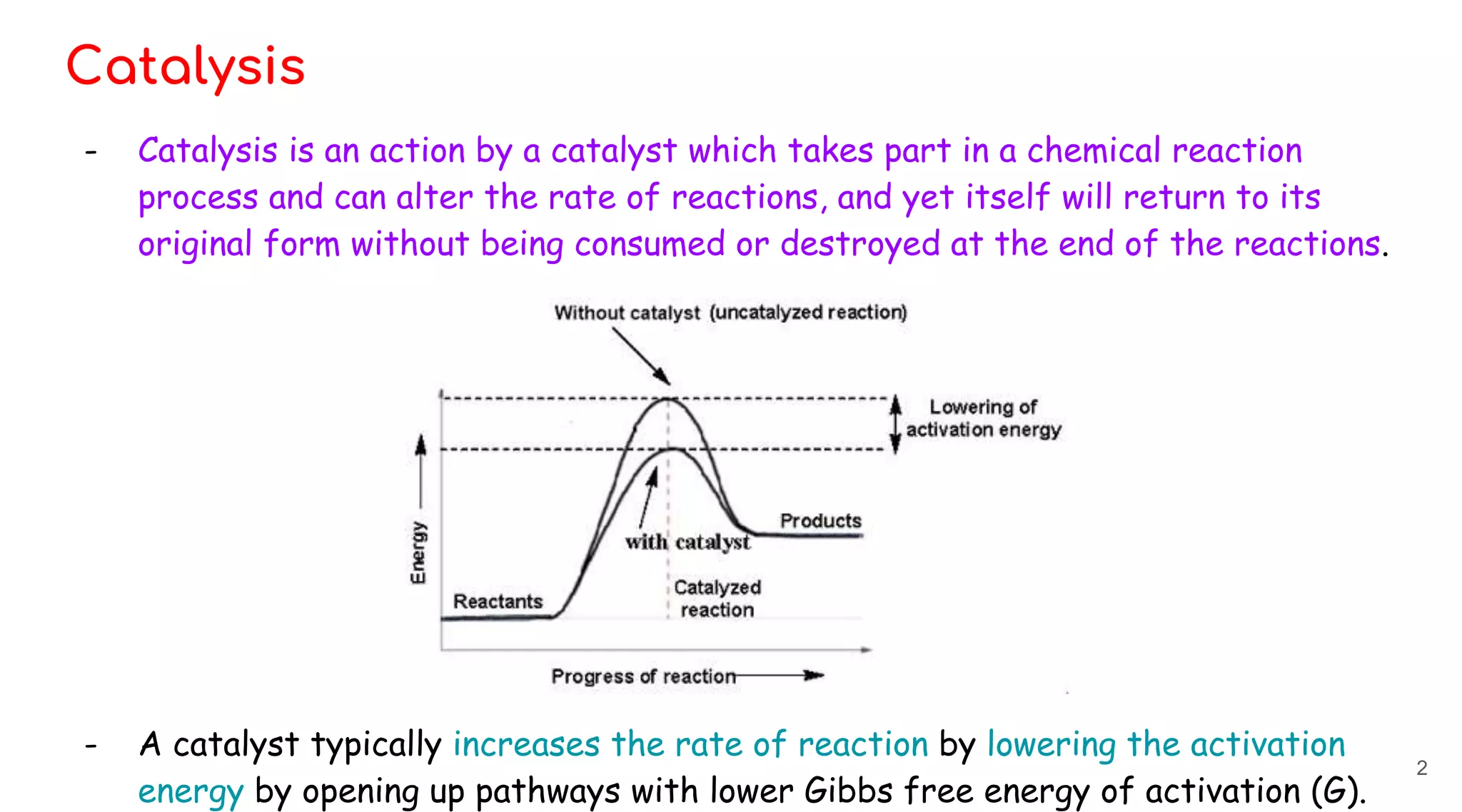
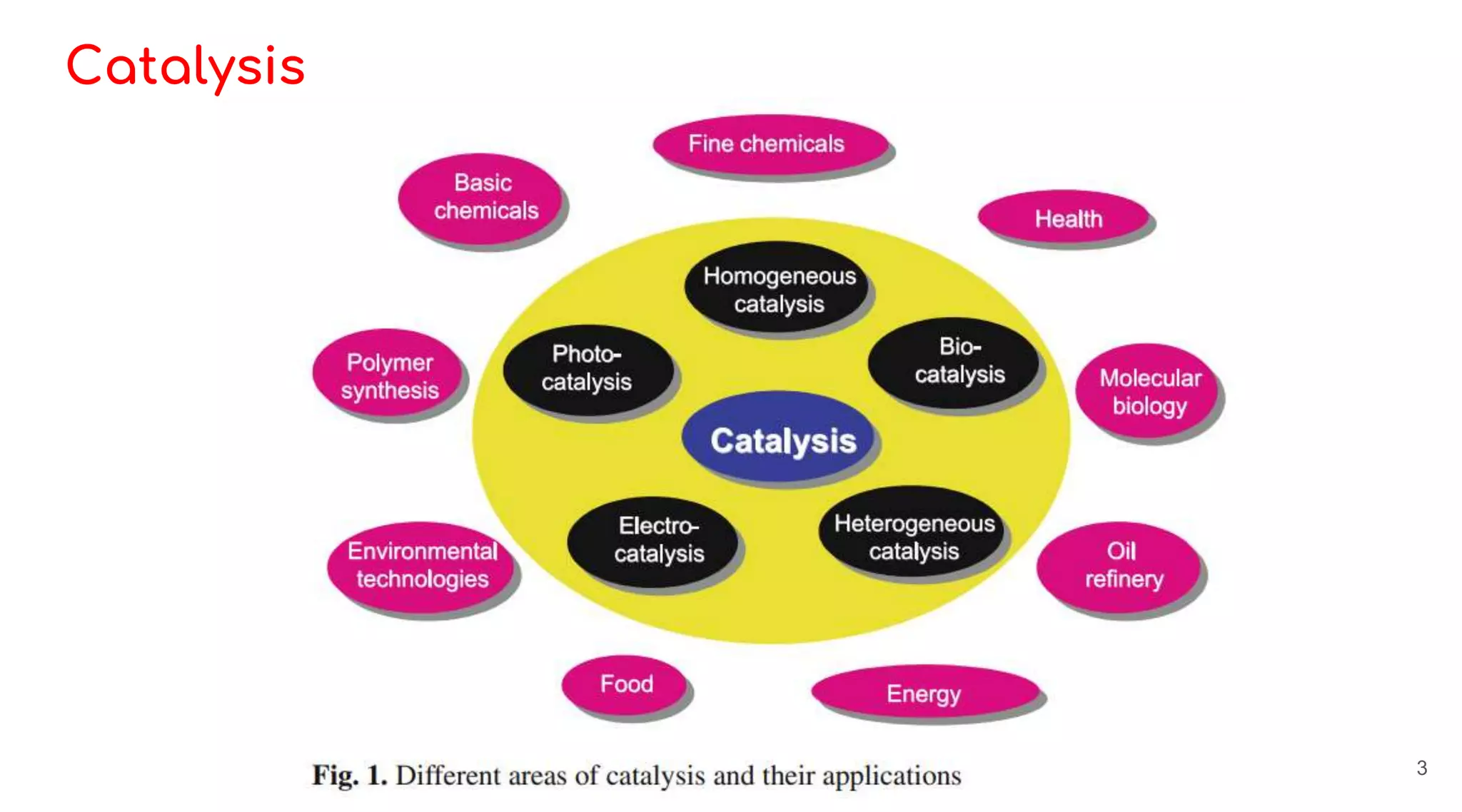
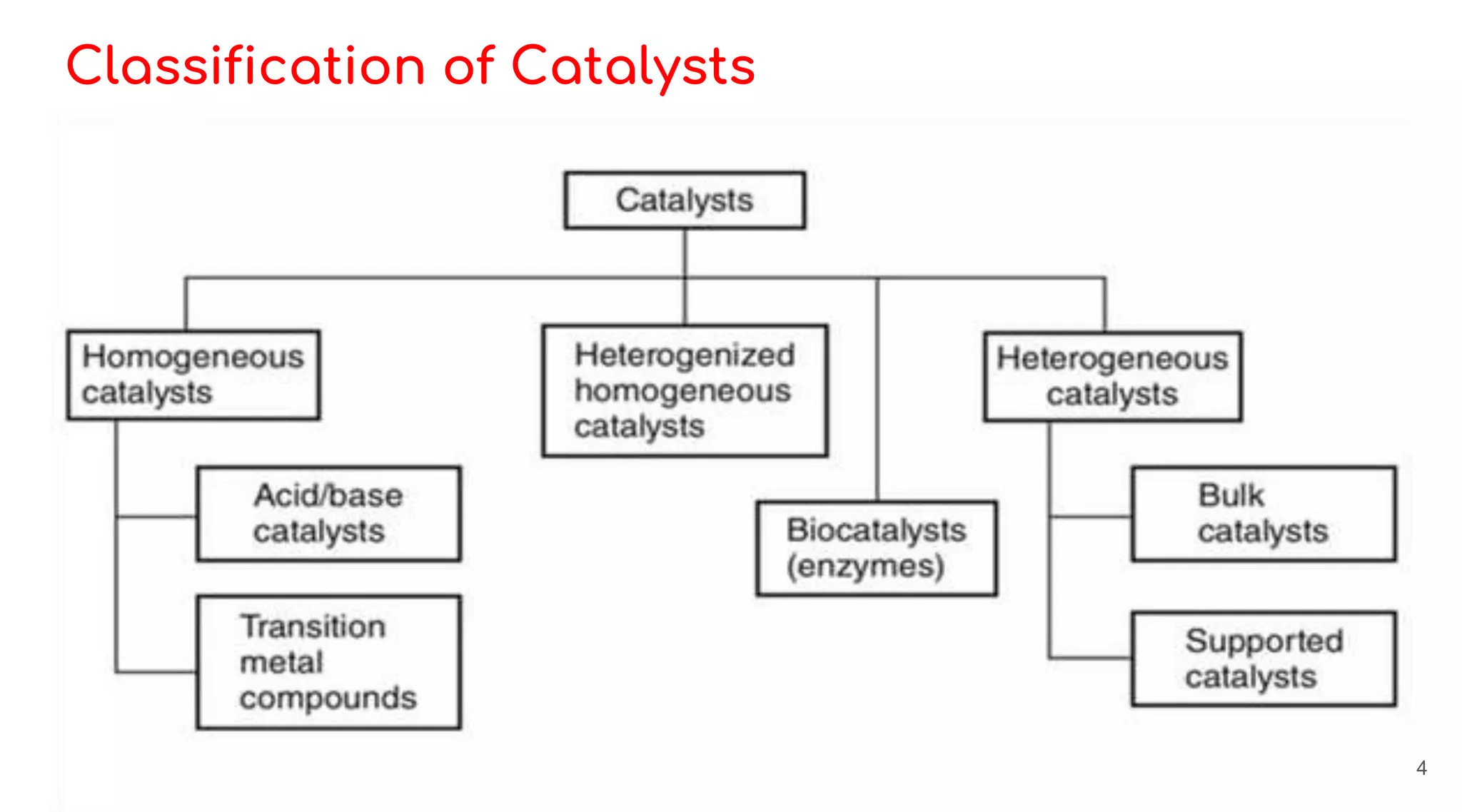
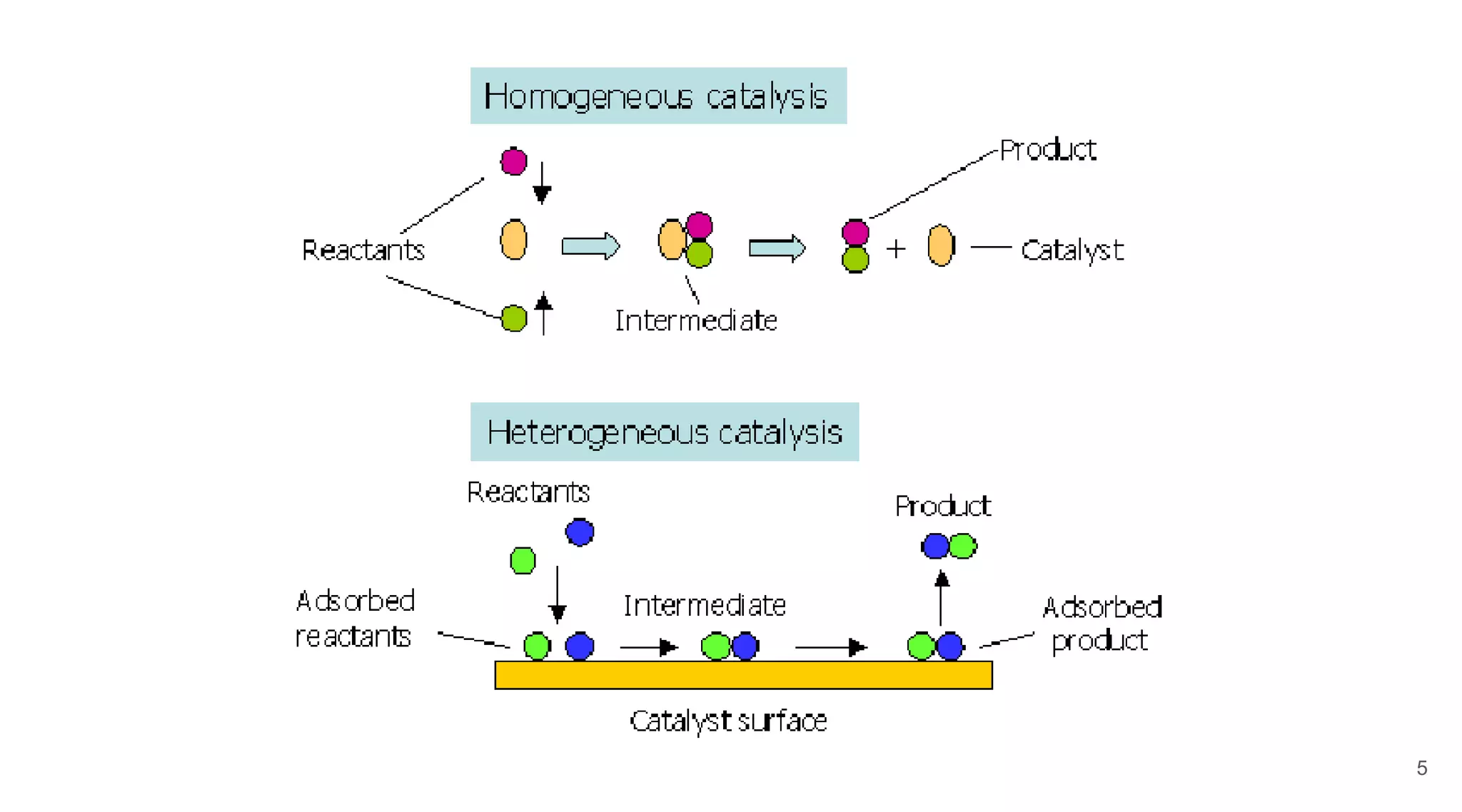
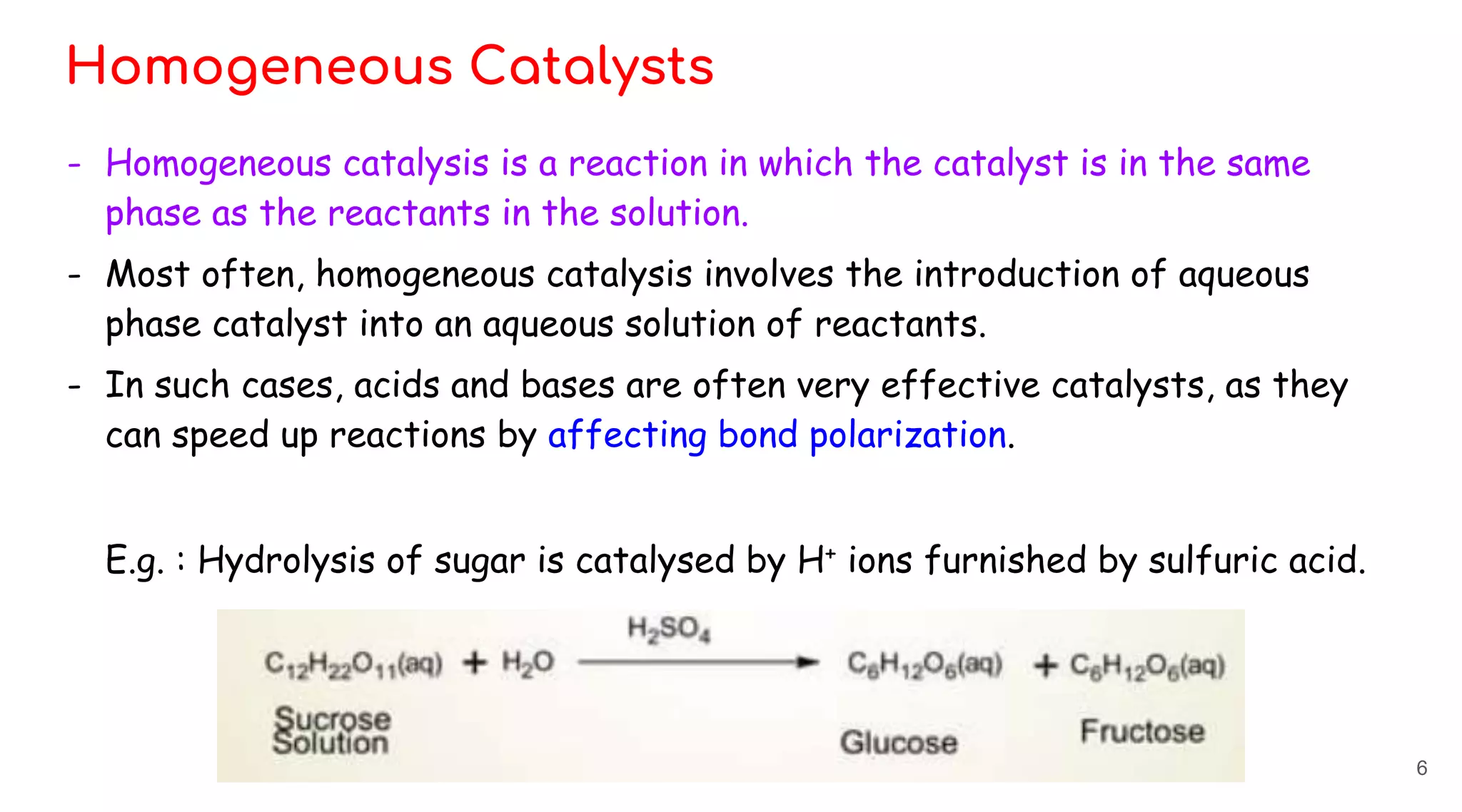
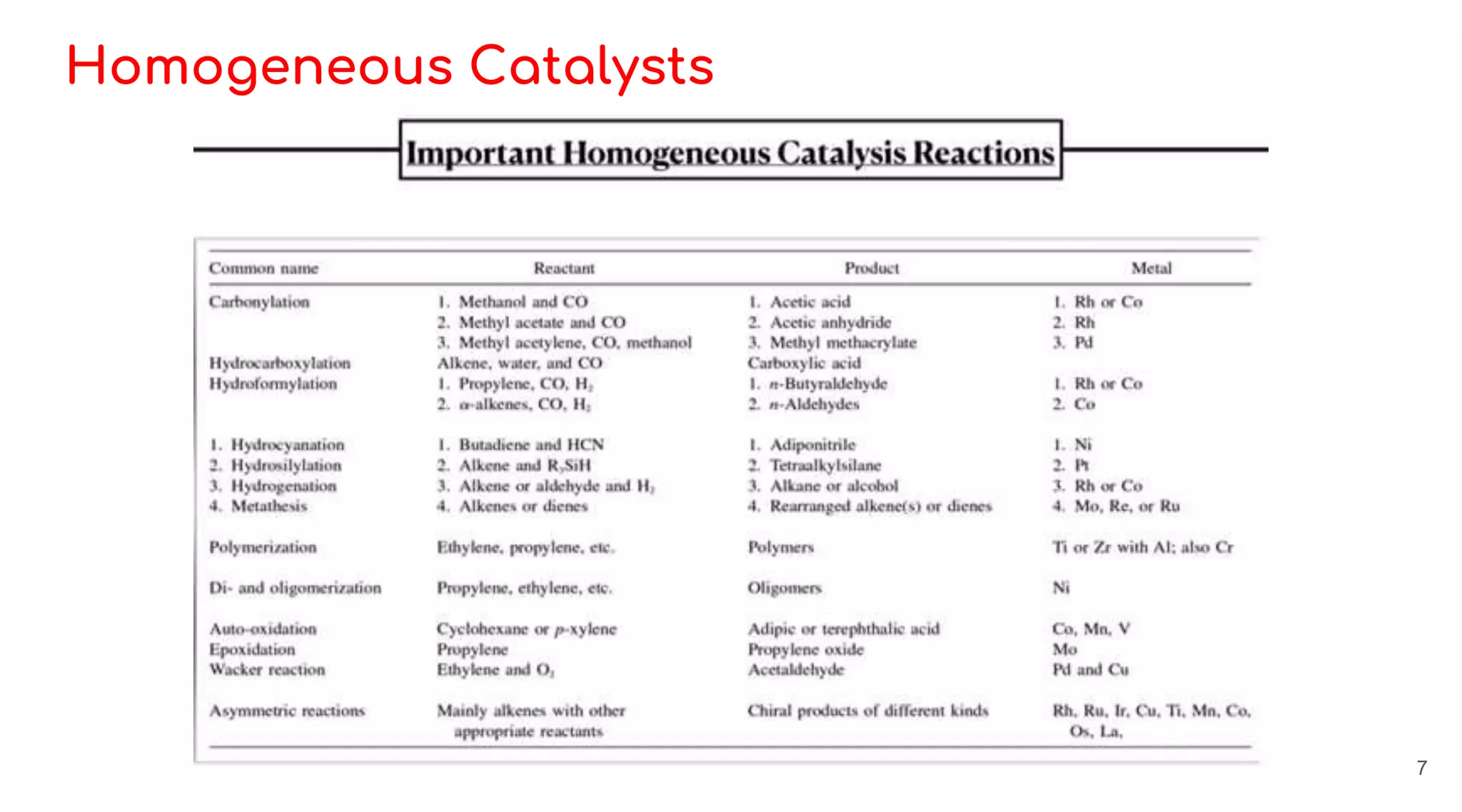
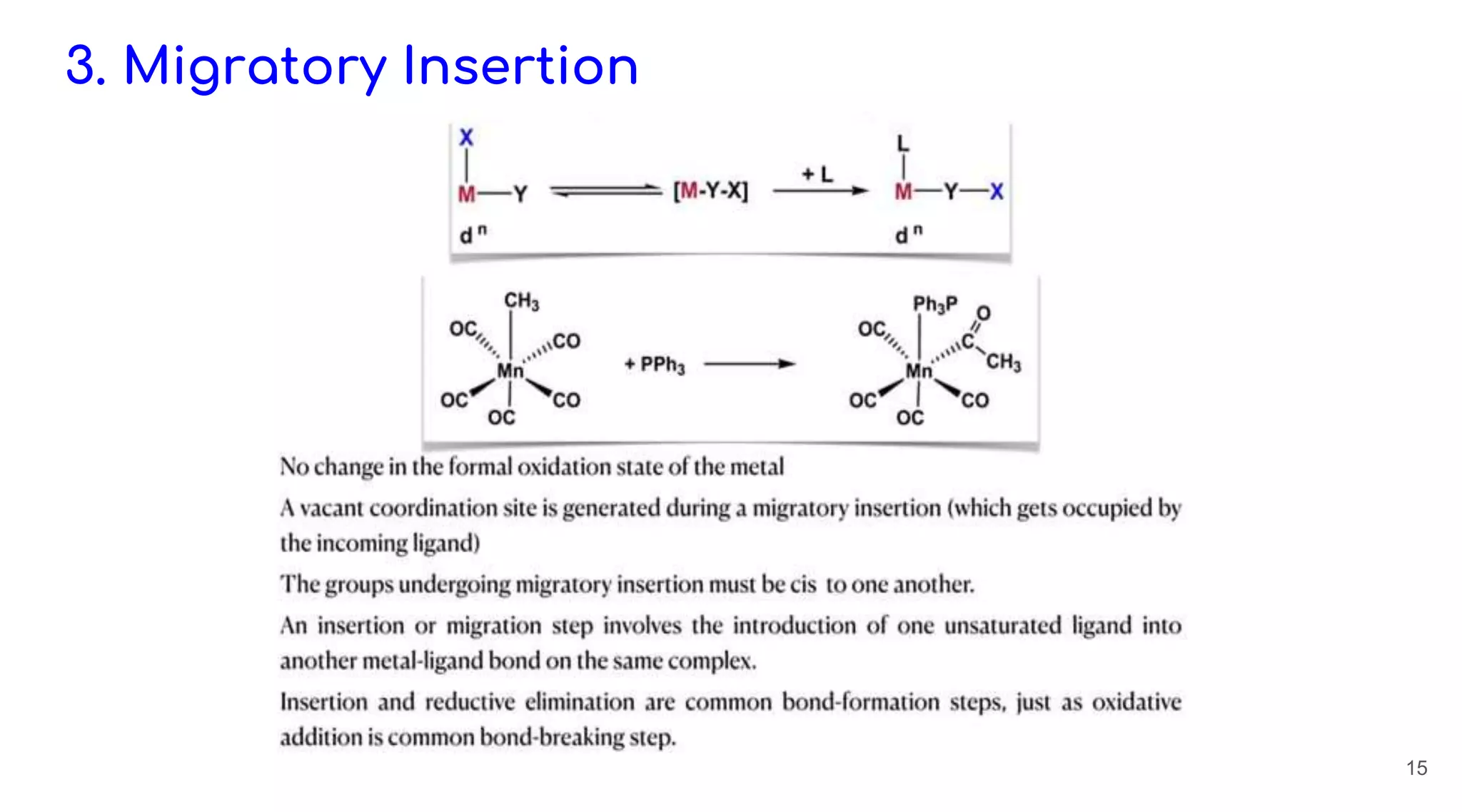
Homogeneous catalysis refers to reactions where the catalyst is in the same phase as the reactants. Common homogeneous catalysts include acids and bases in aqueous solutions. Homogeneous catalysts can provide selectivity in terms of chemoselectivity, regioselectivity, diastereoselectivity, and enantioselectivity. Important reaction types for homogeneous catalysis include oxidative addition, reductive elimination, migratory insertion, and β-hydride elimination. Key reactions discussed are hydrogenation, hydroformylation, hydrocyanation, and applications of Ziegler-Natta catalysts and Wilkinson's catalyst. Chiral induction with chiral ligands is also discussed for producing chiral molecules in drug synthesis such as L-DOPA
![Selectivity of Catalysts
1] Chemoselectivity
When two chemically different functionalities are present such as an alkene
and an aldehyde which both can be hydrogenated, the chemoselectivity tells us
whether the aldehyde or the alkene is being hydrogenated; or when more than
one reaction can take place for the same substrate.
