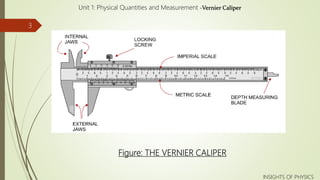
The Vernier caliper is a precision instrument used to measure internal and external distances. It consists of two jaws - a fixed jaw with a main scale and a movable jaw with a Vernier scale. The Vernier scale has 10 divisions over 0.9 mm, allowing measurements to be read to 0.1 mm. To take a reading, the object is placed between the jaws and the main and Vernier scales are aligned. The Vernier division that lines up gives the measurement, which is calculated using the least count and added to the main scale reading along with any zero correction. The Vernier caliper provides accurate measurements but requires good eyesight and an understanding of how to use it.