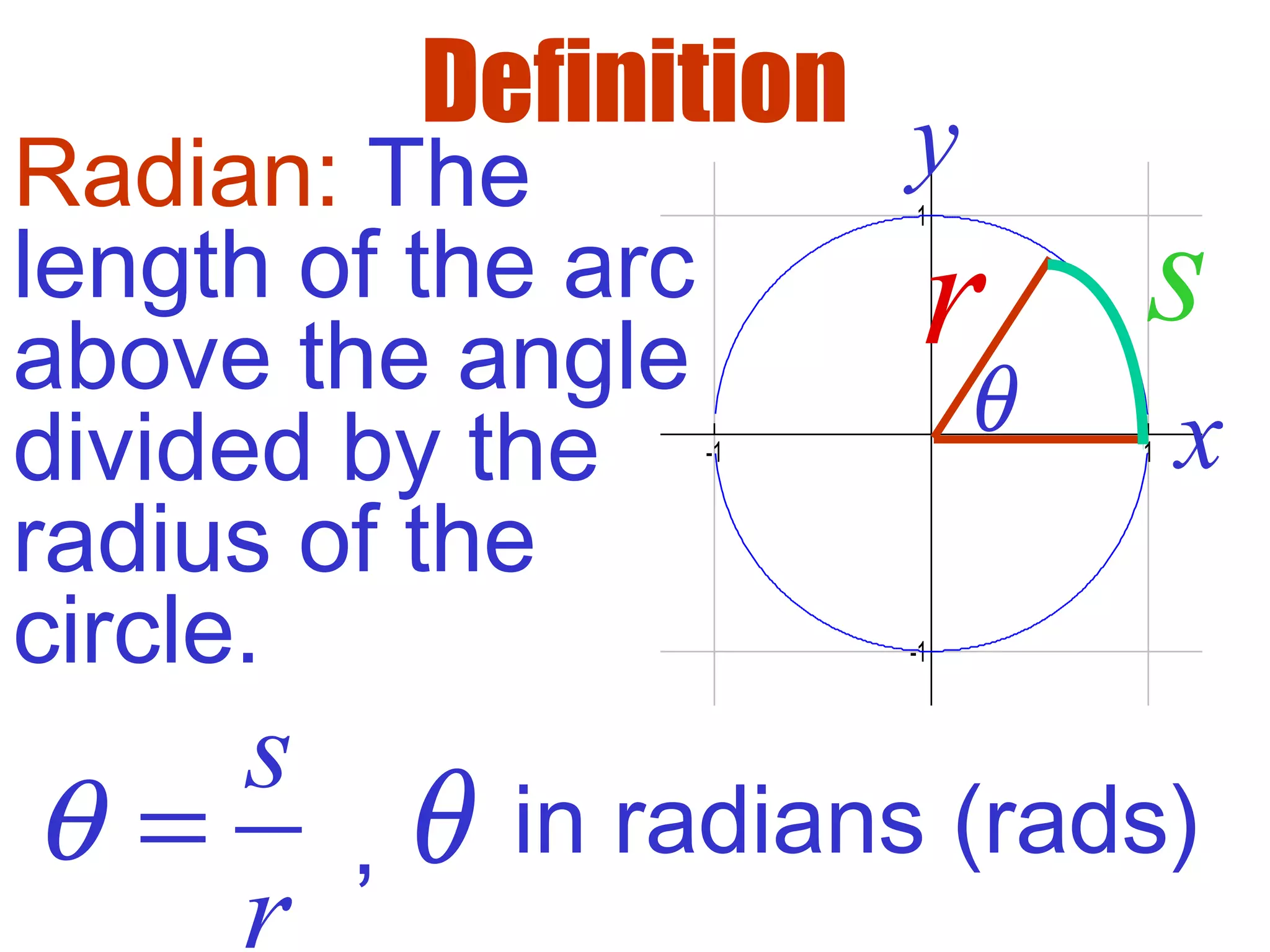
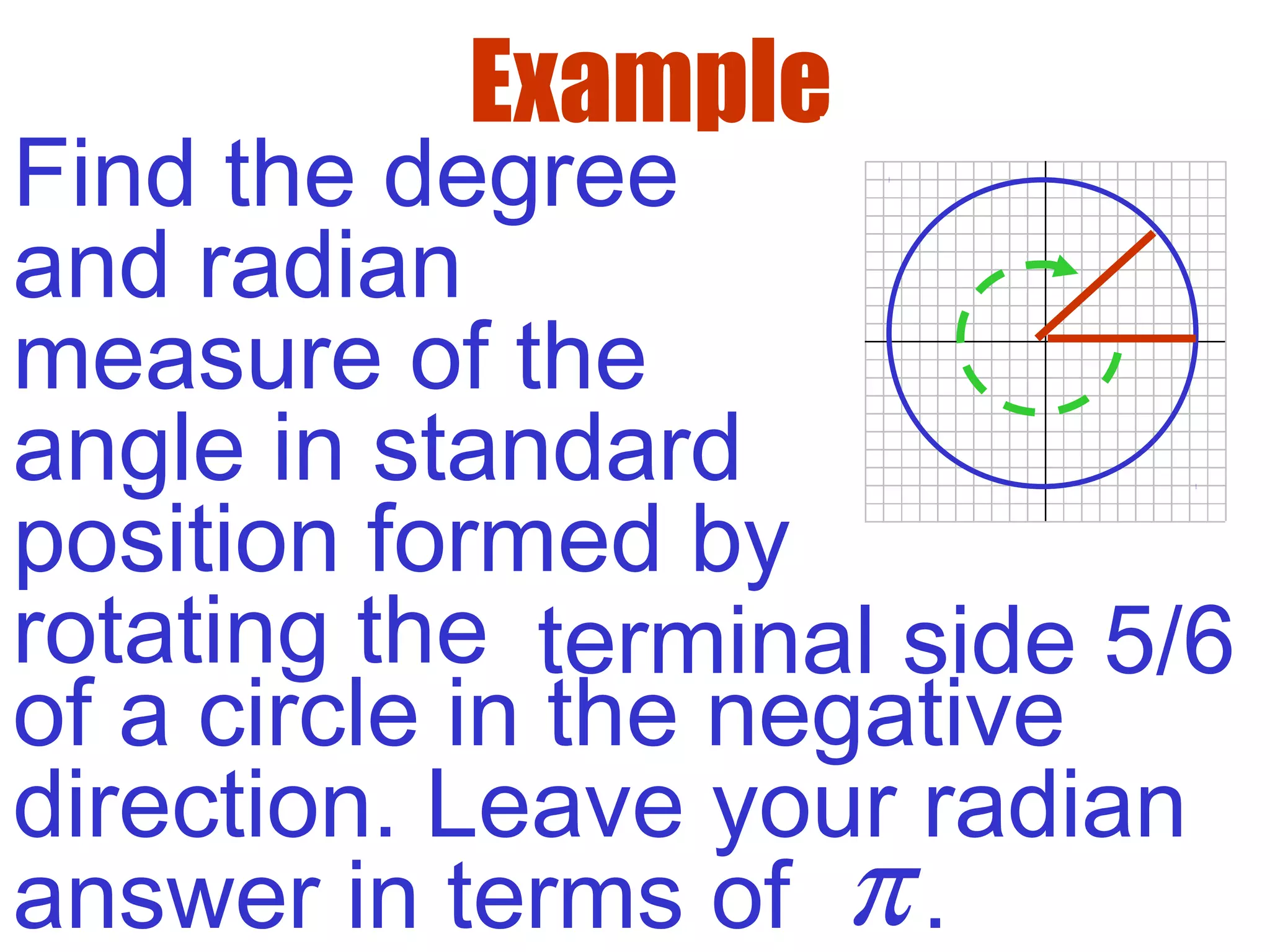
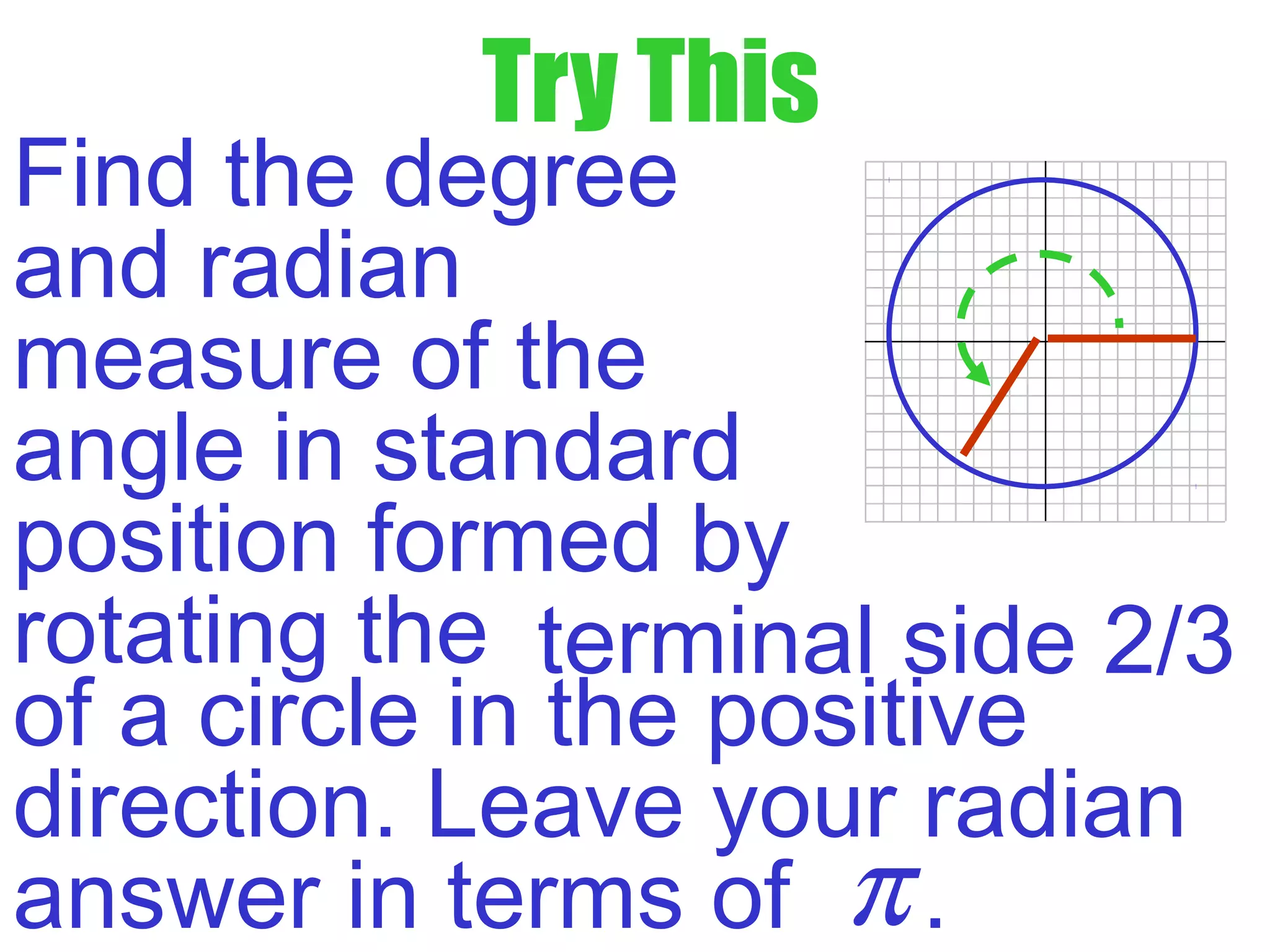
