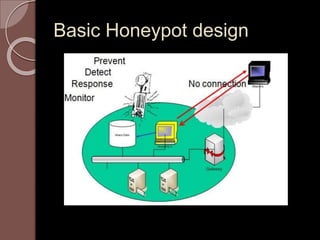
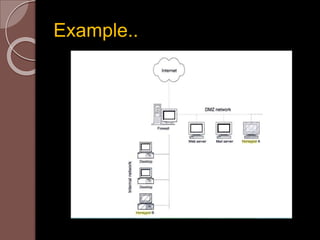
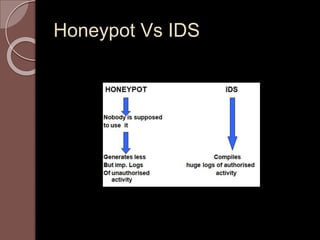
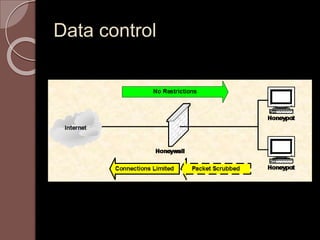
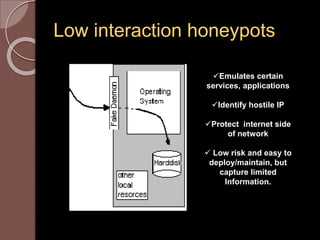
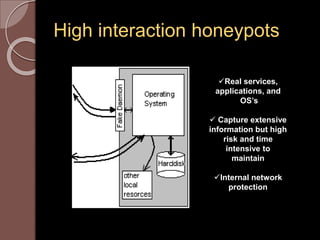
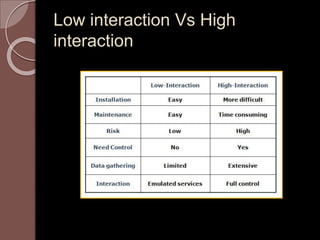
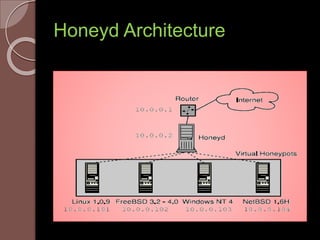
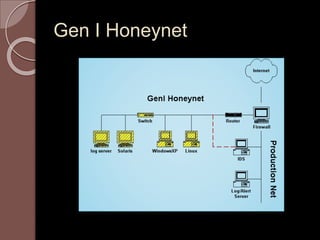
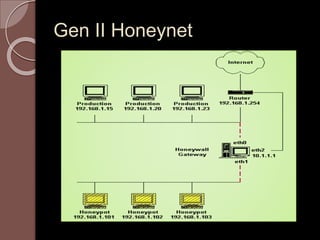
A honeypot is an information system resource designed to attract unauthorized use for data collection to improve security against threats. There are low and high interaction honeypots, each with distinct capabilities, advantages, and disadvantages in terms of information capture and risk. Future developments include easier installation and better integration with existing security technologies.