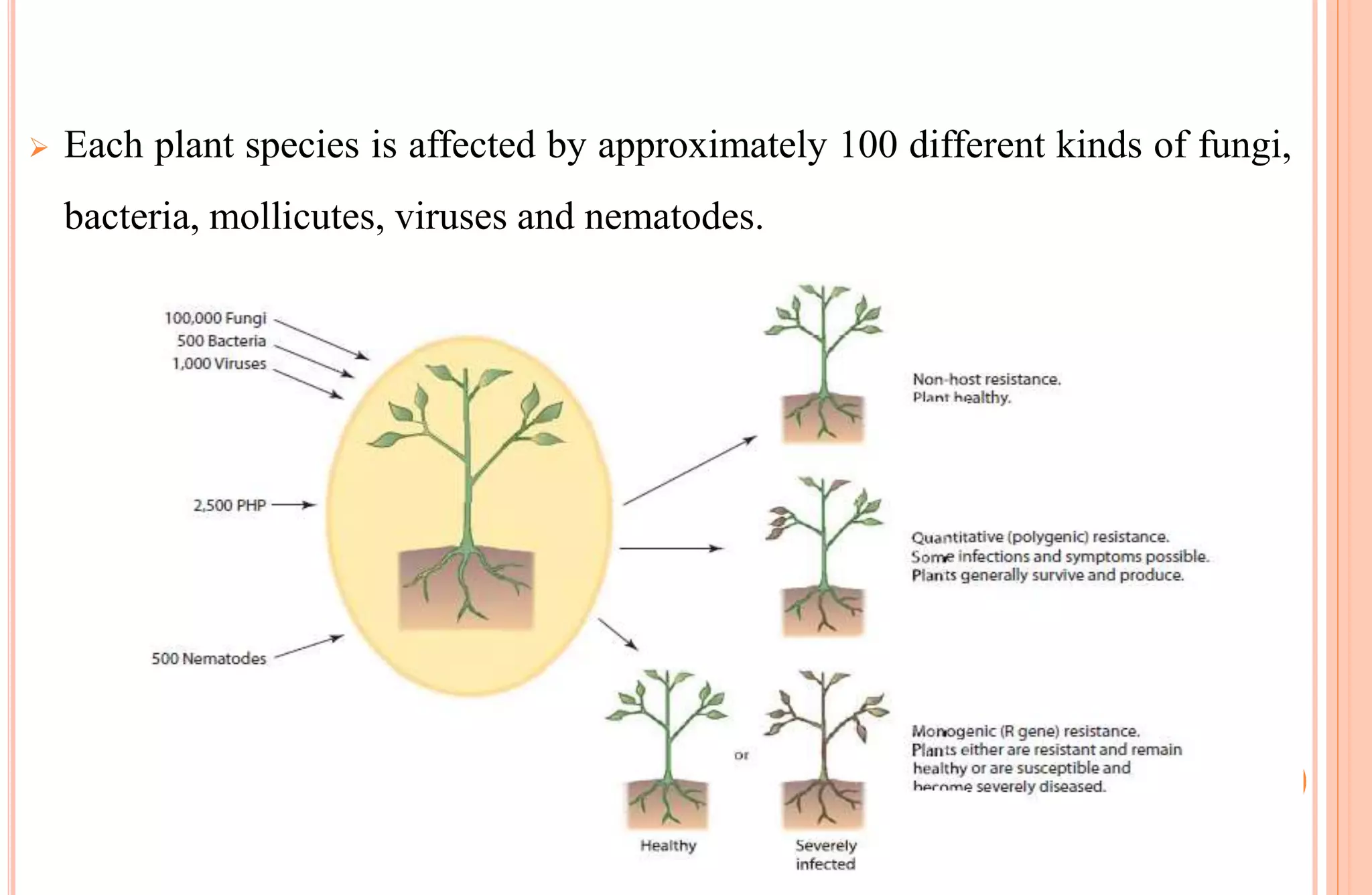
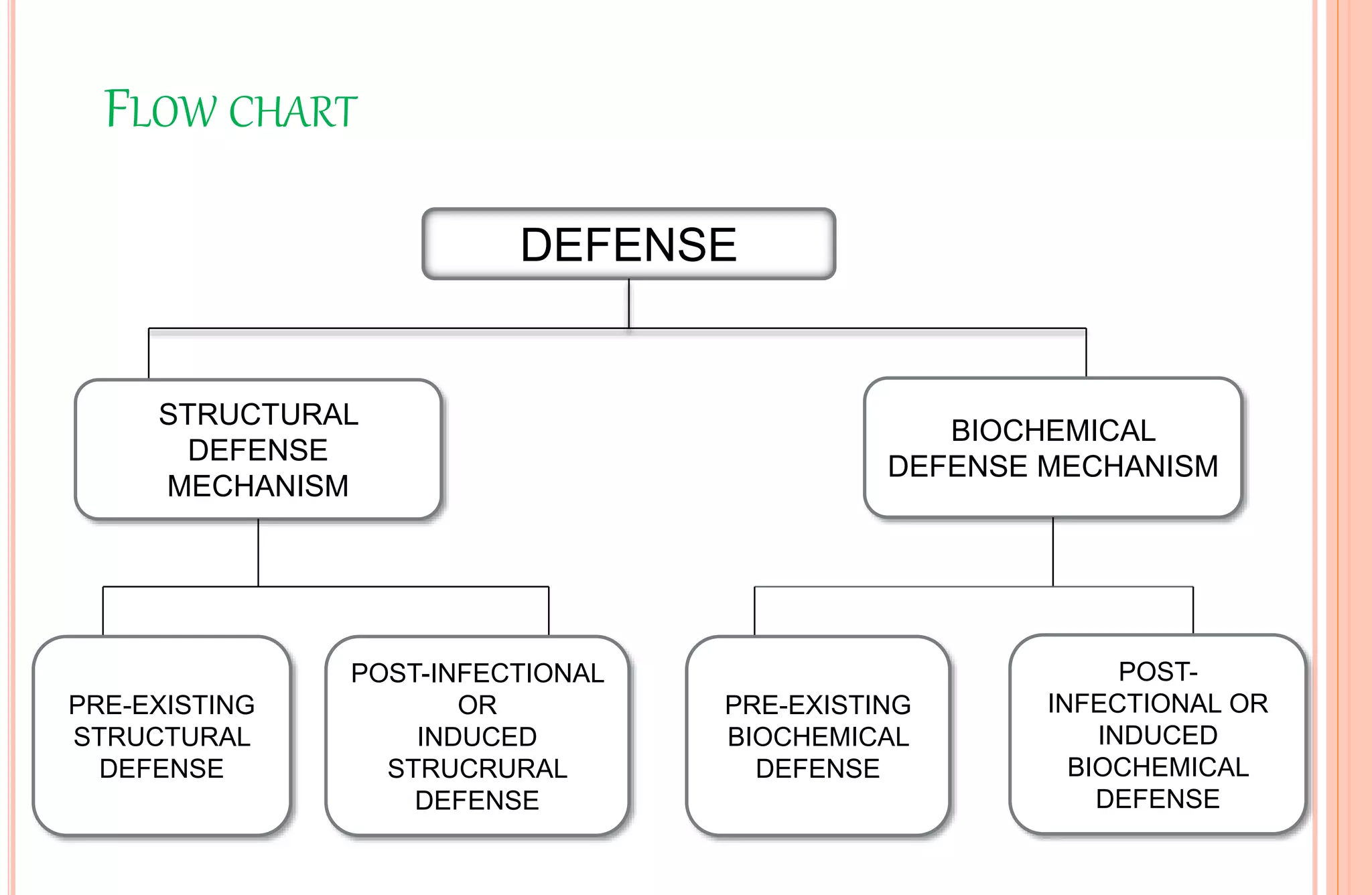
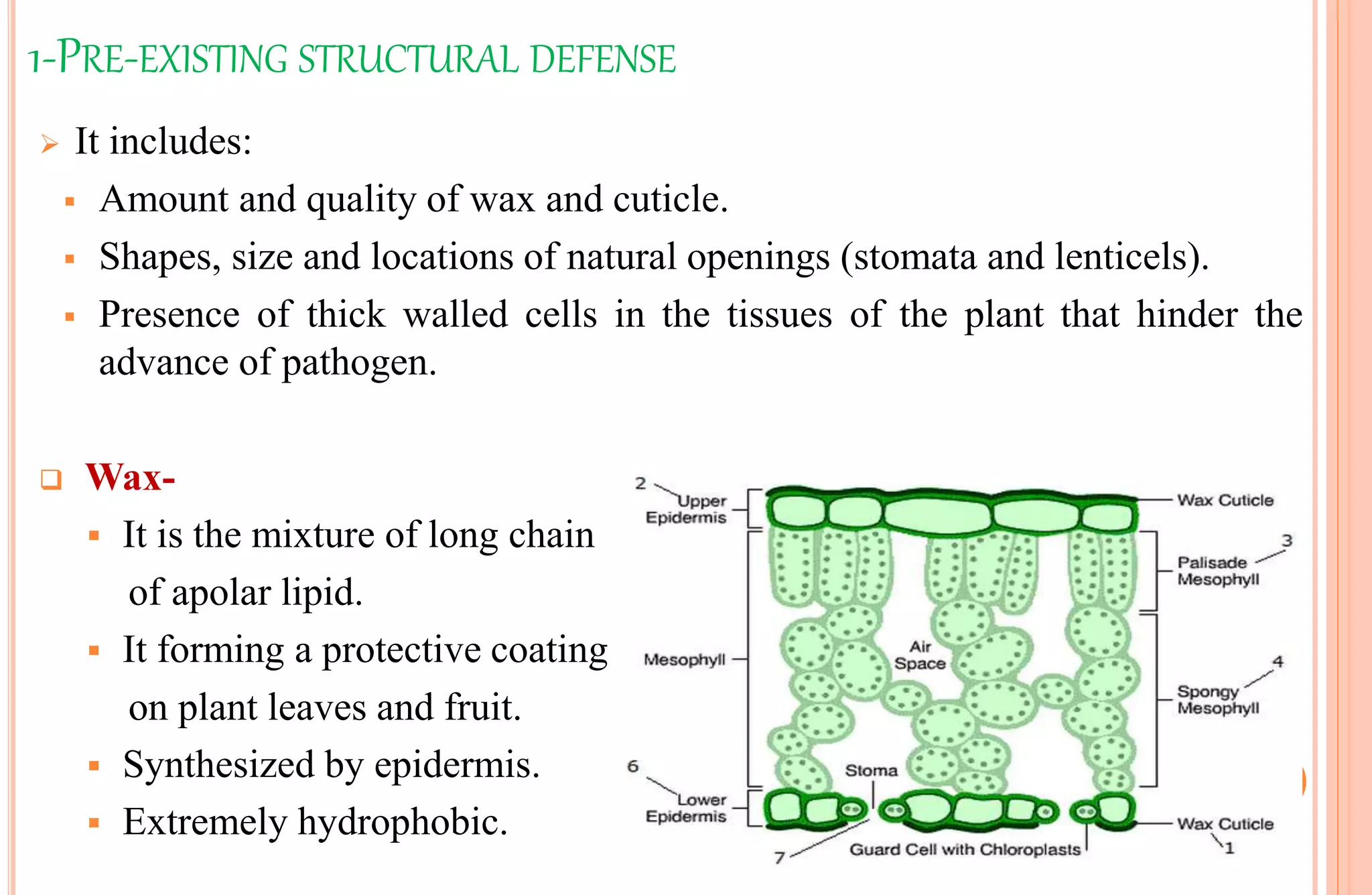
