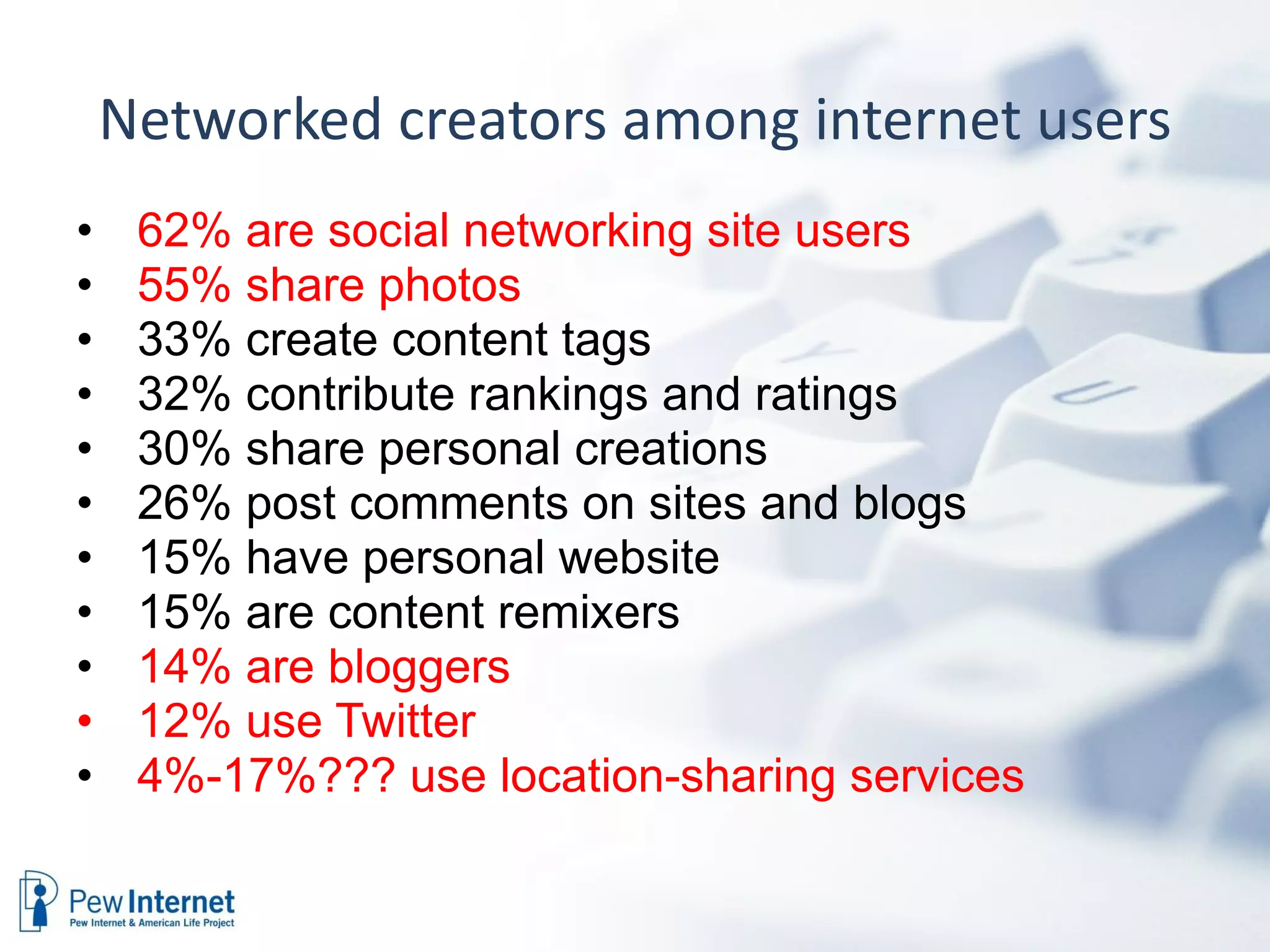
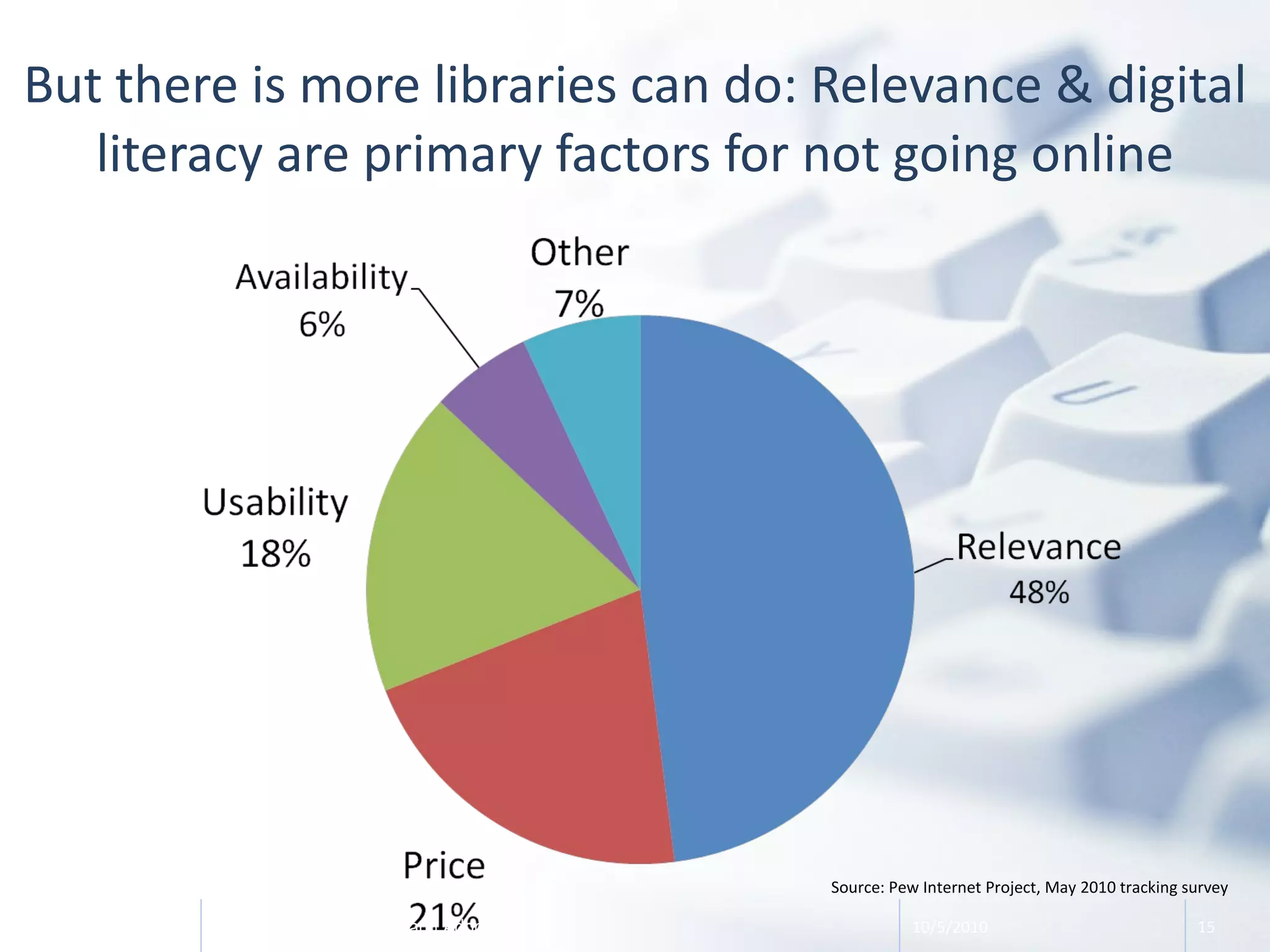
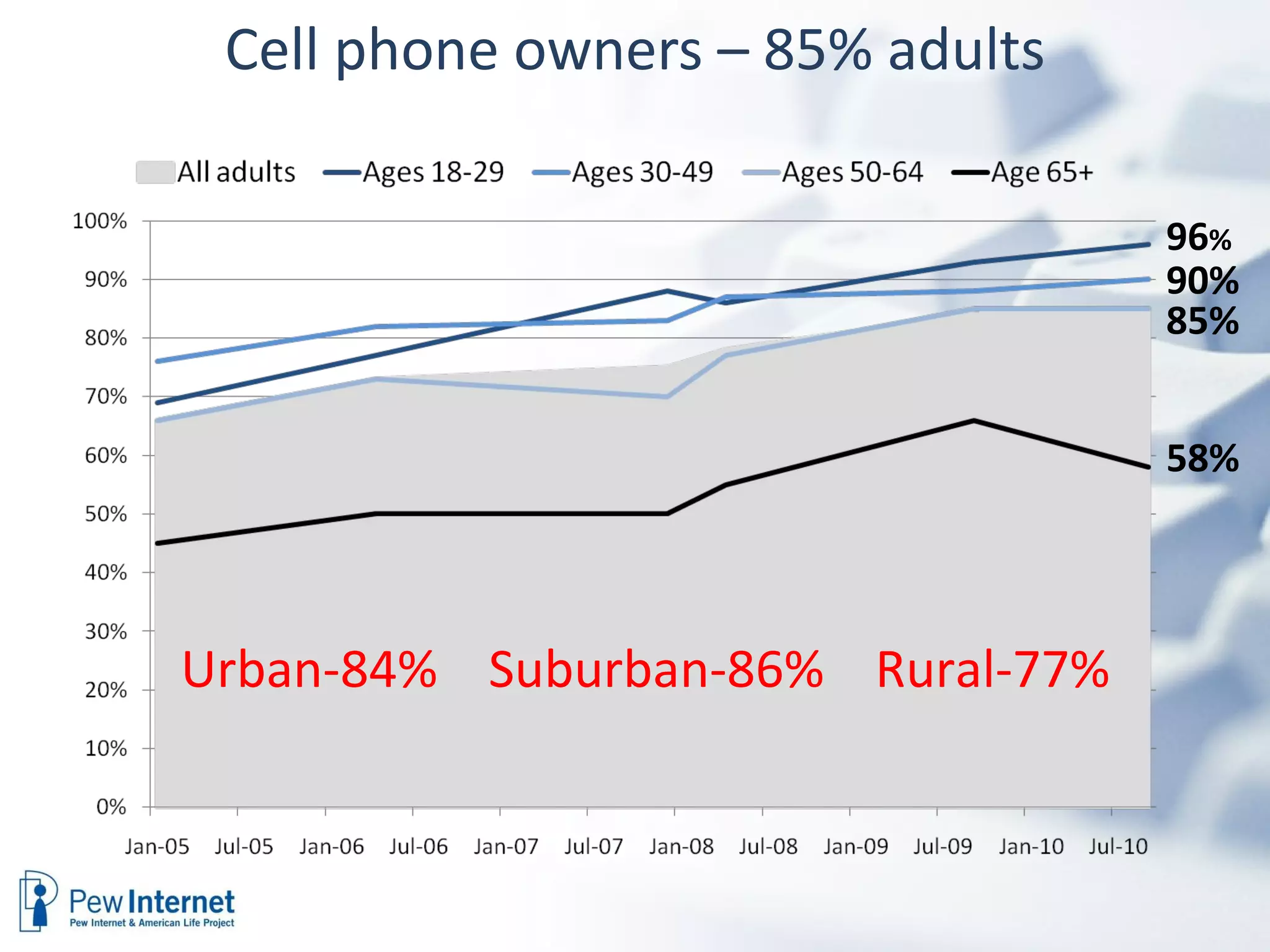
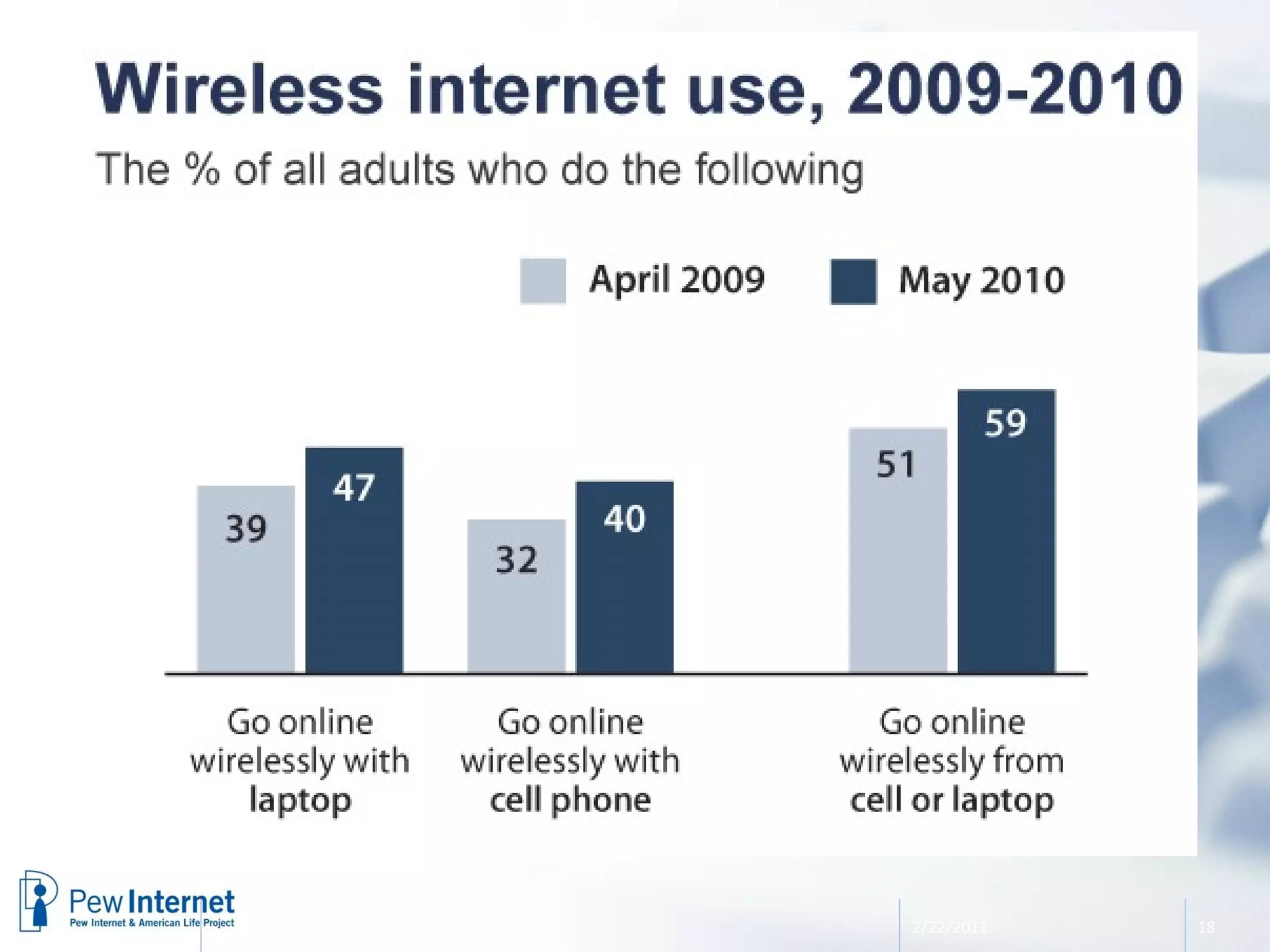
