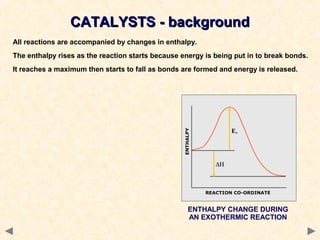
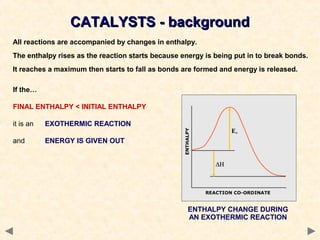
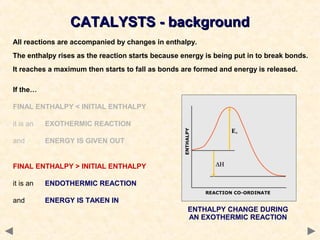
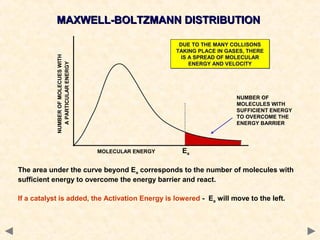
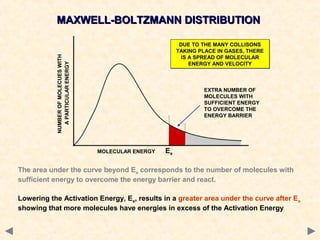
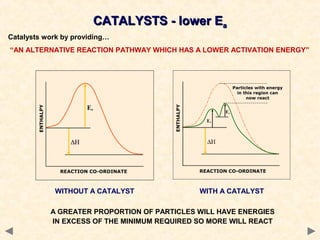
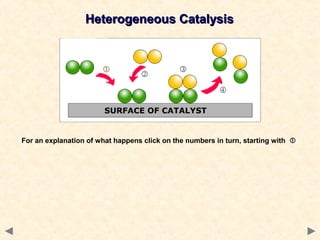
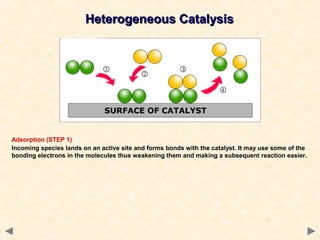
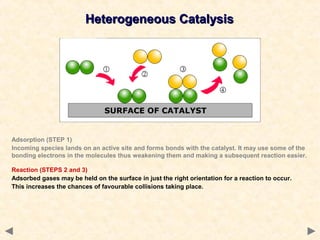
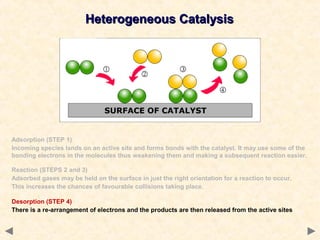
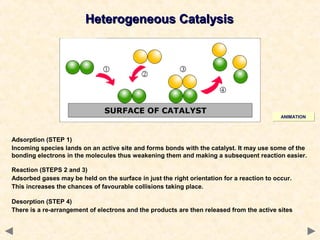
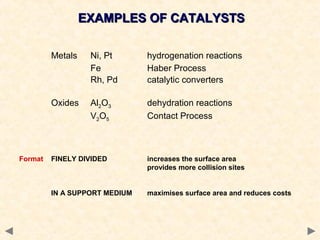
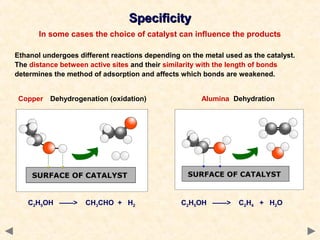
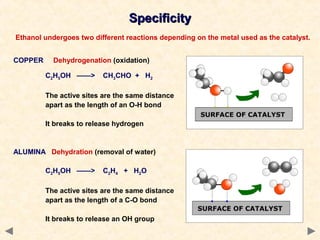
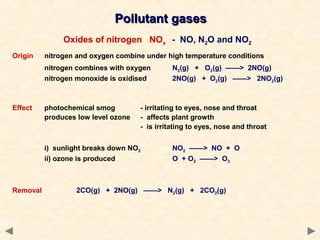
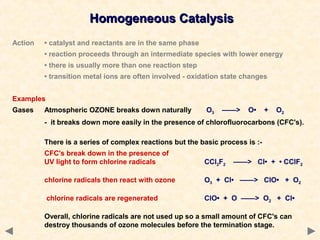
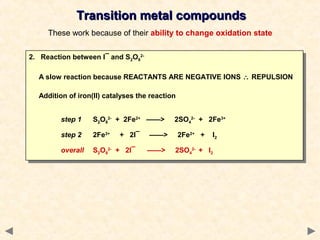
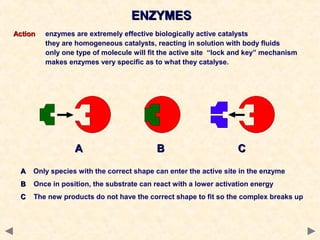
This document provides an overview of catalysis for A-level chemistry students. It begins with background information on enthalpy changes and activation energy in chemical reactions. It then discusses the principles of heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysis, including how catalysts lower the activation energy of reactions by providing alternative reaction pathways. Specific examples discussed include catalytic converters used to reduce automobile emissions. The document also covers concepts such as catalytic specificity, poisoning of catalysts, and auto-catalysis involving transition metal compounds.