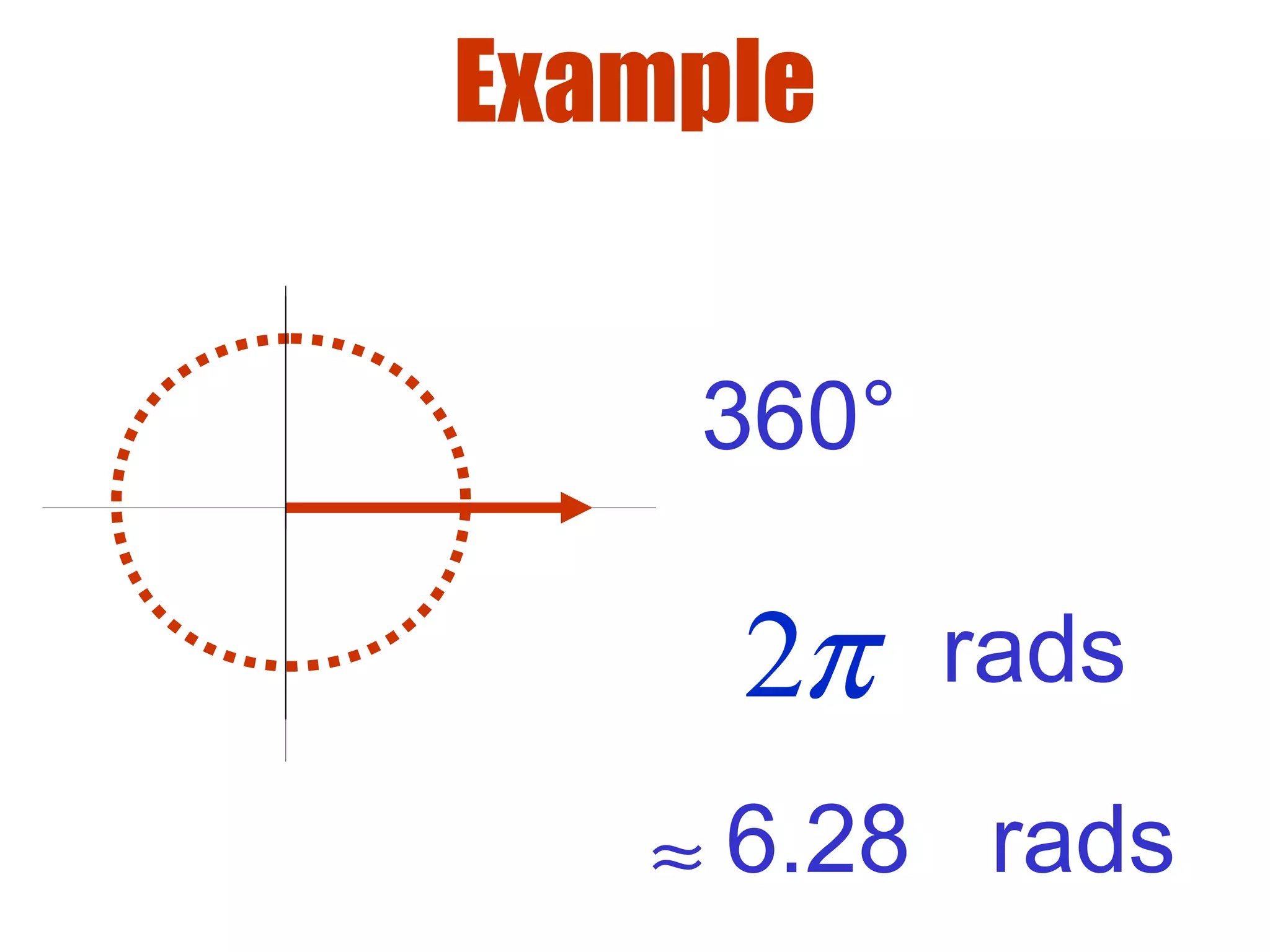
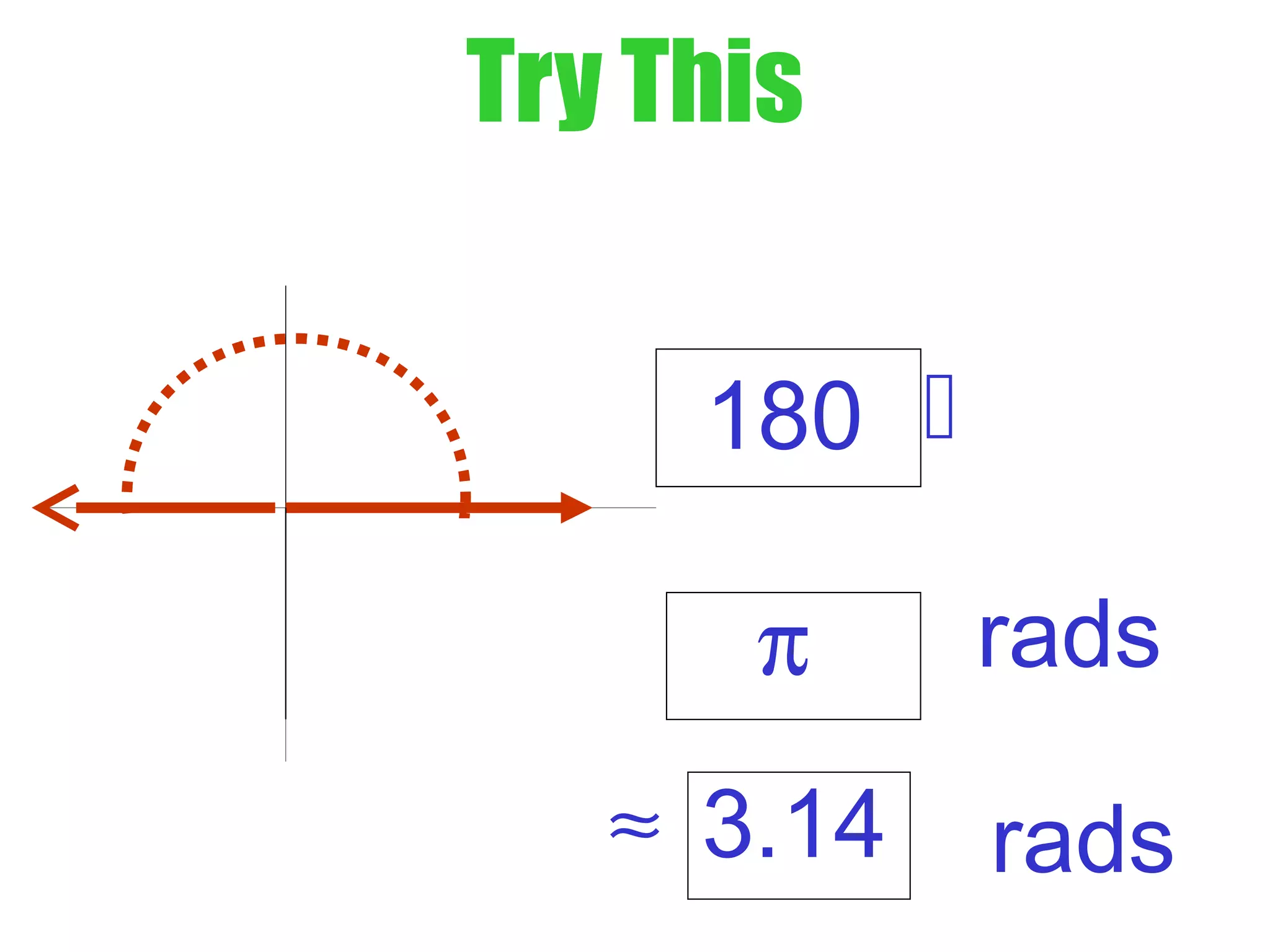