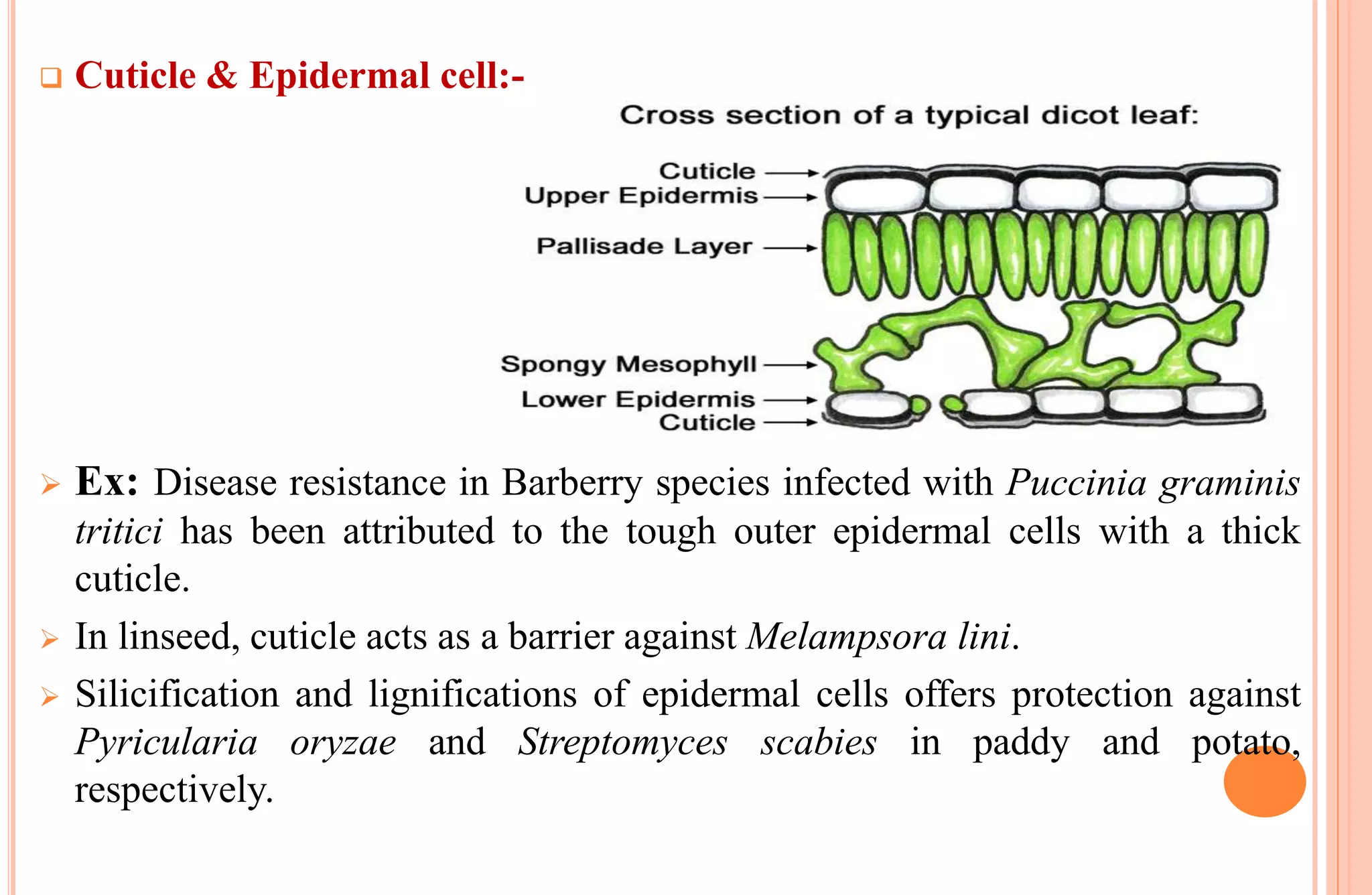
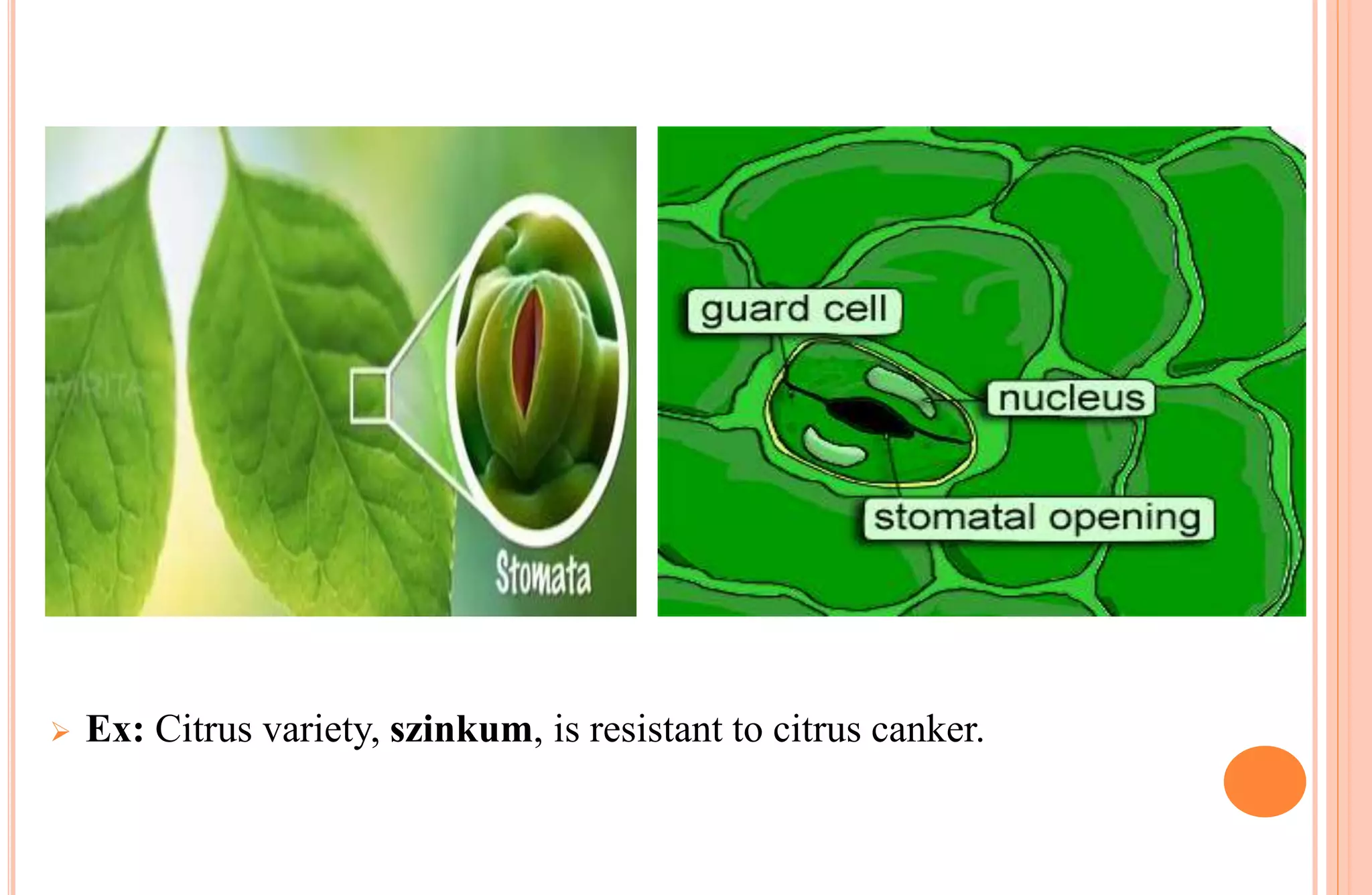
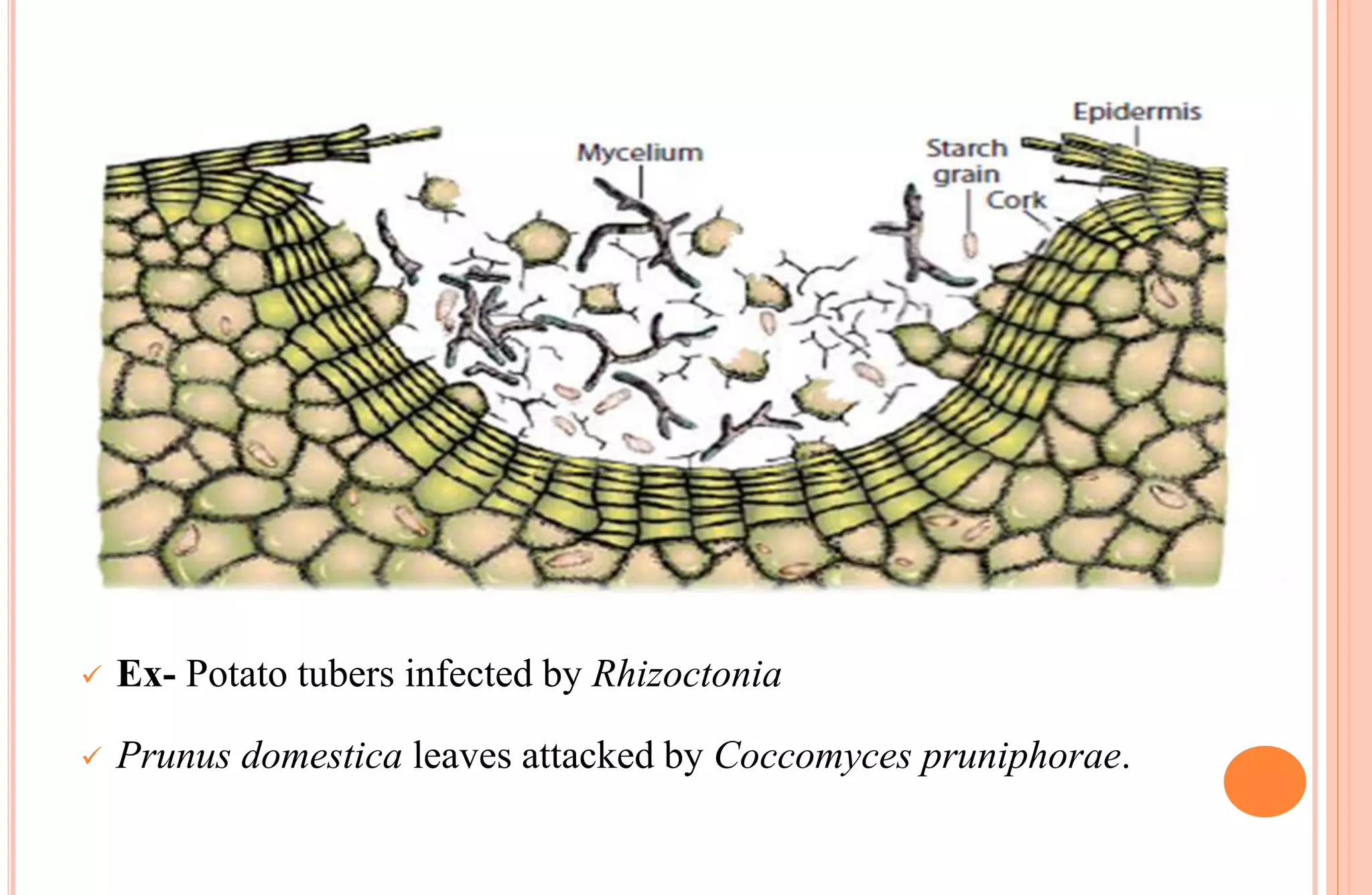
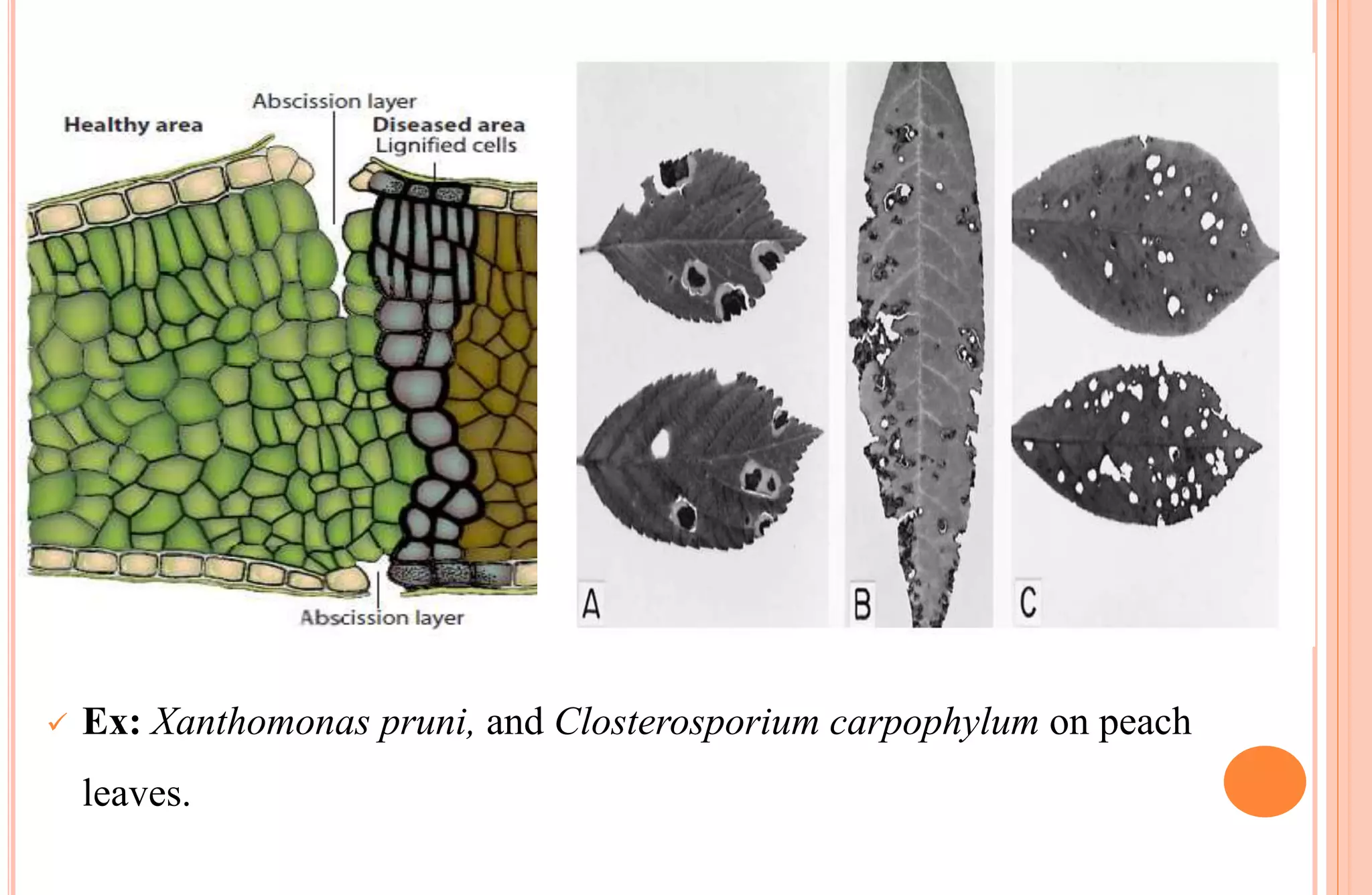