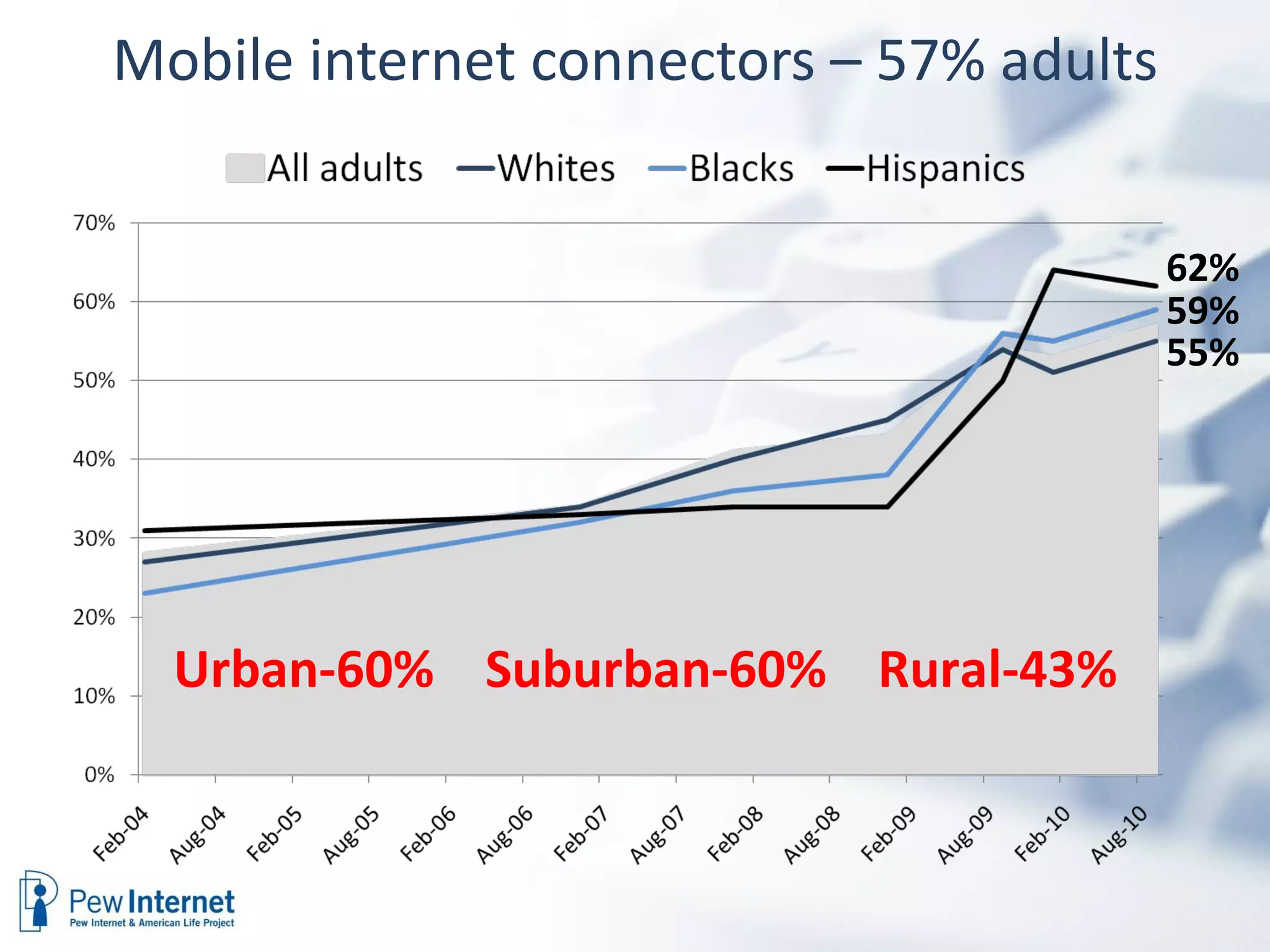
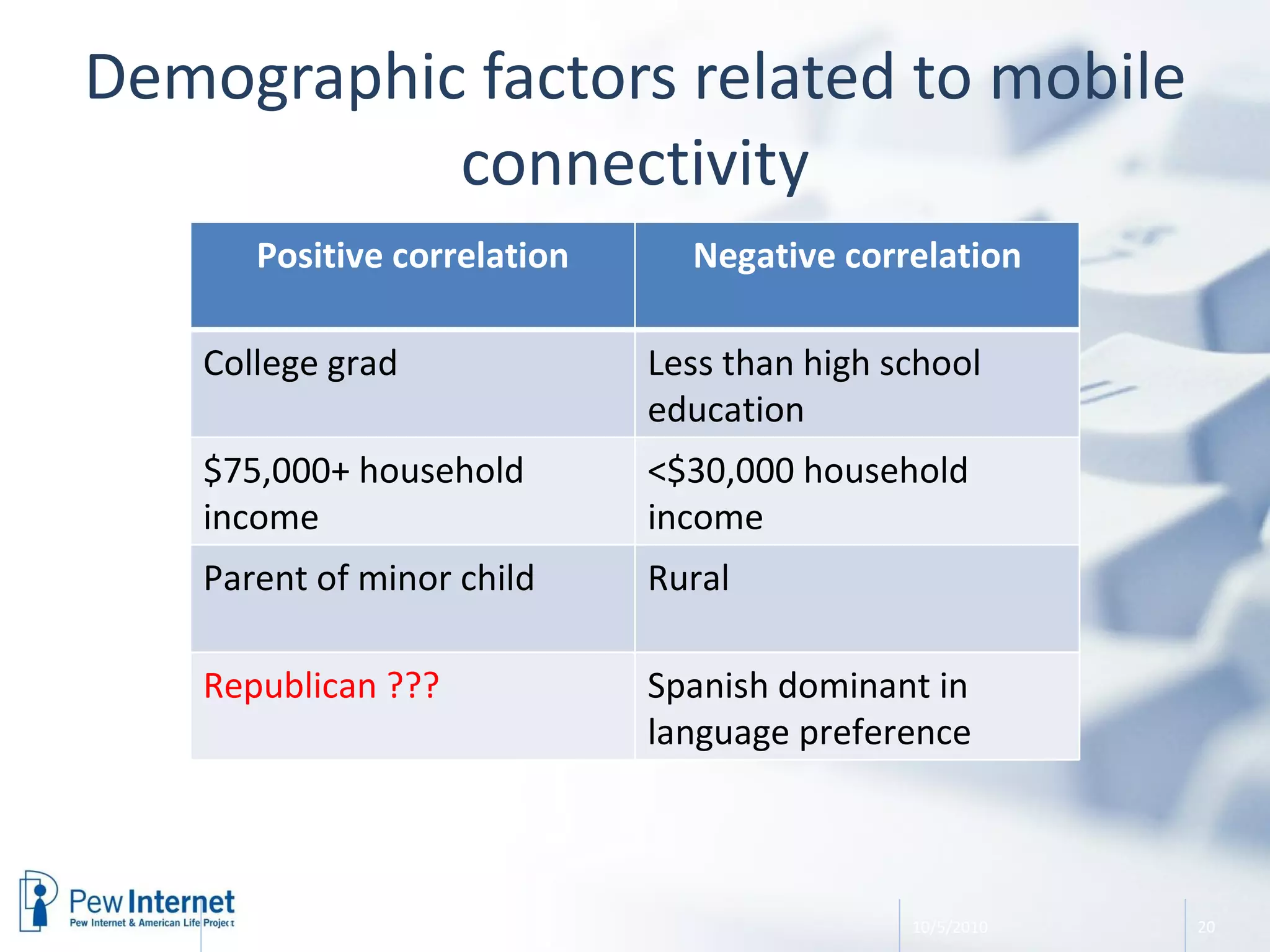
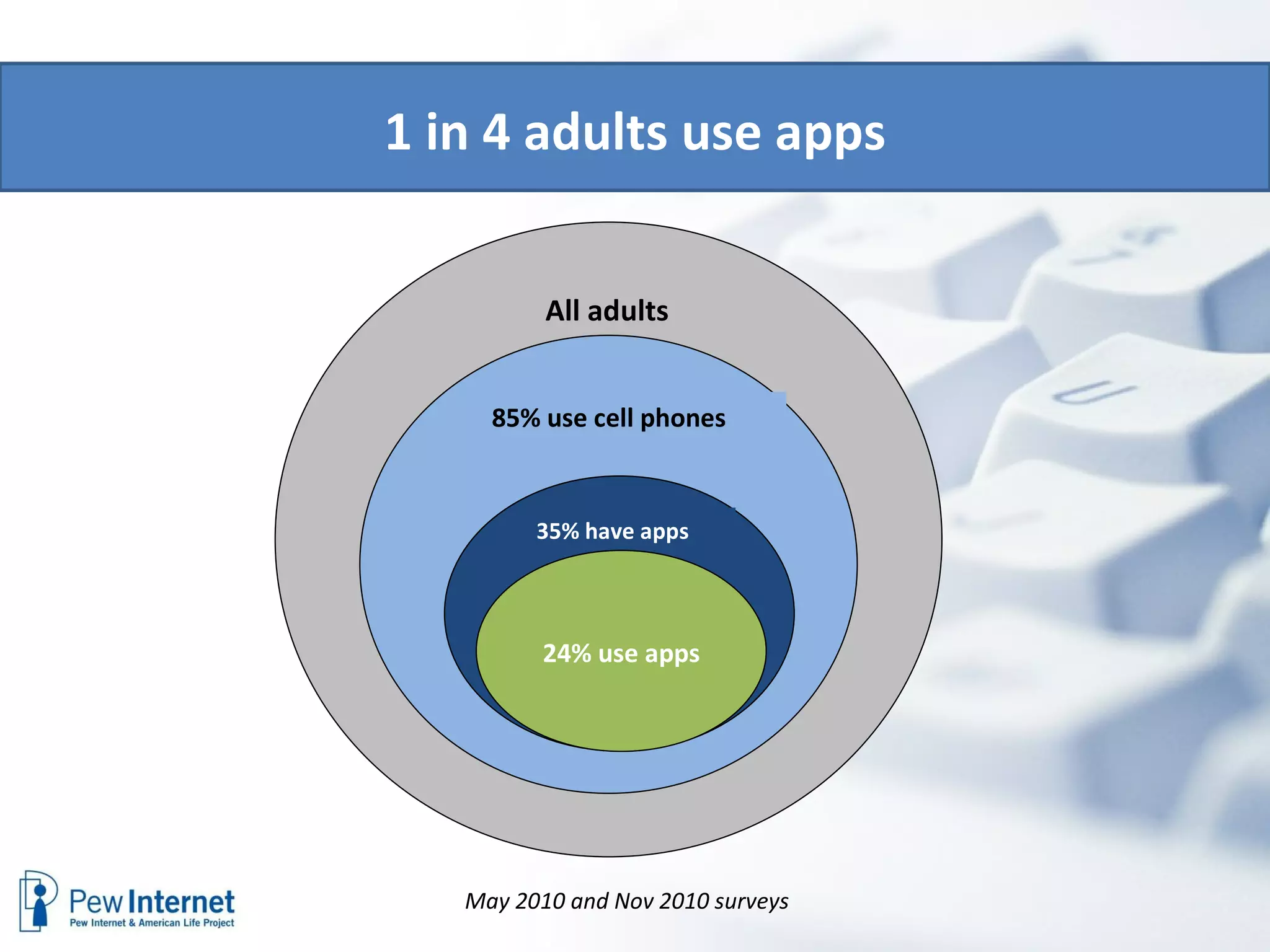
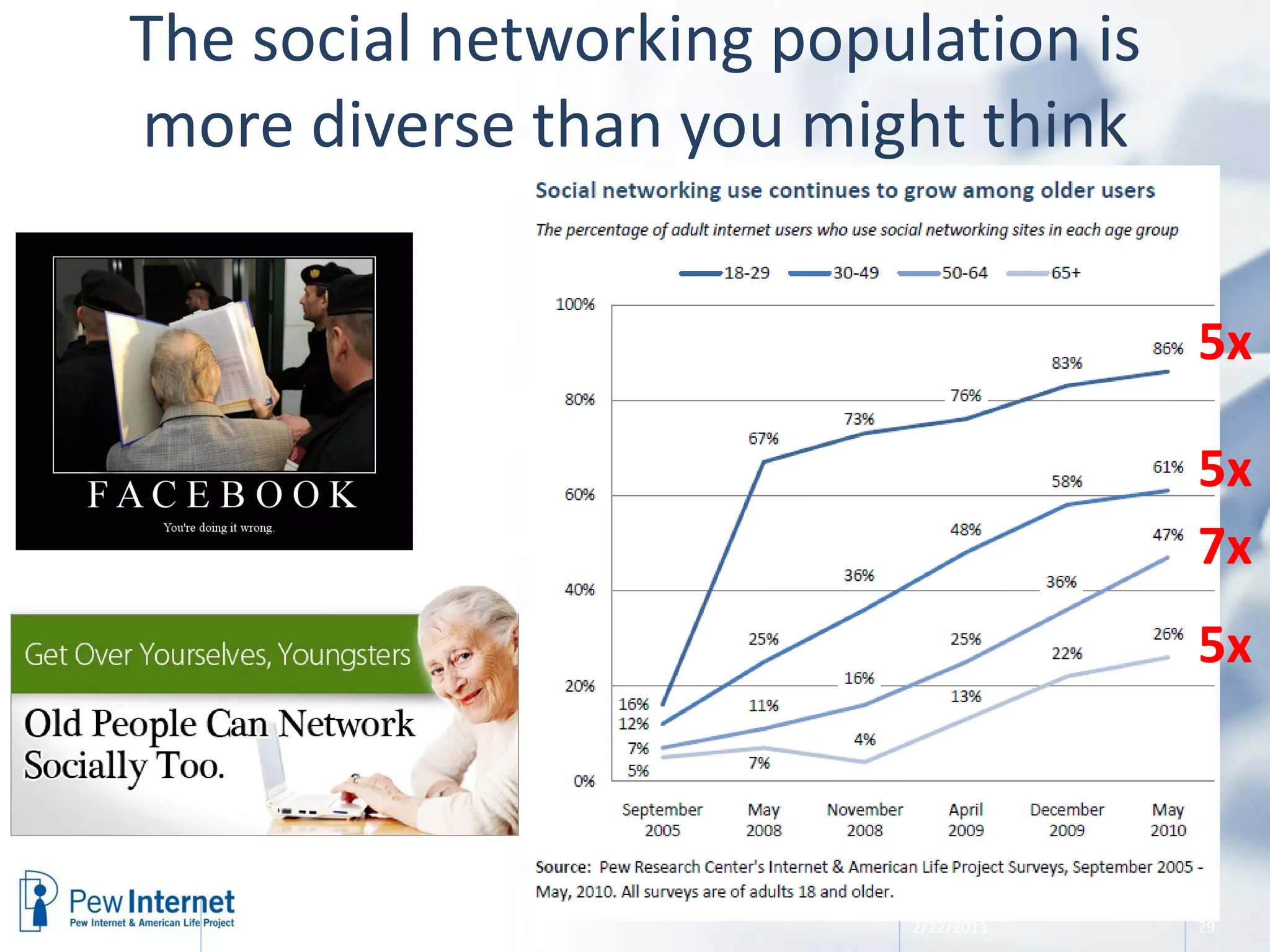
