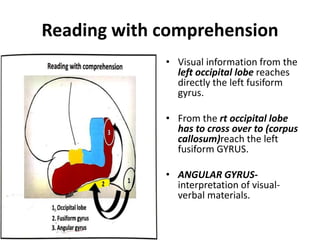
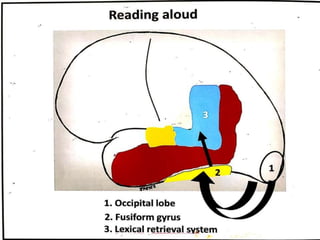
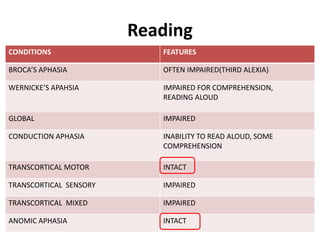
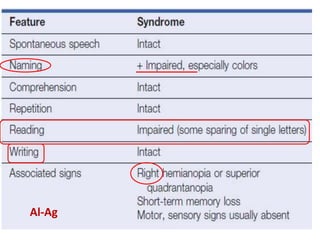
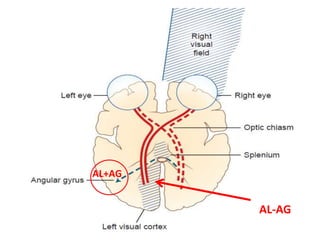
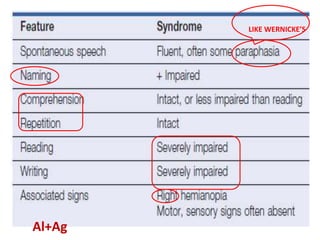
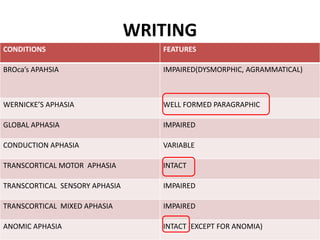
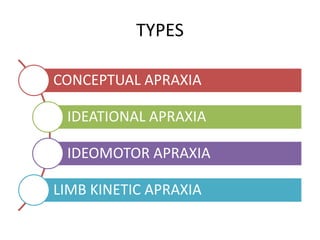
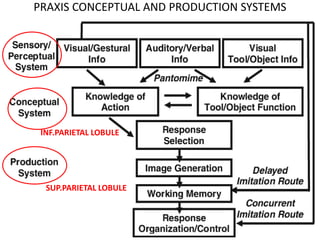
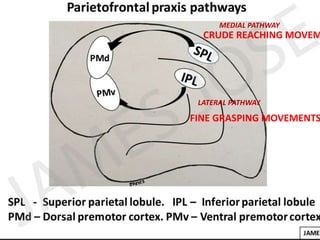
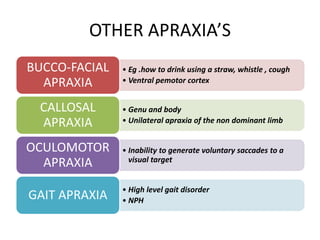
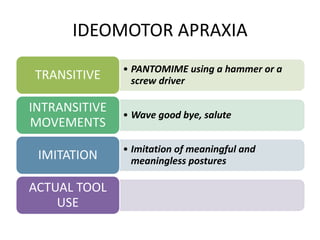
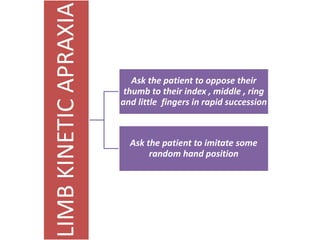
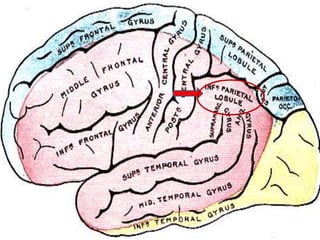
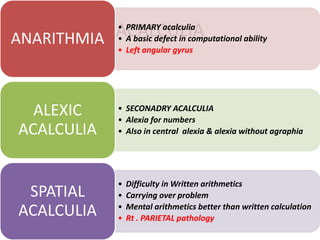
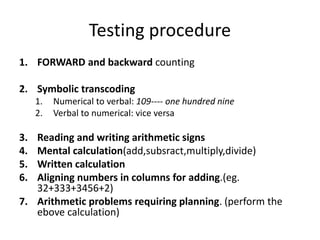
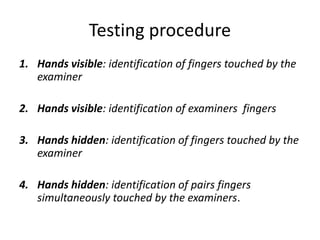