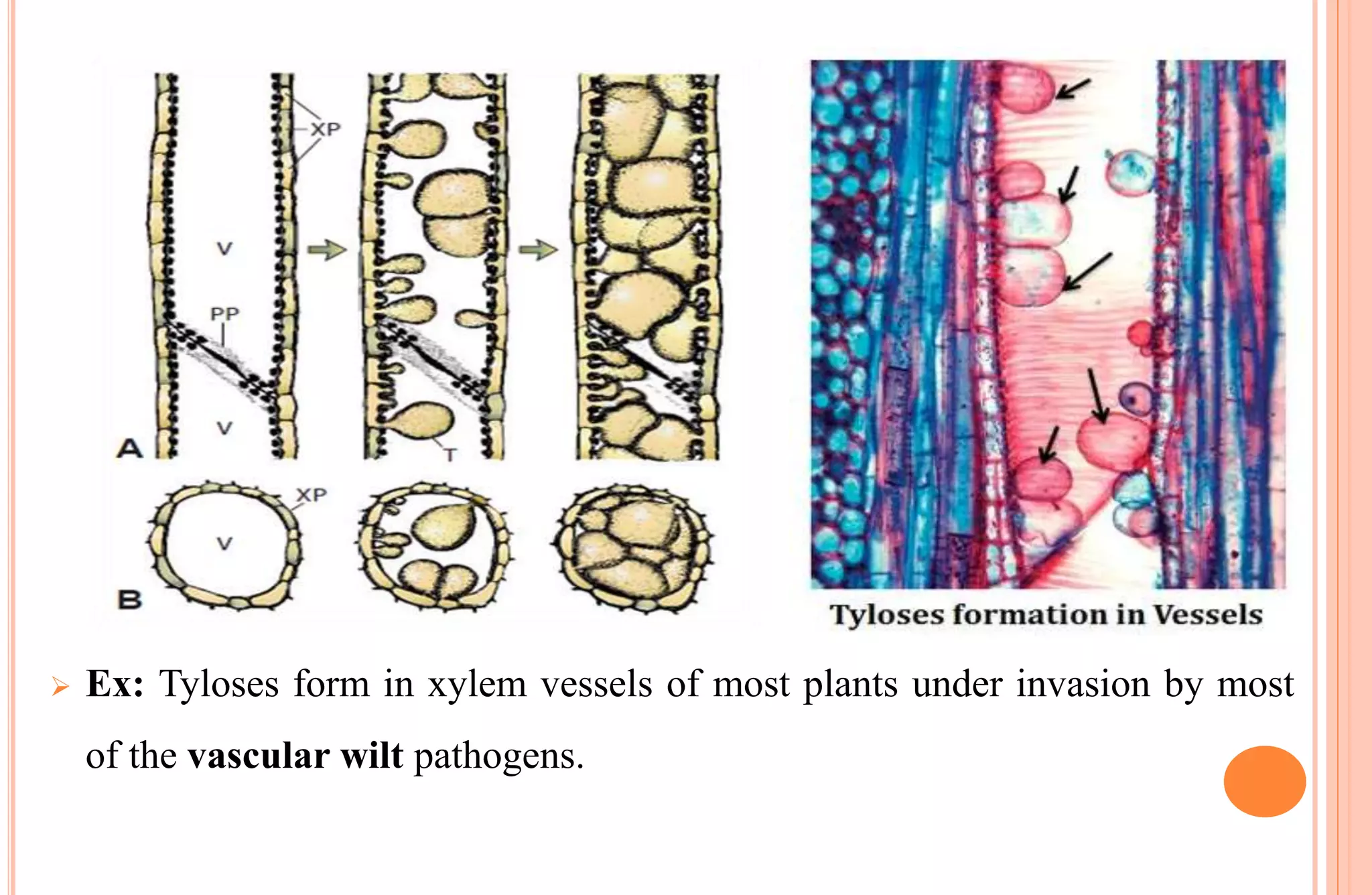
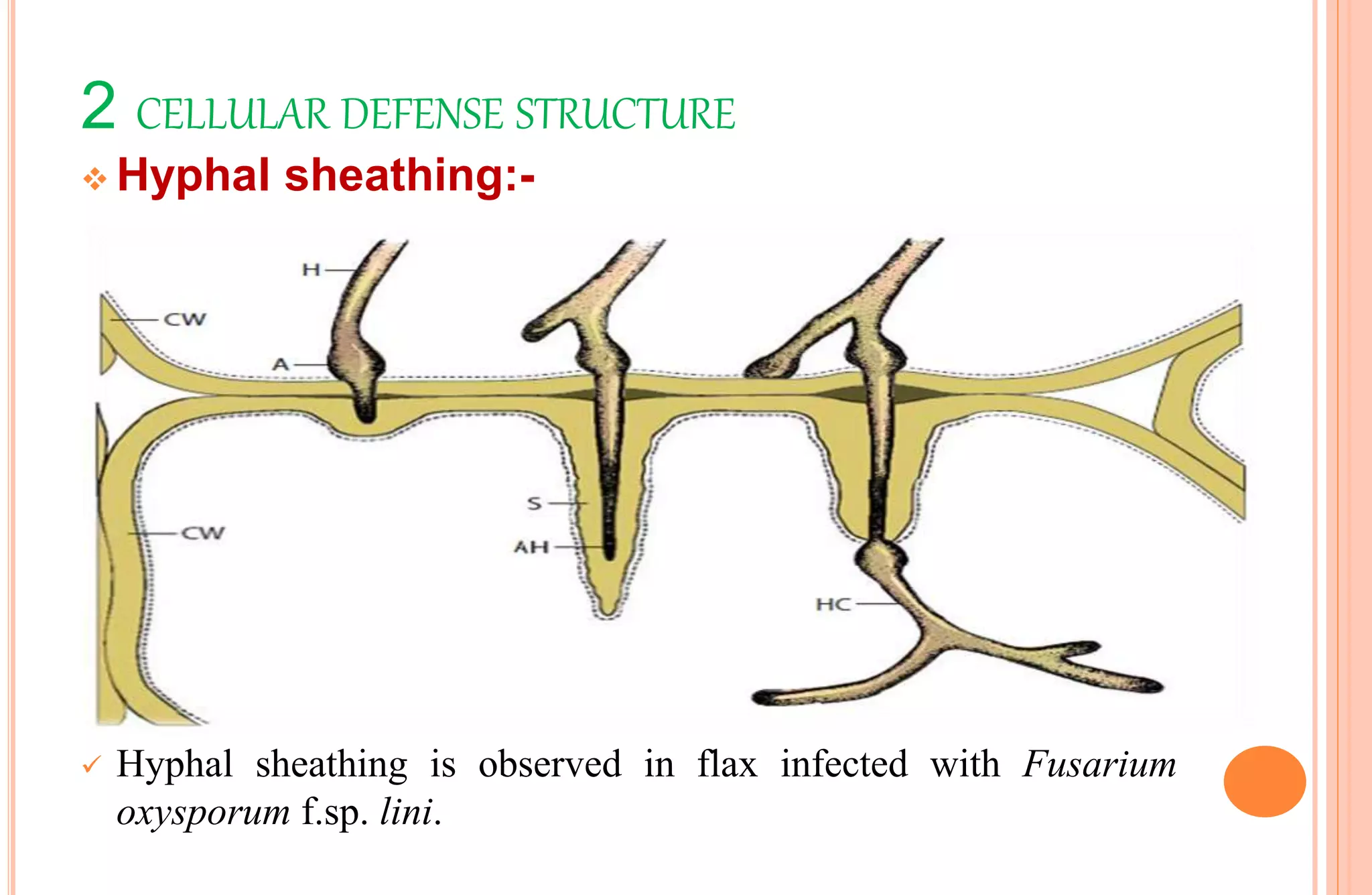
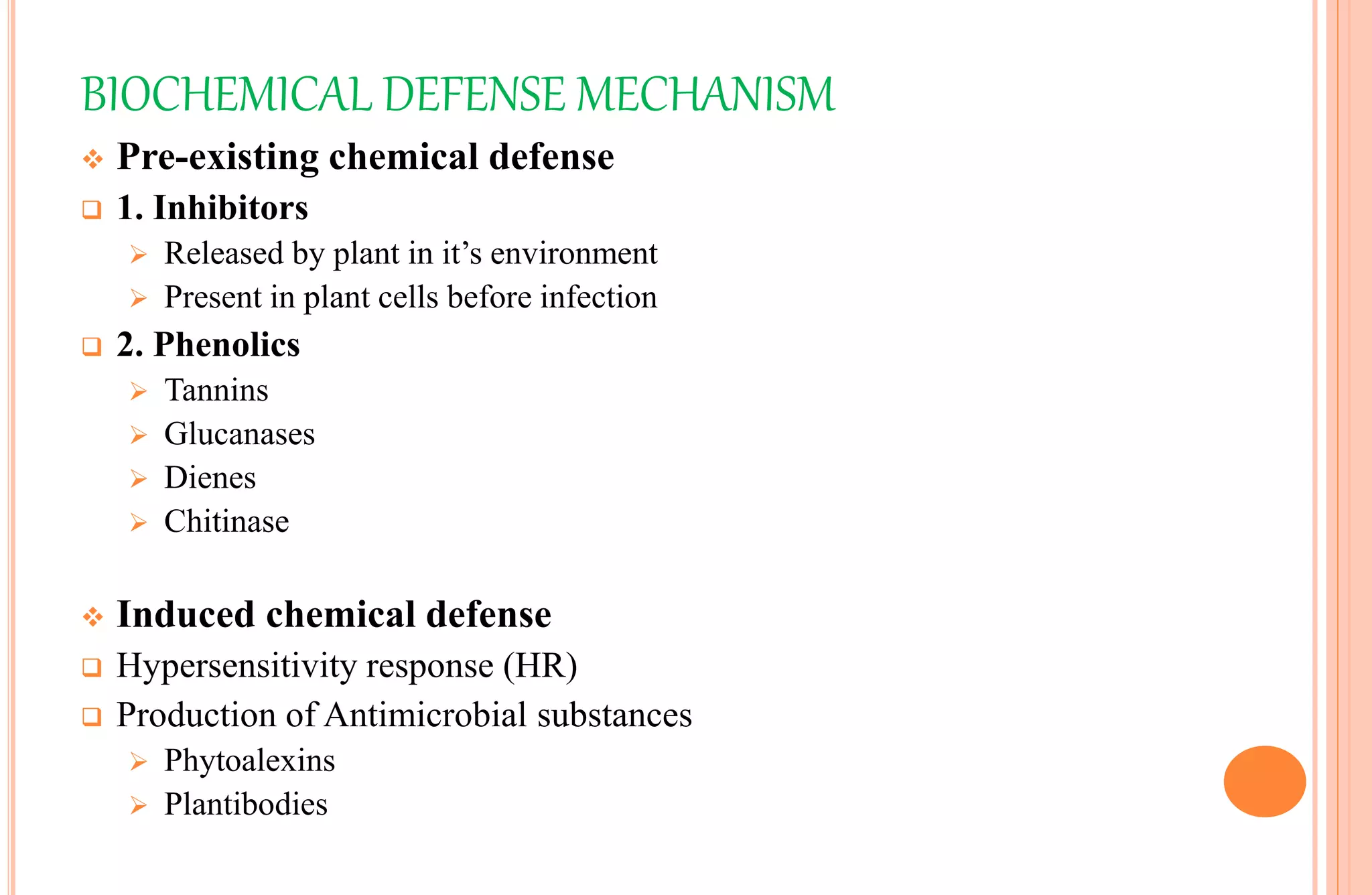
