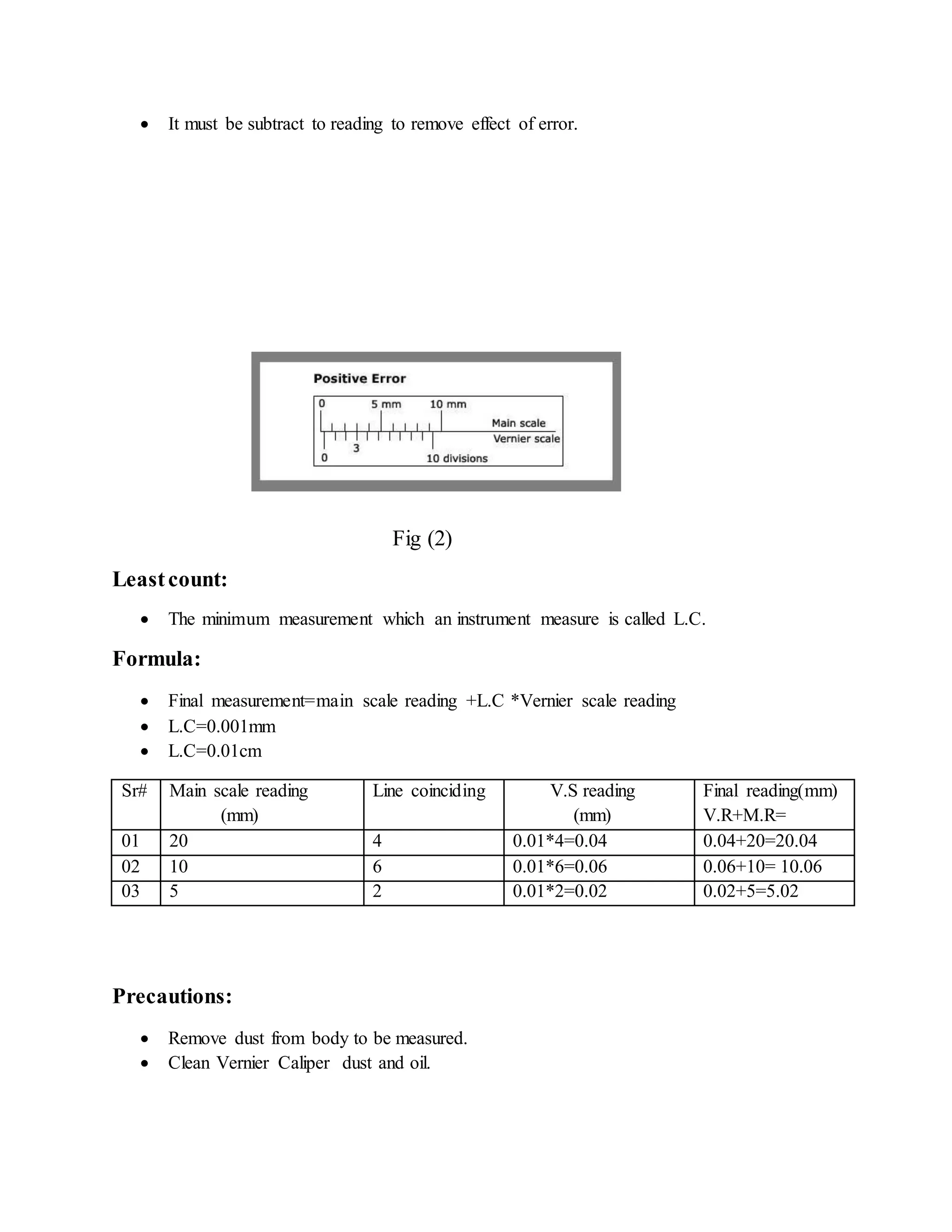
This document describes how to use a Vernier caliper to take measurements. It defines true value as the average of infinite measurements with zero average deviation, while measured value is the approximated true value found from multiple readings. Static error is the difference between measured and true values. The procedure explains how to check for zero error, take main and Vernier scale readings, calculate the measurement using least count, and record results from different specimens. Precautions include cleaning the caliper and items measured to minimize errors and get accurate readings.