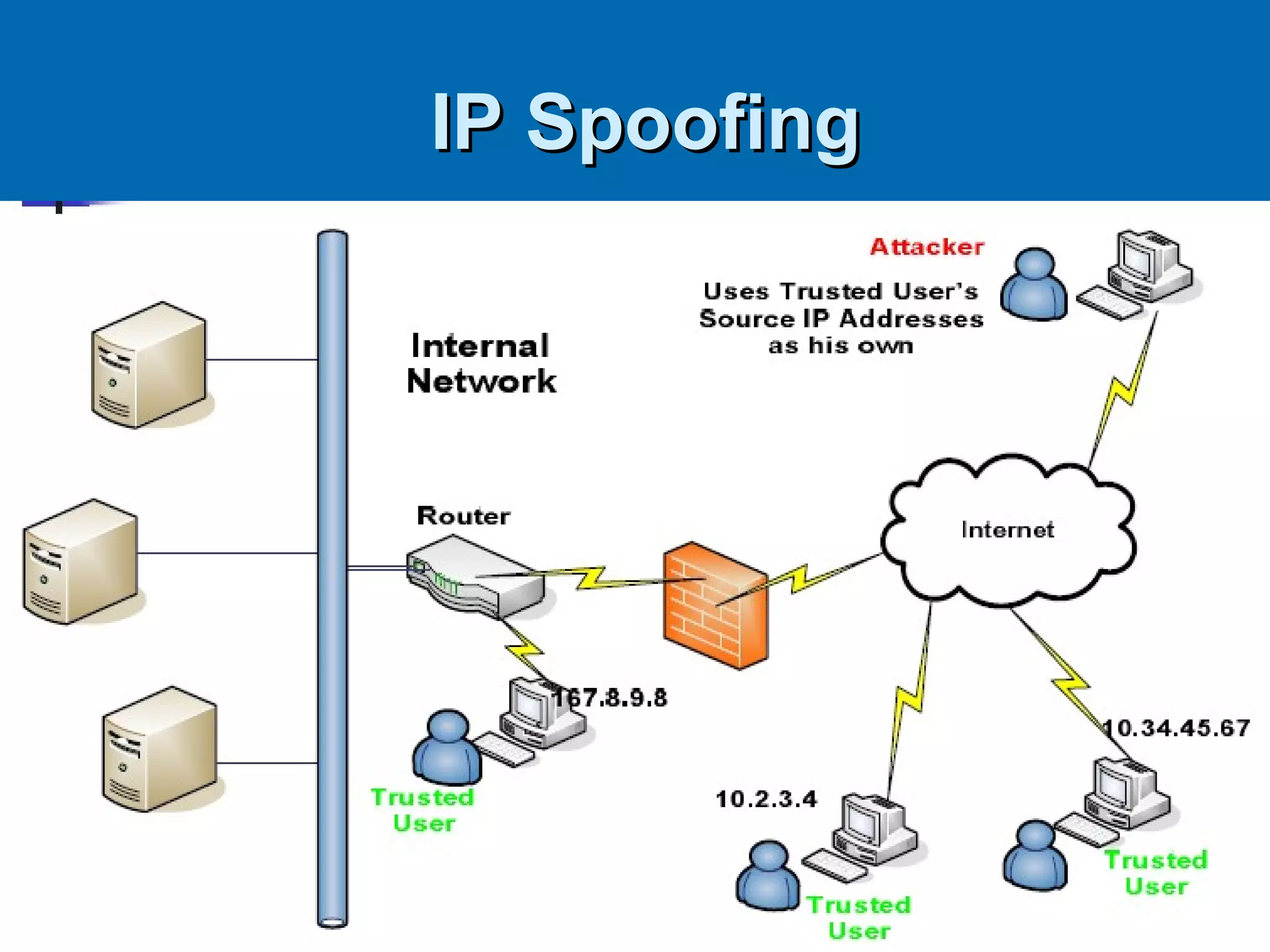
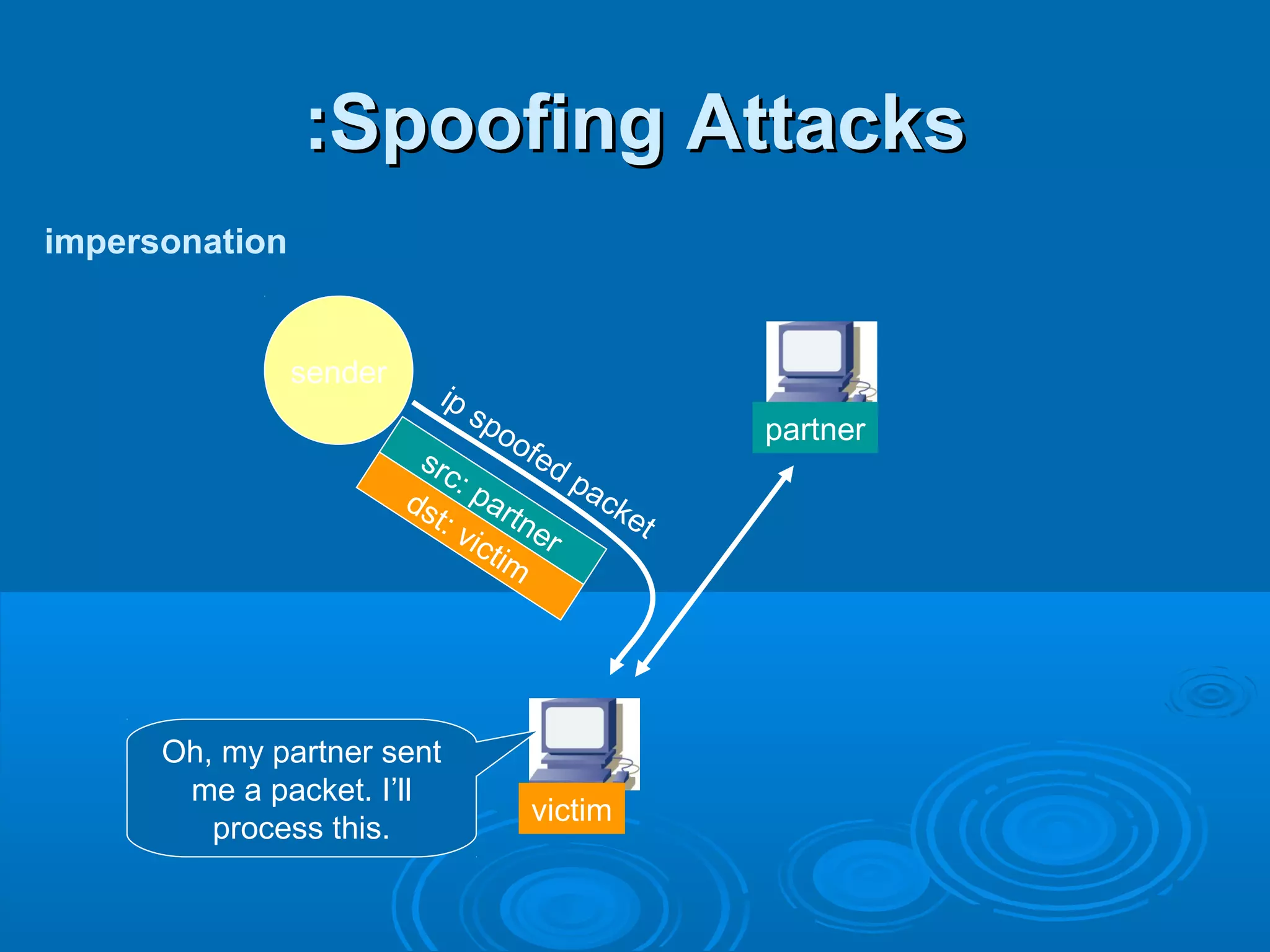
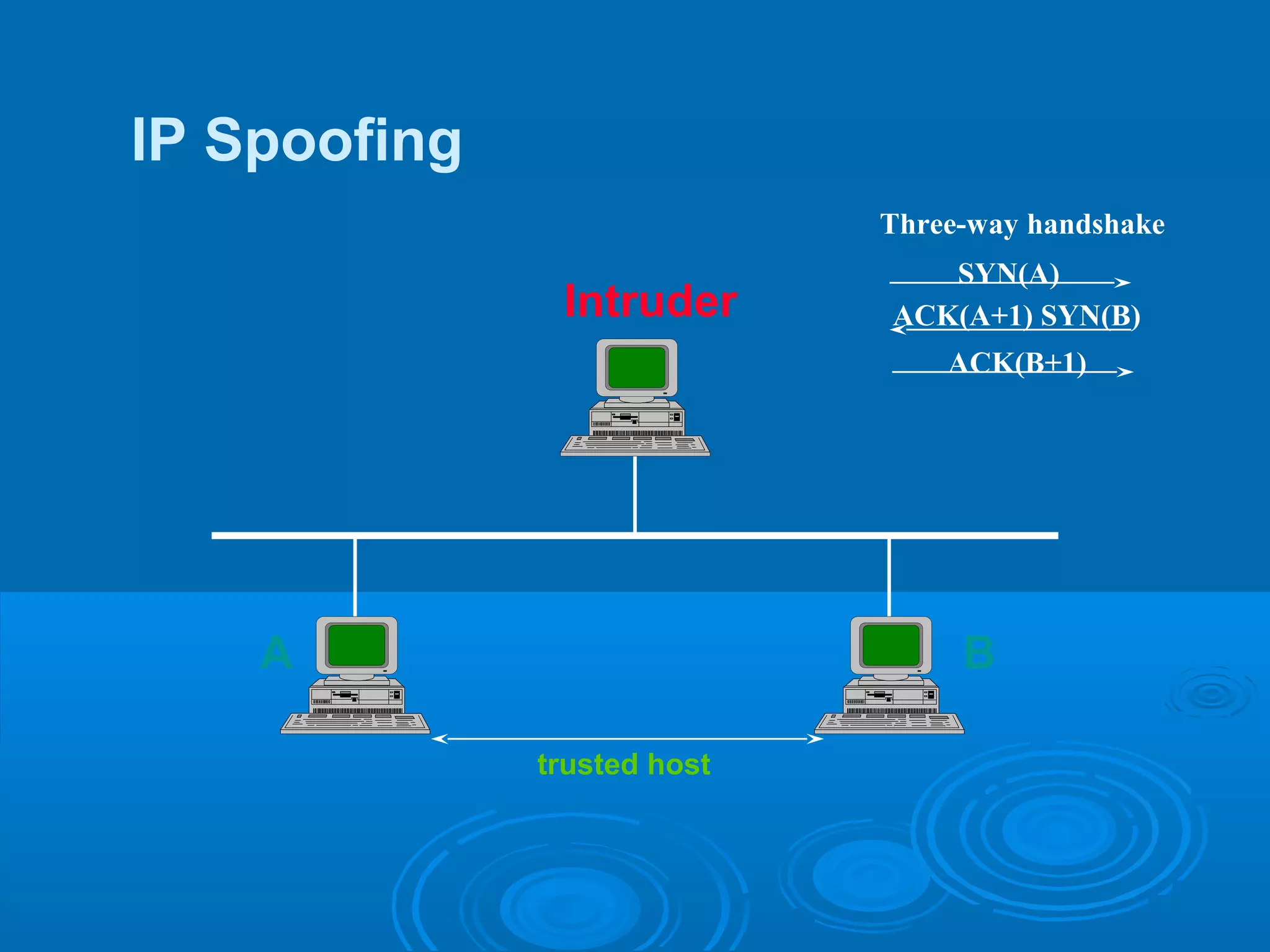
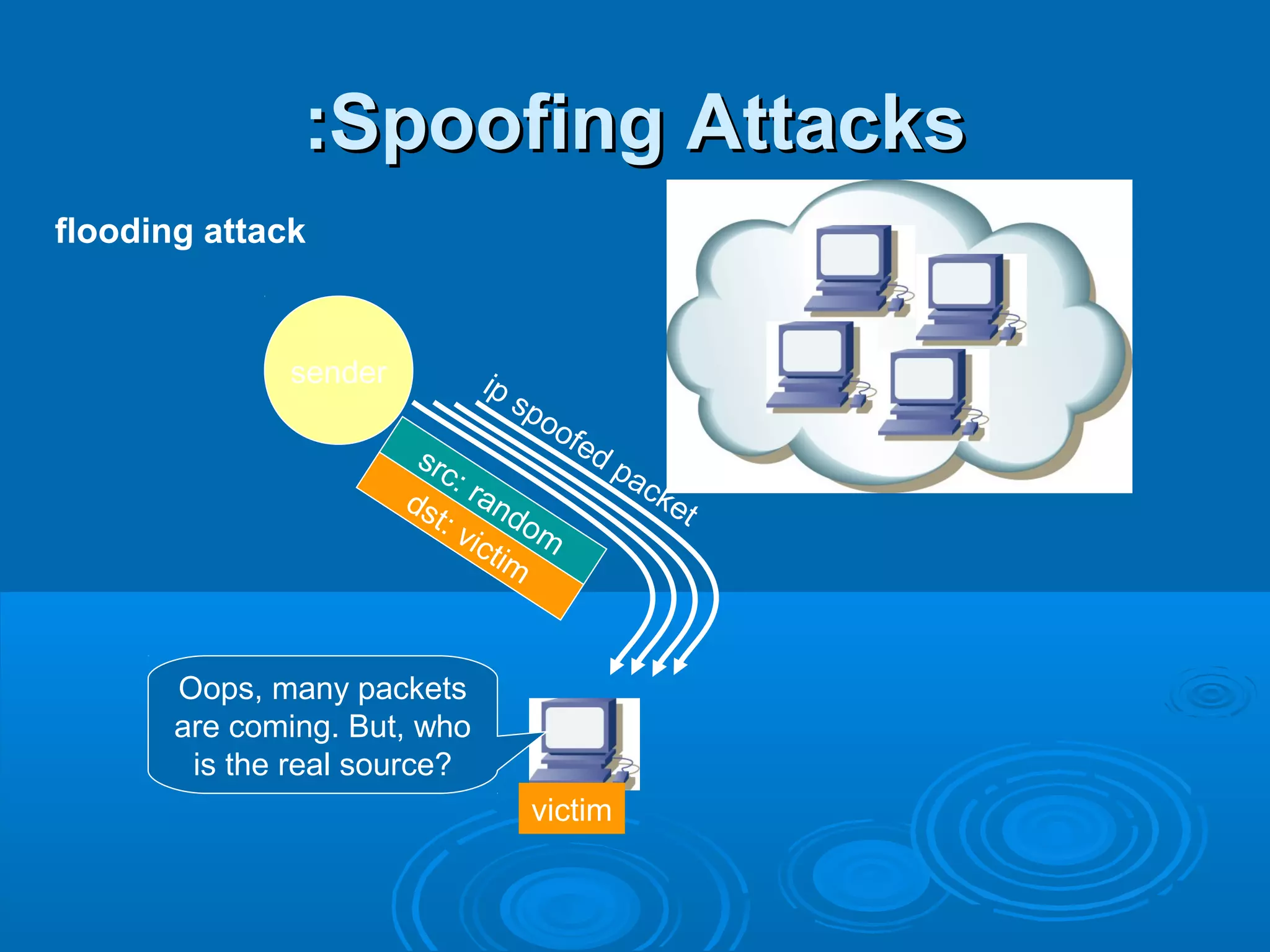
