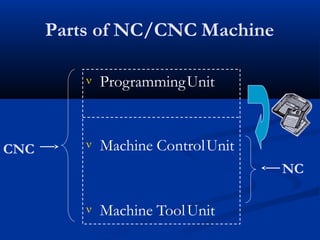
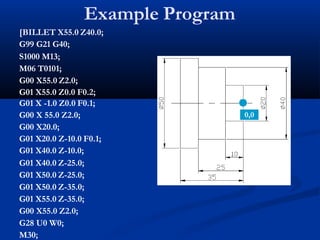
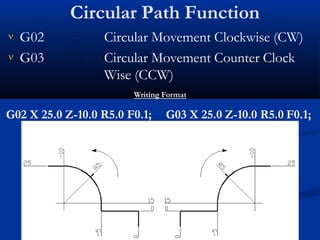
This document provides an introduction to CNC turning. It discusses the parts of a CNC machine, including the programming unit, machine control unit, and machine tool. It also covers fundamental CNC turning concepts like G-codes for linear and circular movements, M-codes for machine functions, and modal and non-modal G-codes. An example CNC turning program is included to demonstrate how G-codes are written to machine different shapes and features on a workpiece.