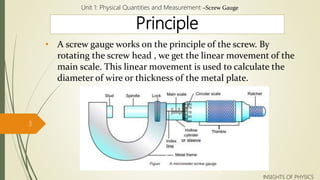
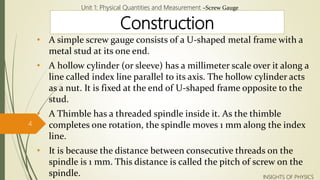
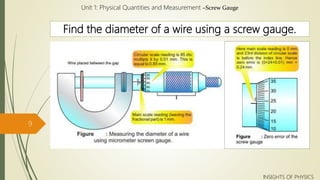
A screw gauge is used to measure small lengths and diameters more accurately than a Vernier caliper. It works on the principle of a screw, where rotating the thimble causes the threaded spindle to move linearly. The spindle is connected to a main scale with millimeter divisions. Each division on the thimble's circular scale corresponds to 0.01mm movement. The least count is therefore 0.01mm. To take a measurement, the object is placed between the spindle and stud. Its diameter can be read where the thimble's zero aligns with the main scale.