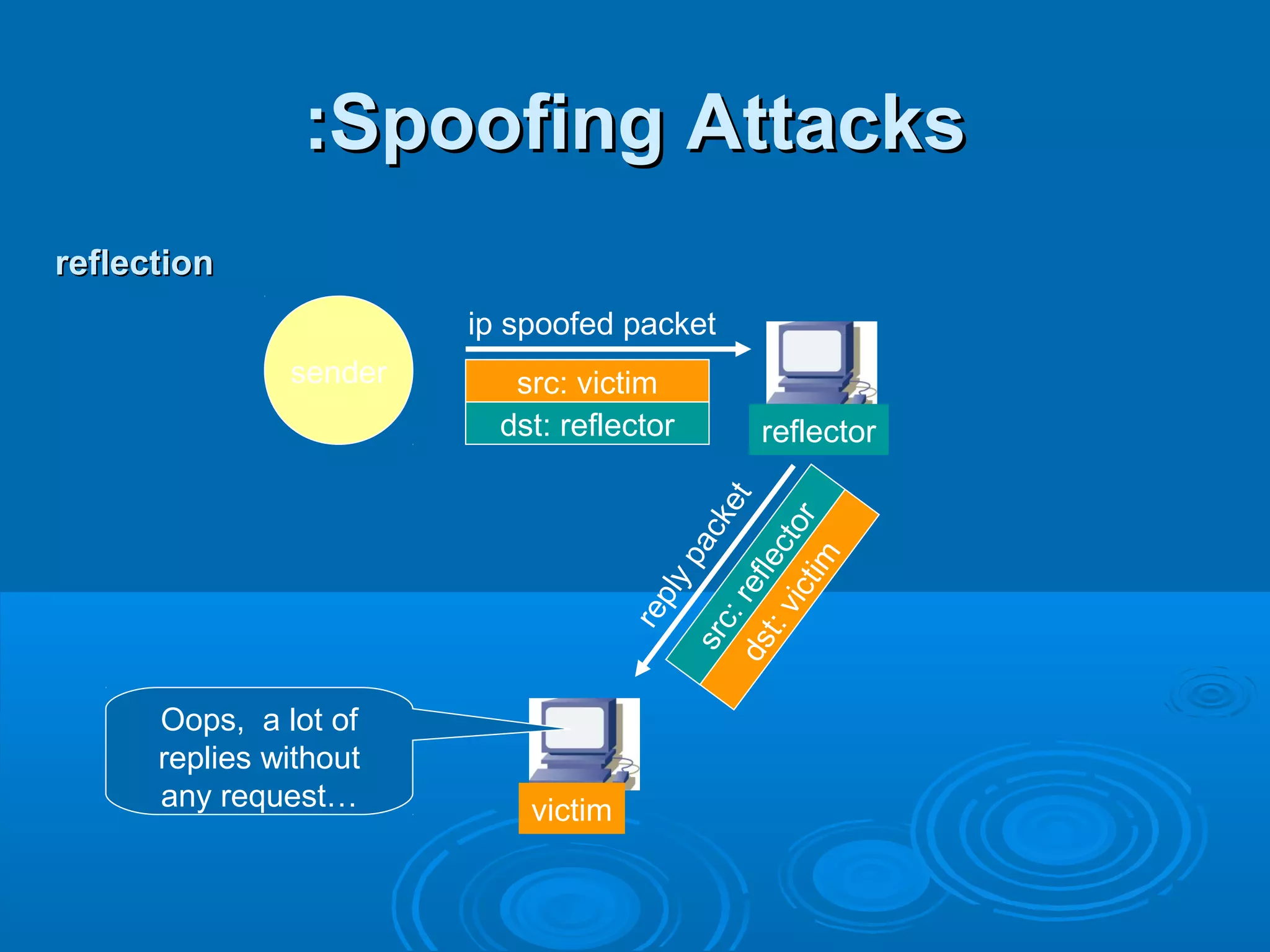
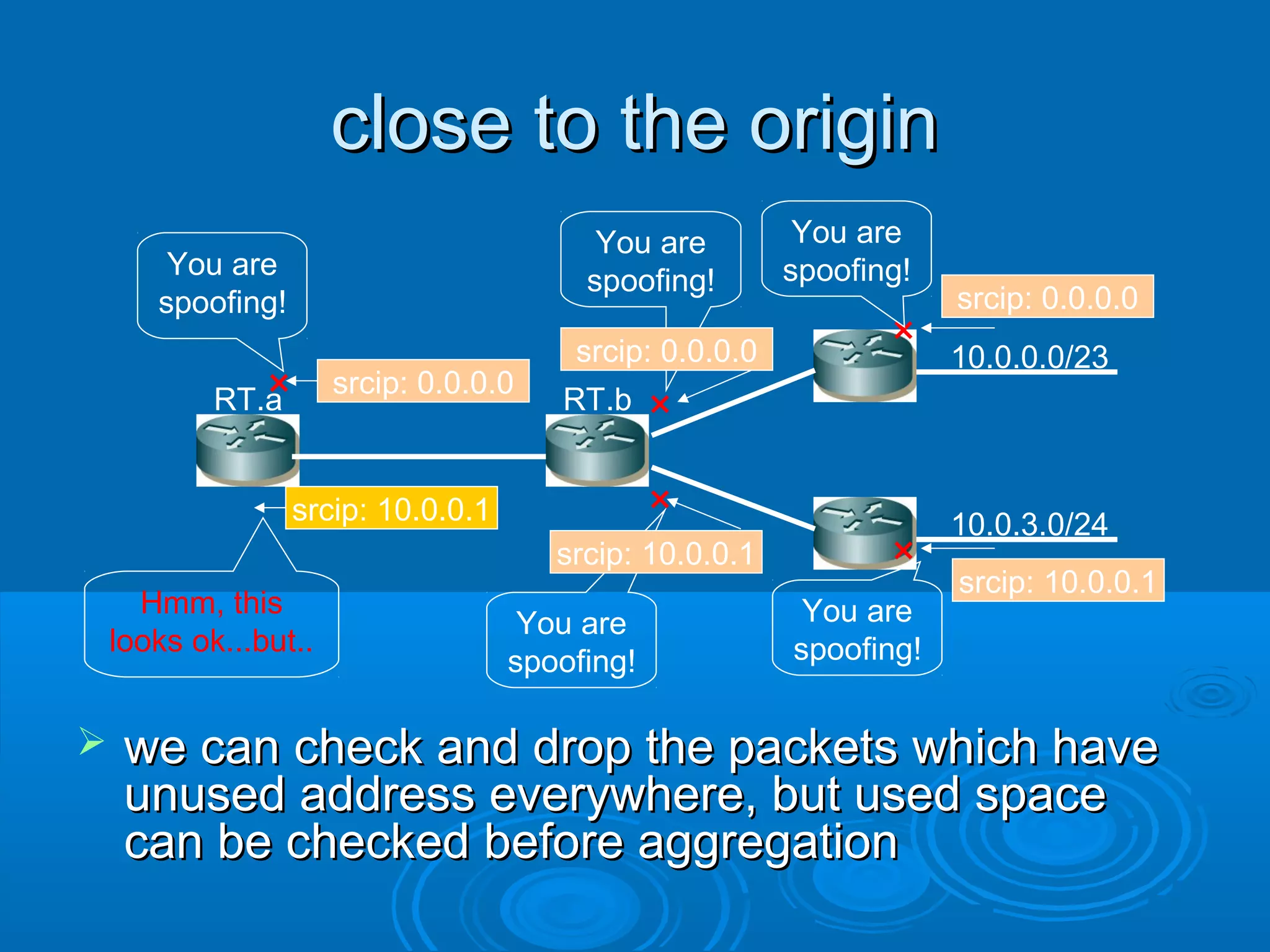
This document discusses IP spoofing, which is a technique hackers use to gain unauthorized access to computers. It does this by forging the source IP address of messages, making it appear they are coming from a trusted host. Two main techniques are using an internal IP address or an authorized external address. IP spoofing is commonly used in denial of service attacks and network intrusions by defeating security like authentication based on IP addresses. It allows impersonating trusted computers and intercepting communications. However, IP spoofing alone does not fully hide one's identity as responses will go to the spoofed address rather than the actual source.