E.g.: Hydrogenation
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/homogeneouscatalysis-230517172621-517eafcd/75/Homogeneous-Catalysis-pptx-8-2048.jpg)
![Selectivity of Catalysts
2] Regioselectivity
The formyl group can be attached to either the primary, terminal carbon atom
or the secondary, internal carbon atom, which leads respectively to the linear
and branched product.
E.g.: Hydroformylation
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/homogeneouscatalysis-230517172621-517eafcd/75/Homogeneous-Catalysis-pptx-9-2048.jpg)
![Selectivity of Catalysts
3] Diastereoselectivity
The substrate contains a stereogenic centre and this together with the
catalyst can direct the addition of dihydrogen in the example to give two
diastereomers, the selectivity for either one is called the diastereoselectivity.
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/homogeneouscatalysis-230517172621-517eafcd/75/Homogeneous-Catalysis-pptx-10-2048.jpg)
![Selectivity of Catalysts
4] Enantioselectivity
The substrate is achiral in this instance, but the enantiopure or enantio-
enriched catalyst may give rise to the formation of one specific product
enantiomer.
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/homogeneouscatalysis-230517172621-517eafcd/75/Homogeneous-Catalysis-pptx-11-2048.jpg)





















![Ziegler-Natta Catalysts
1] Regioselectivity
For propene polymerization, most ZN catalysts are highly regioselective,
favouring 1,2-primary insertion due to electronic and steric effects.
2] Stereoselectivity
The relative stereochemistry of adjacent chiral centers within a
macromolecule is defined as tacticity. Three kinds of stereochemistry are
possible: isotactic, syndiotactic and atactic.
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/homogeneouscatalysis-230517172621-517eafcd/75/Homogeneous-Catalysis-pptx-34-2048.jpg)

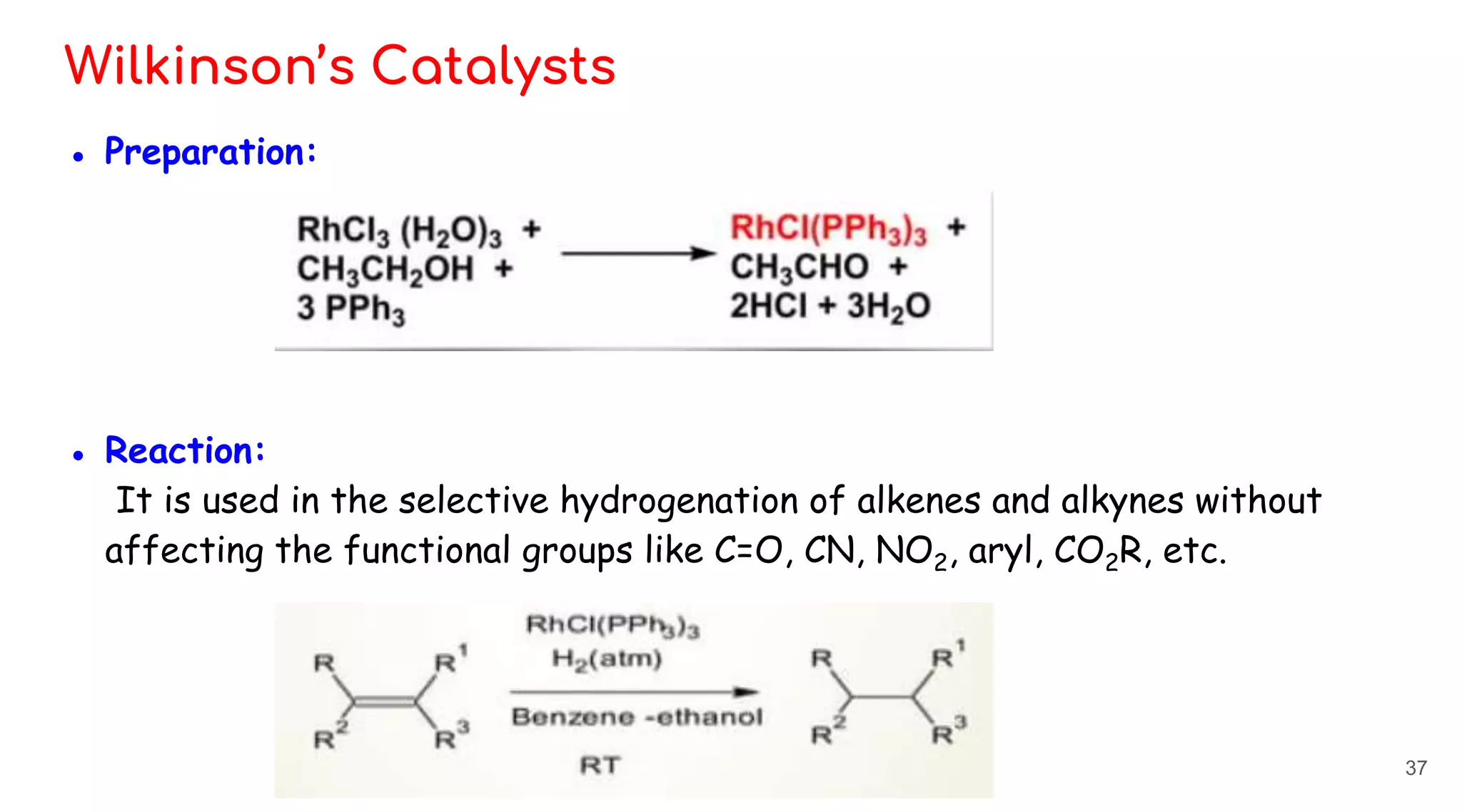
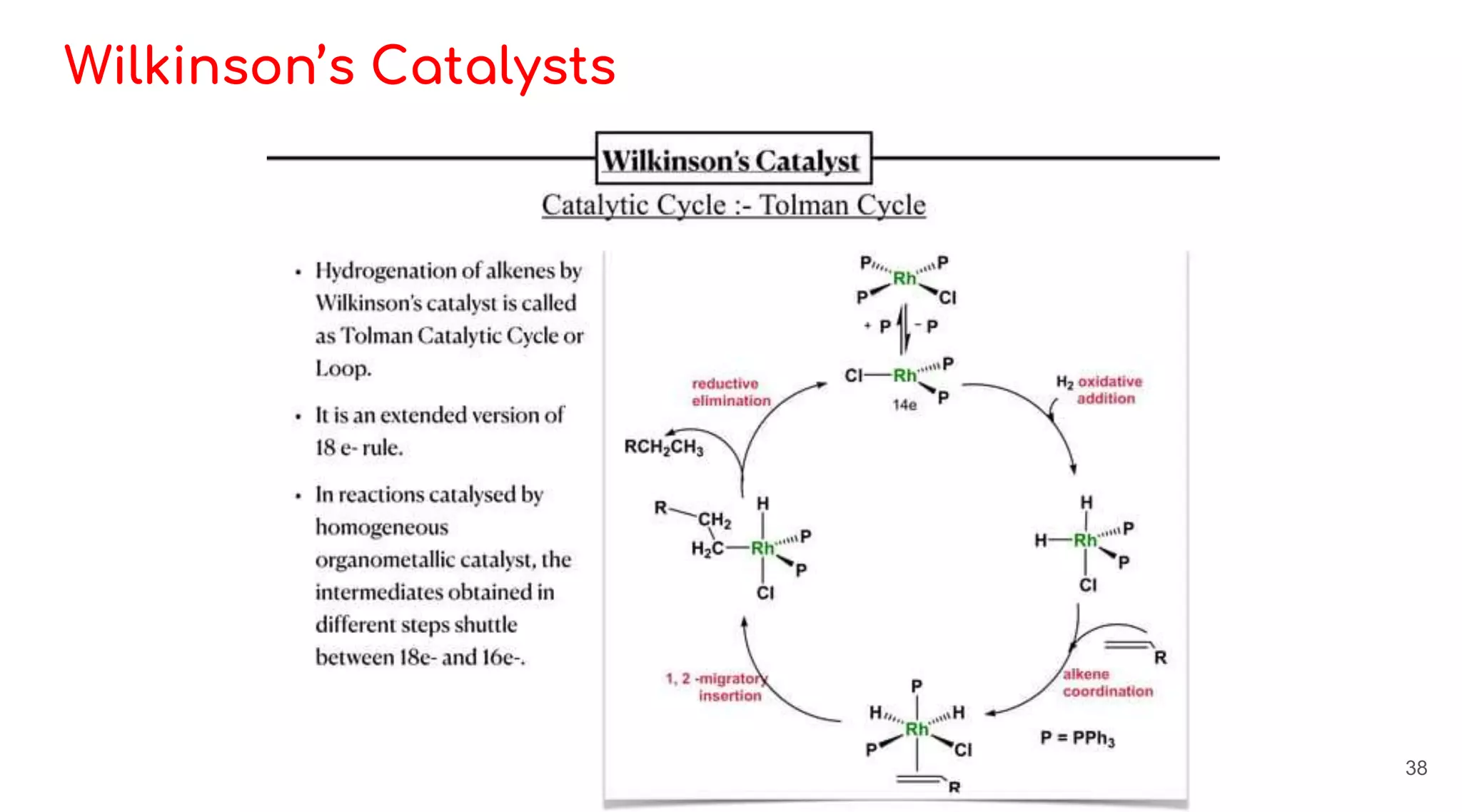
![Wilkinson’s Catalysts
- Wilkinson’s catalyst is the common name for
chlorotris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium (I) [(C6H5)3P]3RhCl.
