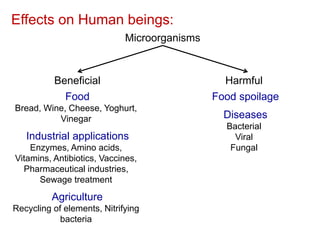
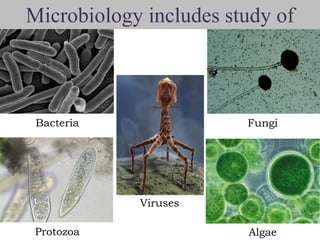
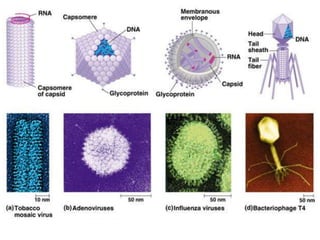
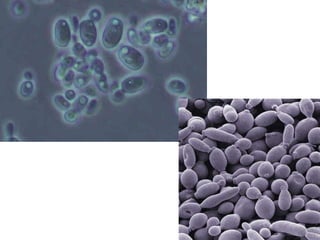
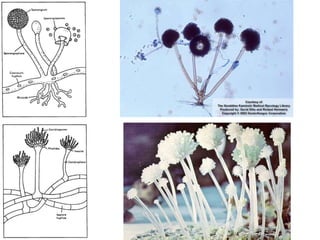
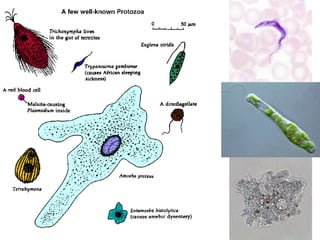
Microbiology is the study of microscopic organisms like bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa and algae. It examines their classification, physiology, distribution in nature, and relationship to humans and other organisms. Microorganisms can be beneficial by producing foods and medicines, or harmful by causing spoilage, diseases, and infections. Important discoveries in microbiology history include the first observations of microbes by van Leeuwenhoek, the germ theory of disease, development of pure culture and staining techniques, and the discoveries of pathogens like the anthrax bacillus and tuberculosis bacillus. Landmark figures who advanced the field include Pasteur, Koch, Lister, Ehrlich, Fleming and Metchnikoff.










![Varo & Columella [1st century BC]: Diseases caused by
invisible organisms (Animalia minuta)
Girolamo Fracastorius of verona [1546]: Living germs
(contagium vivum) cause infectious diseases
Von Plenciz [1762]: Each disease caused by different agent
Kircher [1659]: reported finding minute worms in blood of
plague patients.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionhistory-131228081340-phpapp02-160308180850/85/Microbiology-23-320.jpg)
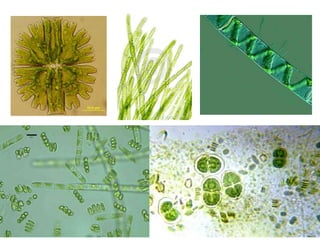
![Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek [1632-1723]:
• 1st to observe and describe single celled
organisms, “animalcules”, we now refer to as
microorganisms.
• Described different morphological forms of
bacteria
• 1st to record observations of muscle fibers,
bacteria, spermatozoa and blood flow in
capillaries (small blood vessels).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionhistory-131228081340-phpapp02-160308180850/85/Microbiology-24-320.jpg)
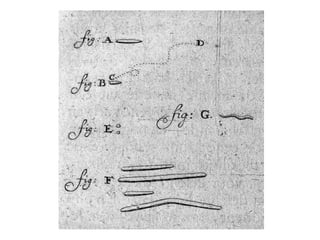
![Robert Hooke [1678]:
• Developed Compound microscope
• 1st to coin the term ‘Cell’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionhistory-131228081340-phpapp02-160308180850/85/Microbiology-26-320.jpg)
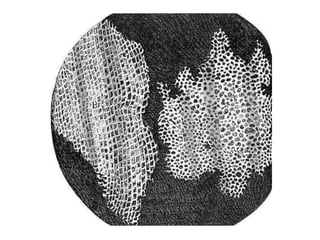
![Earliest discovery of pathogenic role of microorganism:
Augustino Bassi [1835]:
Muscardine diseases of silk worms was caused by a fungus.
Oliver Holmes [1840] & Ignaz Semmelweis [1846]:
Concluded that puerperial sepsis was transmitted by
contaminated hands of obstetricians, nurses and medical
students.
This could be prevented by washing hands in antiseptic
solutions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionhistory-131228081340-phpapp02-160308180850/85/Microbiology-28-320.jpg)

