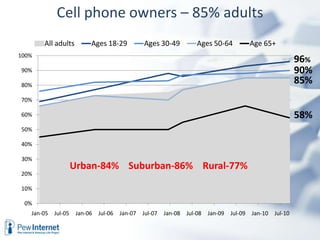
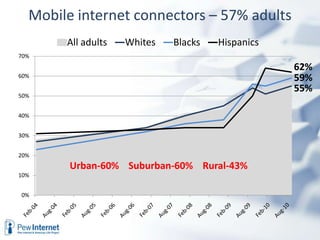
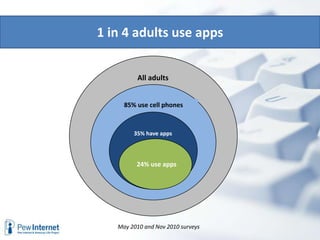
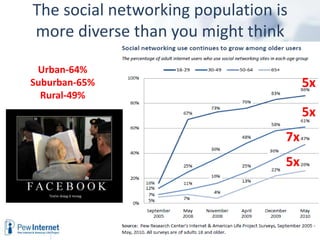
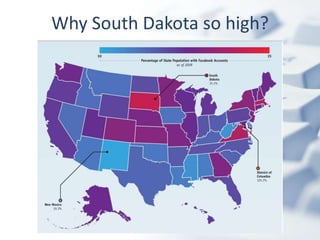
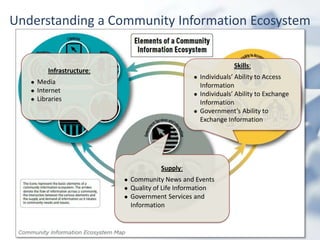
The document outlines the evolving landscape of community learning and information access influenced by new technologies and social networks. It highlights the importance of high-speed internet, transparency in government, and the necessity for citizens to engage with and create knowledge. Several revolutions in connectivity, social networking, and digital literacy are shaping the way communities learn and communicate.