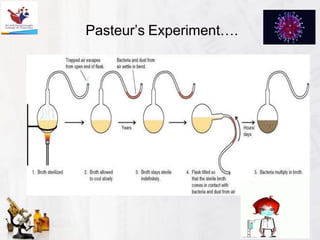
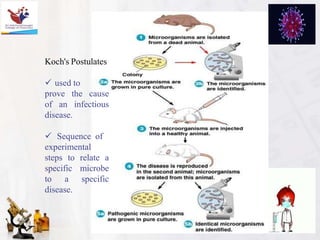
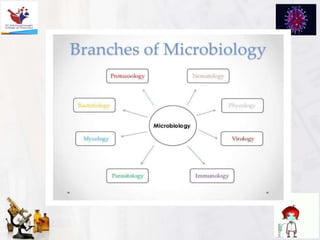
The document provides an introduction to the history and scope of pharmaceutical microbiology. It discusses how microbiology emerged from early theories of spontaneous generation being disproven through experiments showing microbes are present everywhere and can be transmitted. Key figures who advanced the field include Van Leeuwenhoek who first observed microbes under the microscope, Pasteur who disproved spontaneous generation and showed microbes cause fermentation and spoilage, Koch who established criteria to link microbes to specific diseases, and Fleming who discovered the antibiotic penicillin. The document concludes with the scope of microbiology encompassing both basic research on microbes and applied areas like disease treatment, food and industrial production, and medical uses.