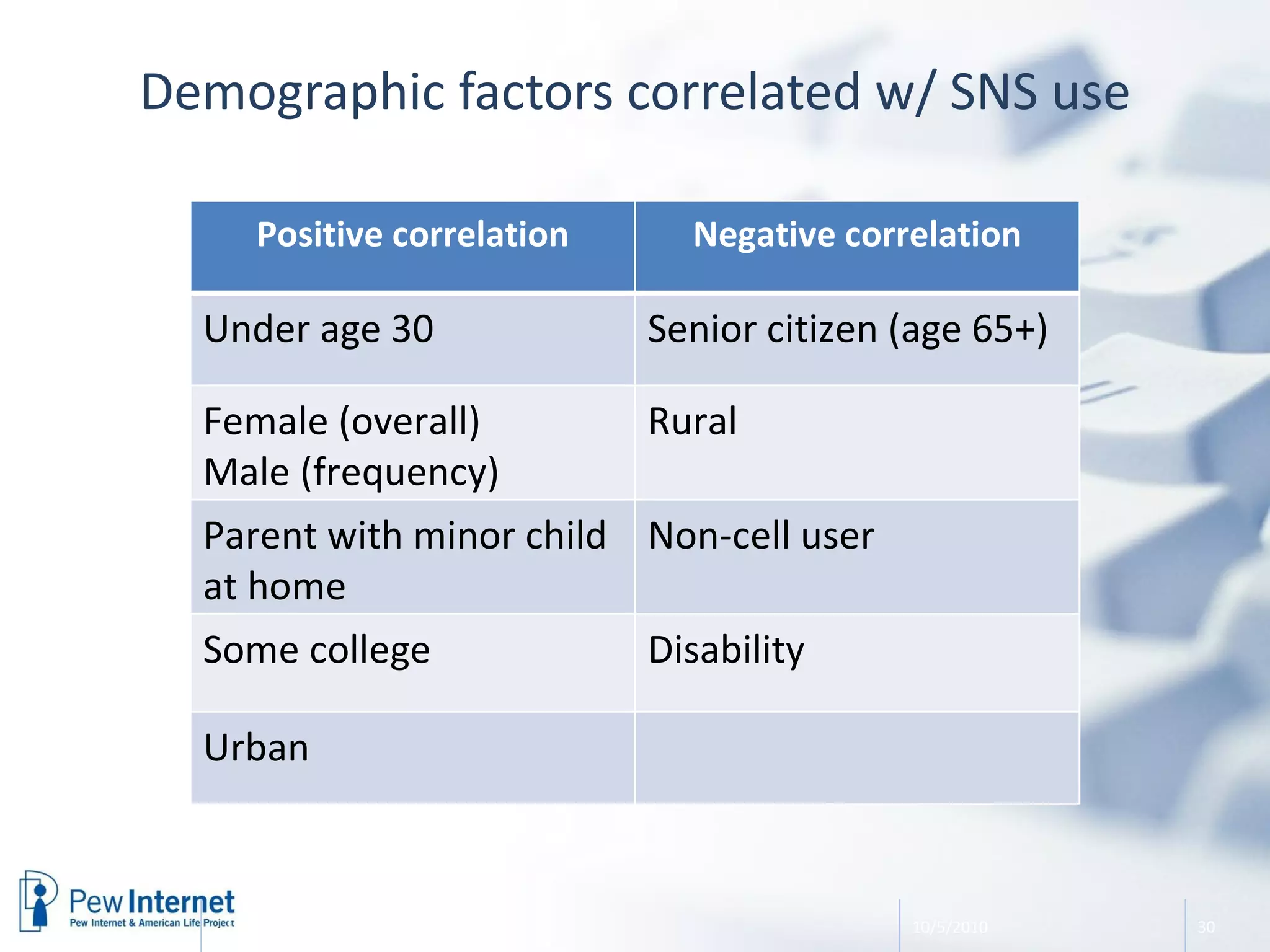
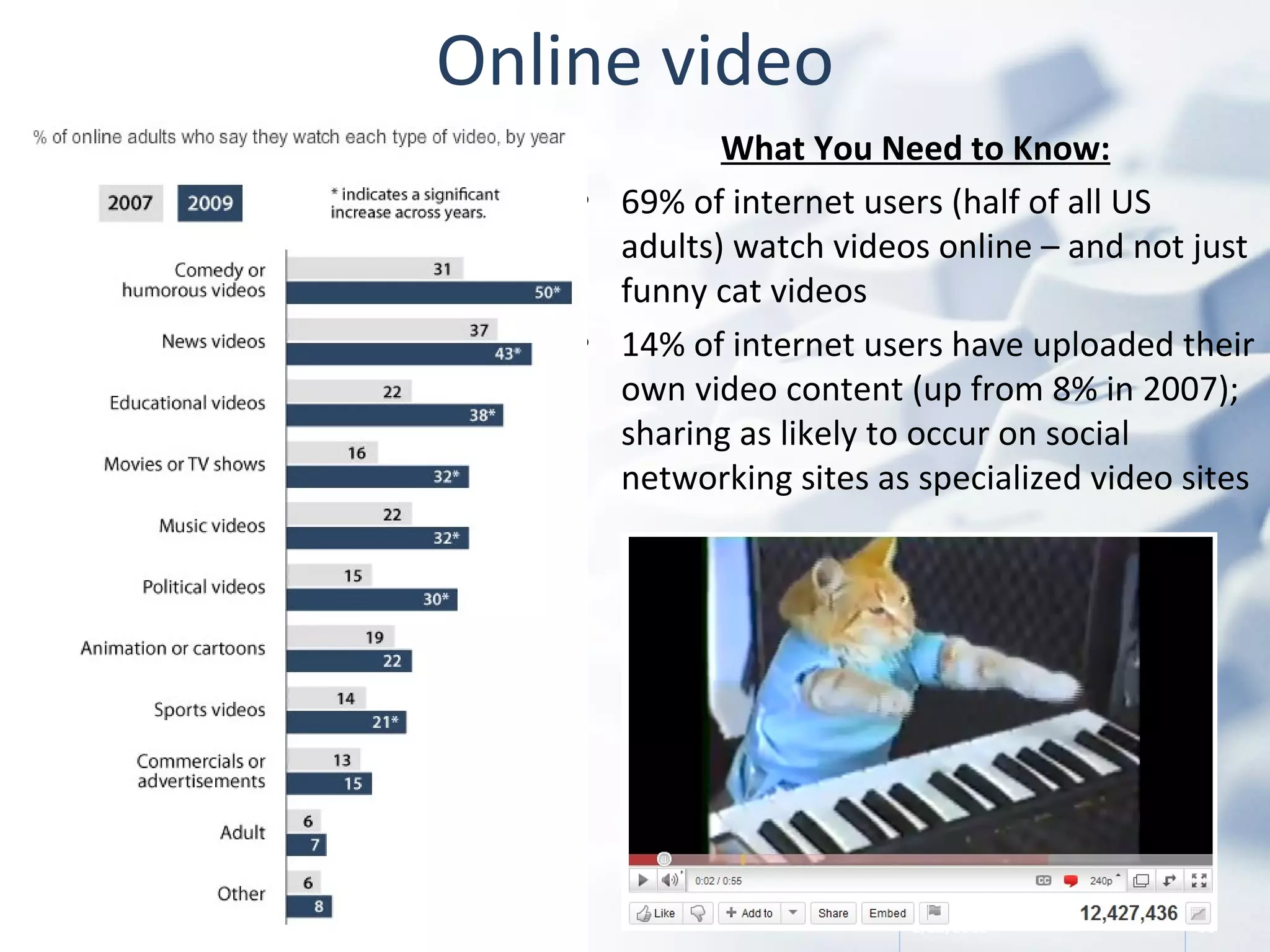
The document discusses the evolution of libraries within the context of social networks and the rise of networked individualism, highlighting how libraries can adapt to and leverage these changes. It presents data on broadband and mobile connectivity, the impact of social media, and the need for libraries to enhance digital literacy and community engagement. Key considerations for the future of libraries include navigating information ecosystems, reimagining roles in civic engagement, and fostering collaboration within local communities.
![Libraries as social networks Lee Rainie, Director, Pew Internet Project 5.6.11 San Francisco library system Email: [email_address] Twitter: @Lrainie](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011-5611-sanfrancisco-librariesassocialnetworks-110506160629-phpapp01/75/The-Networked-Librarian-Libraries-as-social-networks-1-2048.jpg)