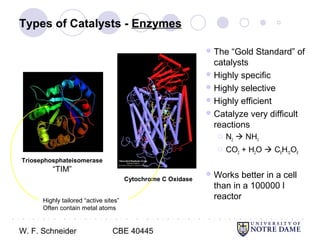
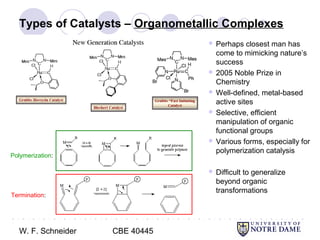
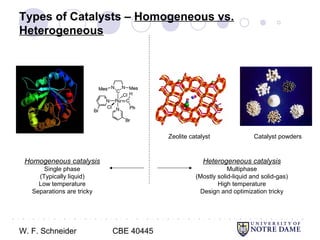
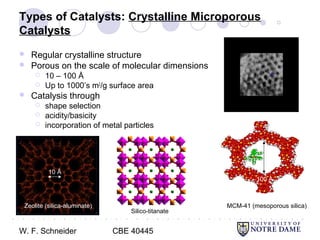
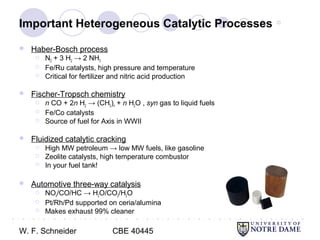
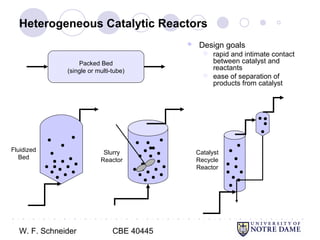
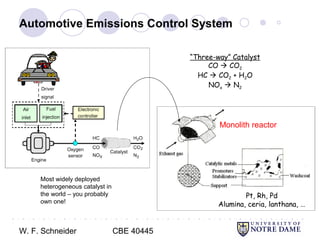
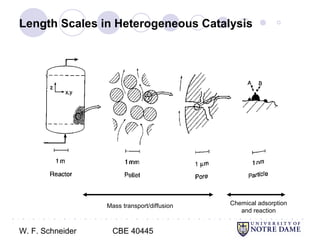
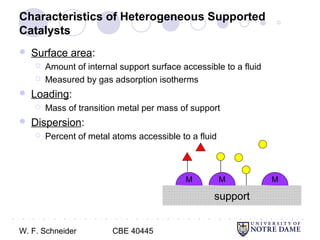
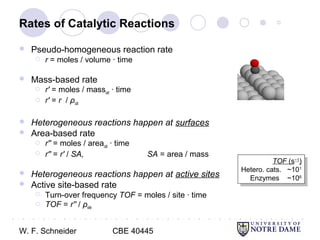
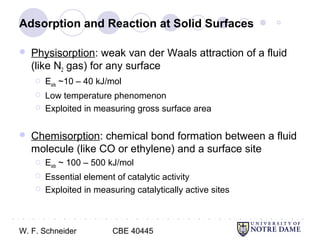
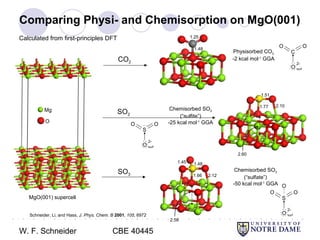
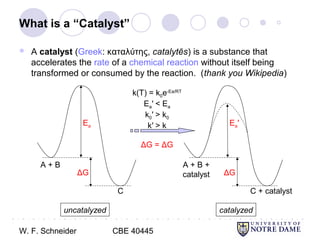
This document provides an introduction to catalysis. It defines a catalyst as a substance that accelerates a chemical reaction without being consumed. It describes how catalysts lower the activation energy of reactions, allowing them to proceed more quickly. It discusses different types of catalysts including enzymes, organometallic complexes, zeolites, and metals supported on high surface area materials. It also describes important industrial catalytic processes and considerations in heterogeneous catalysis such as reactor design, mass transport limitations, and the characterization of catalysts.
![W. F. Schneider CBE 40445
● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ●
○
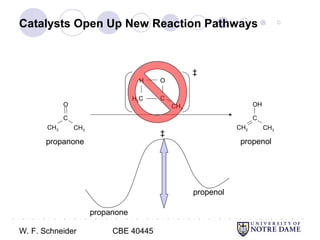
Catalysts Open Up New Reaction Pathways
CH3
C
CH3
O
CH2
C
CH3
OH
propanone propenol
OH−
CH2
C
CH3
O−
+ H2O
−OH−
Base catalyzed
propanone
propenol
intermediate
‡ ‡
rate = k[OH−
][acetone]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/catalysis-180724171149/85/Catalysis-4-320.jpg)
![W. F. Schneider CBE 40445
● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ ●
○
Catalysts Open Up New Reaction Pathways
CH3
C
CH3
O
CH2
C
CH3
OH
propanone
propenol
+ H2O
Acid catalyzed
H3O+
CH3
C
CH3
OH
+
−H3O+
propenol
different
intermediate
‡ ‡
propanone
rate = k[H3O+
][acetone]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/catalysis-180724171149/85/Catalysis-5-320.jpg)