1) The document describes how to use a micrometer screw gauge to measure the diameter of a wire and thickness of a glass plate.
2) A micrometer screw gauge has a frame that holds an anvil and barrel. Turning the thimble moves a screw to take precise measurements.
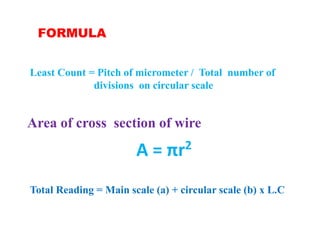
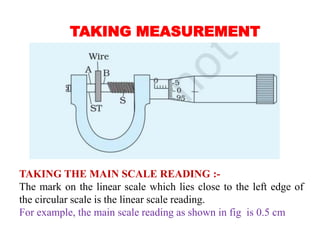
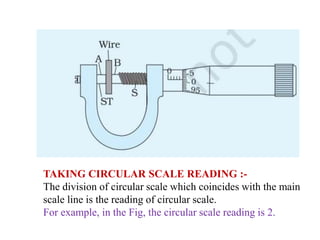
3) To measure the diameter of a wire, it is inserted between the screw and anvil. Readings from the main and circular scales are used to calculate the diameter to within 0.01 mm.