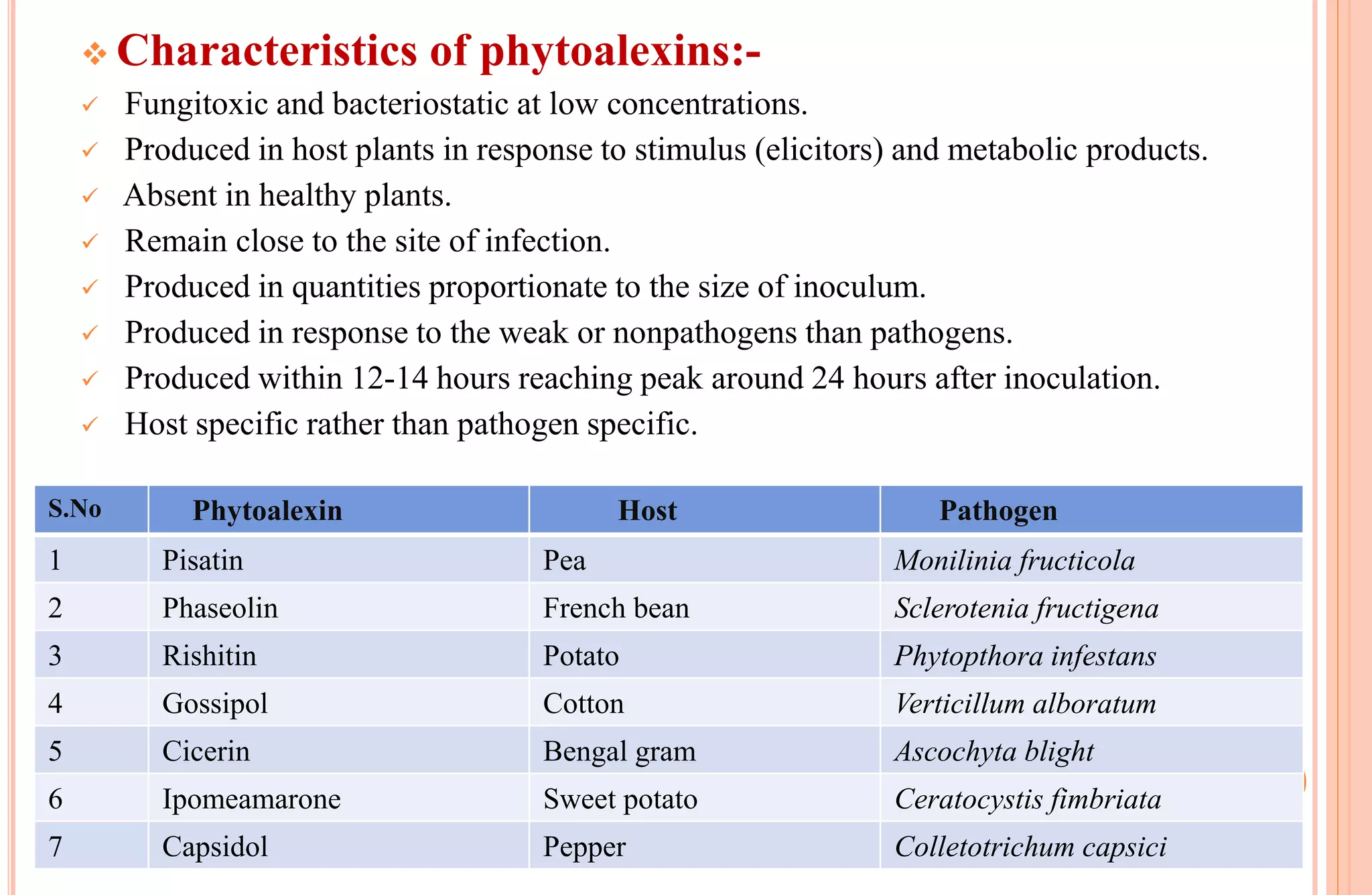
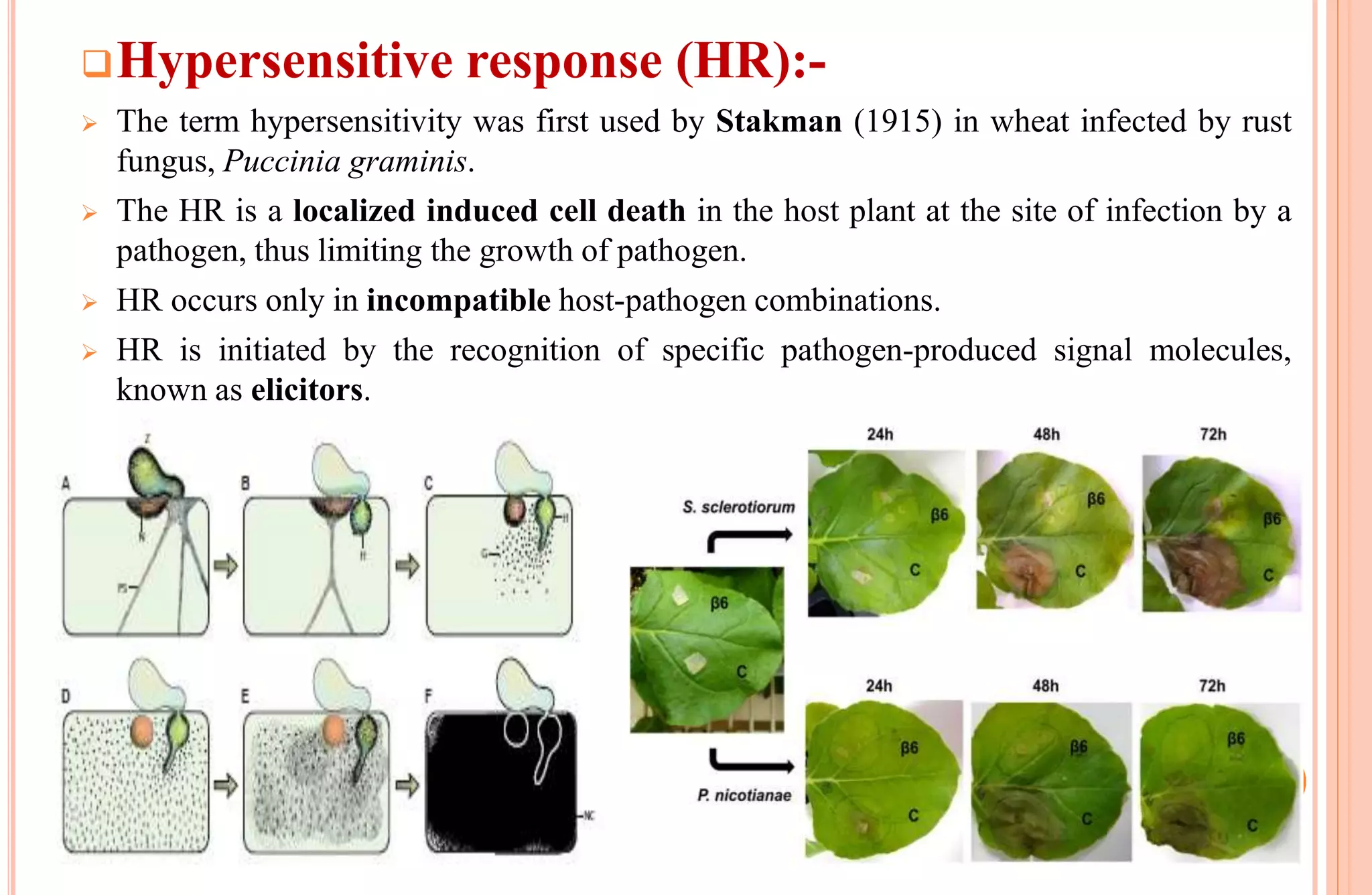
Plants have both structural and biochemical defense mechanisms against pathogens. Structural defenses include pre-existing traits like thick cuticles and presence of thick-walled cells, as well as induced responses like formation of cork layers and tyloses after infection. Biochemical defenses include pre-existing inhibitory compounds and enzymes, as well as induced responses like phytoalexins, hypersensitive response, and transgenic production of plantibodies after pathogen detection. Together these defenses provide multiple layers of protection against the wide variety of fungi, bacteria, viruses and other pathogens that plants encounter.