- It is red brown colored solid that is soluble in hydrocarbon solvents such as
benzene, and more so in THF or DCM.
- The compound is widely used as a catalyst for hydrogenation of alkenes.
- The catalyst is sensitive to the steric influence of the alkene substrate.
- Terminal alkynes are hydrogenated more rapidly than terminal alkenes.
- Conjugated dienes are reduced more slowly than isolated alkenes.
- For disubstituted alkenes, cis are more reactive than trans. Trisubstituted
alkenes are more reactive than tetra-substituted alkenes.
36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/homogeneouscatalysis-230517172621-517eafcd/75/Homogeneous-Catalysis-pptx-36-2048.jpg)





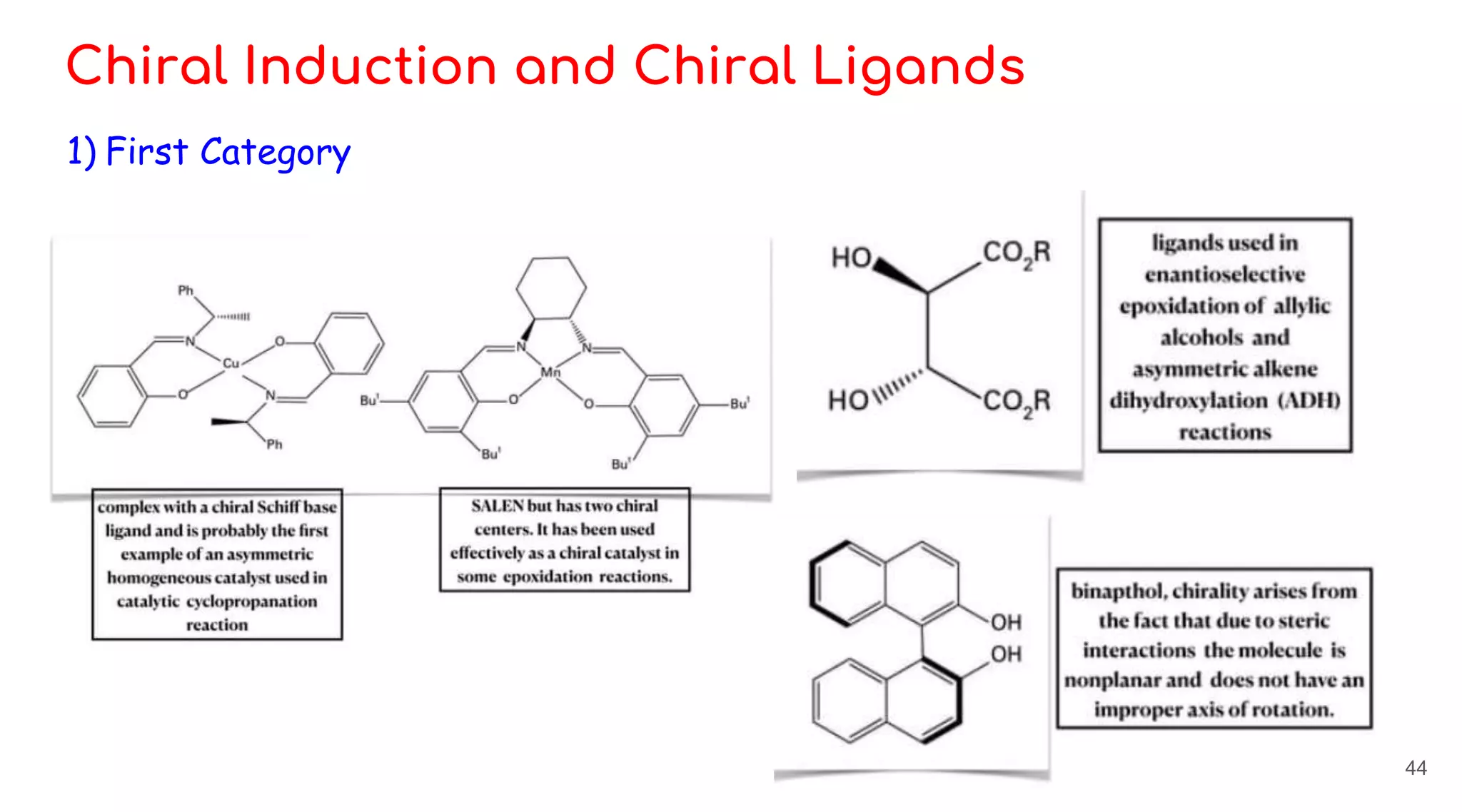

![A] Synthesis of l-DOPA
- The asymmetric hydrogenation of cinnamic acid derivatives involves the
synthesis of L-DOPA.
- The carbon atom bonded to the -NH2 group is the chiral centre.
- The enantiomer D-DOPA is inactive.
- The reaction is carried out in presence of rhodium complex having
asymmetric diphosphine ligand which induces enantio-selectivity.
- The main step in L-DOPA synthesis is the hydrogenation of prochiral alkene
to a specific optical isomer.
47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/homogeneouscatalysis-230517172621-517eafcd/75/Homogeneous-Catalysis-pptx-47-2048.jpg)
![B] Other Examples
48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/homogeneouscatalysis-230517172621-517eafcd/75/Homogeneous-Catalysis-pptx-48-2048.jpg)