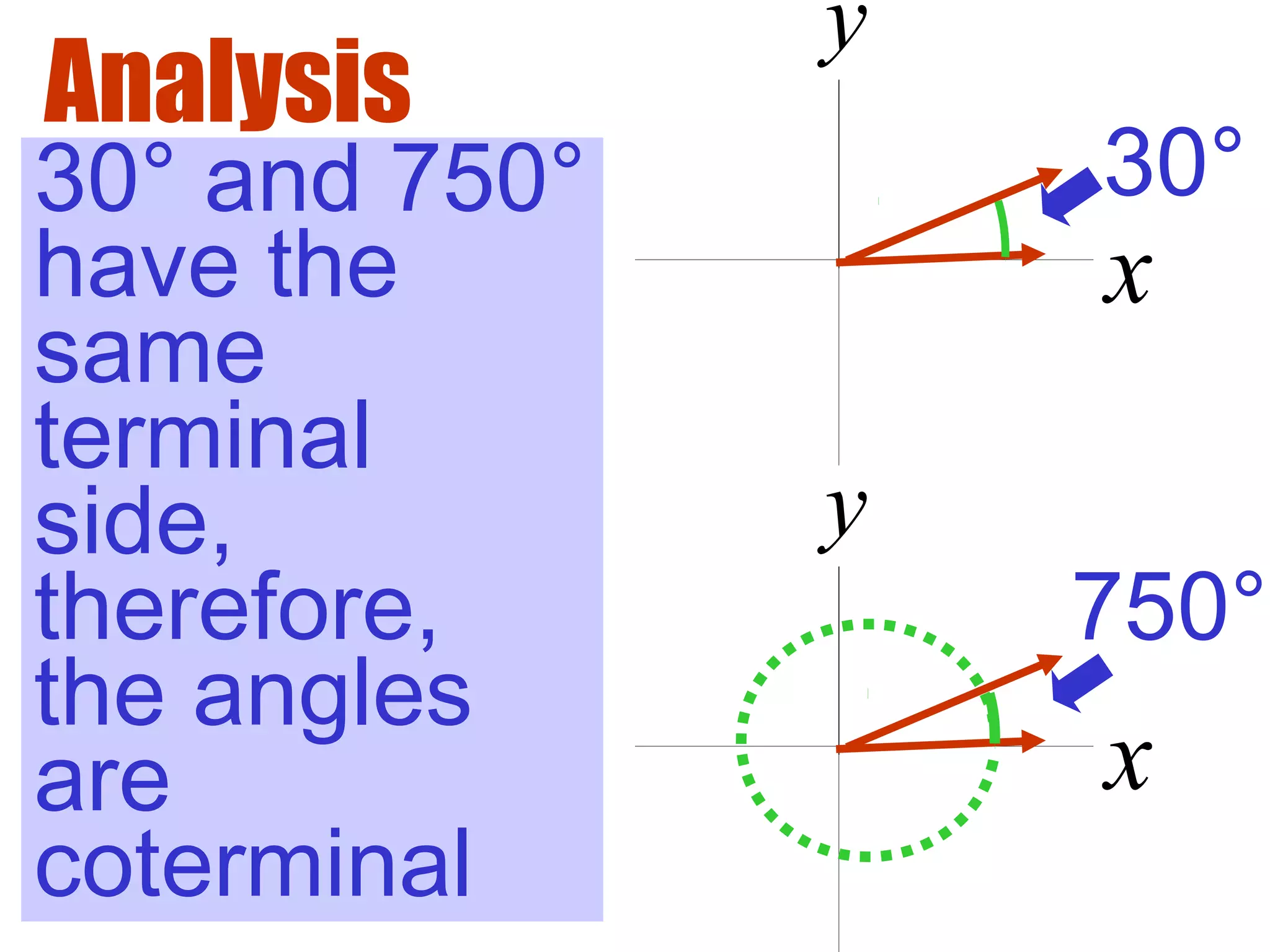
This document defines radians as a unit of measuring angles, where the radian measure of an angle is defined as the arc length of a unit circle subtended by the angle divided by the radius. It discusses converting between degree and radian measures, defines quadrantal angles in radians, and introduces the concept of coterminal angles which have the same terminal side.