![Louis Pasteur [1822-1895]:
Father of Microbiology
• Trained chemist from France
• Established that Fermentation was
caused by microbial agents
• Demonstrated anaerobic fermentation by
both bacteria and yeasts (bacteria
produce acid and yeast produce alcohol)
• Developed pasteurization to prevent spoilage of wine by
bacteria
• Noted that different types of fermentations were associated with
different kinds of microbes
• Development of methods and techniques of Bacteriology
• proved that microbes arise only from their like](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionhistory-131228081340-phpapp02-160308180850/85/Microbiology-30-320.jpg)
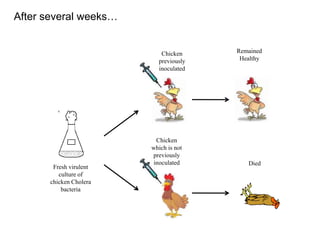
![• Introduction of sterilization techniques: development of steam
sterilizer, autoclave and hot-air oven
• Studies on Anthrax, Cholera and hydrophobia
• Introduced live attenuated (weakened) vaccines
[Accidental observation: chicken cholera bacillus cultures left for
several weeks lost their pathogenicity but retained their ability to
protect the chickens from infection]
Pure culture of
chicken Cholera
bacteria
8 weeks old
Chicken
inoculated
Remains
Healthy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionhistory-131228081340-phpapp02-160308180850/85/Microbiology-31-320.jpg)


![Joseph Lister [1827-1912]:
Father of Antiseptic surgery
• Professor of surgery
• Applied Pasteur’s work and introduced
Antiseptic techniques in Surgery
• Use of Carbolic acid in Antiseptic
surgery
• Resulted in drop in morbidity and
mortality due to surgical sepsis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionhistory-131228081340-phpapp02-160308180850/85/Microbiology-37-320.jpg)
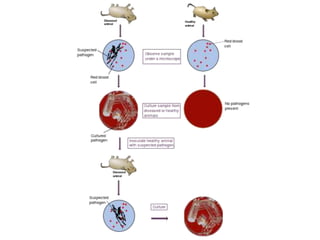
![Robert Koch [1843-1910]:
Father of Bacteriology
• Introduced methods for isolation of
pure culture
• use of solid media for isolation of
bacteria
• Staining techniques
• discovered Anthrax bacillus (1876),
Tubercle bacillus (1882) and cholera
vibrios (1883)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionhistory-131228081340-phpapp02-160308180850/85/Microbiology-38-320.jpg)

![Paul Ehrlich [1854-1915]:
Father of Chemotherapy
• Applied stains to cells and tissues for
study of their functions.
• Reported the acid-fast nature of
tubercle bacillus
• Discovered Salvarsan (derivative of
arsenic) sometimes called as ‘Magic
Bullete’
• Salvarsan: capable of destroying
spirochetes of syphilis.
• Gave rise to new branch of medicine:
‘Chemotherapy’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionhistory-131228081340-phpapp02-160308180850/85/Microbiology-41-320.jpg)
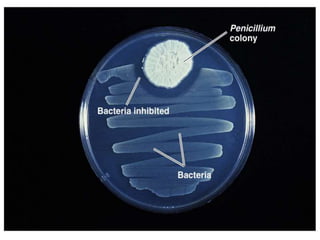
![Alexander Fleming [1928]:
• Discovery of 1st Antibiotic
• Accidentally discovered Penicillin produced by a fungus
Penicillium
• Left his Staphylococcus culture on an agar plate for 2 weeks →
went on vacation → came back & found mold on his plate which
prevented bacterial growth](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionhistory-131228081340-phpapp02-160308180850/85/Microbiology-43-320.jpg)