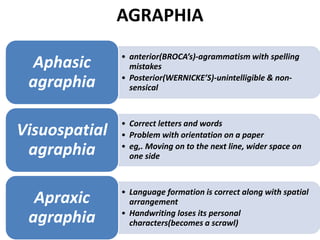
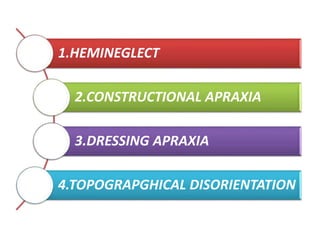
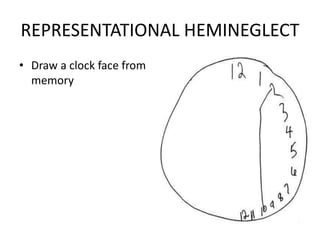
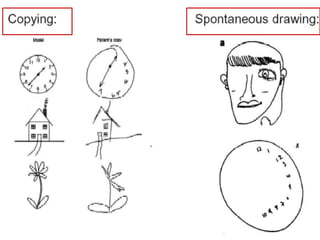
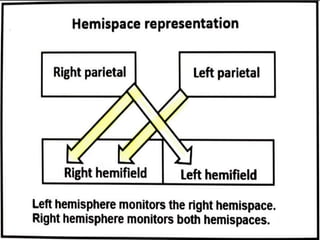
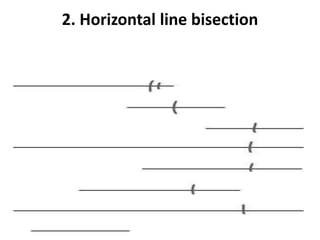
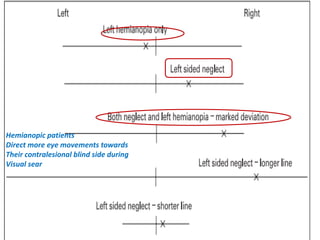
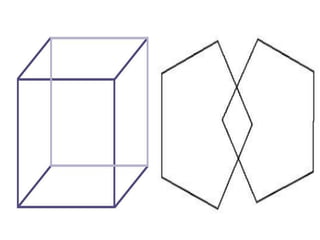
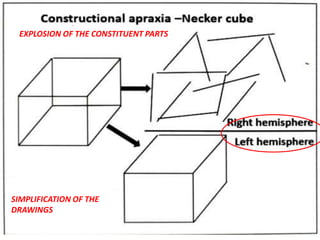
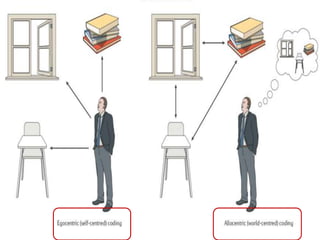
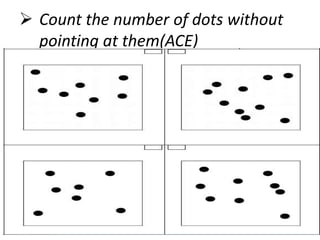
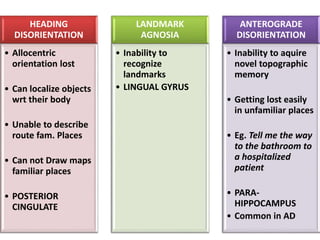
The document discusses various neurological conditions related to language and praxis dysfunction, including alexia, agraphia, and Gerstmann syndrome. It outlines the associated brain regions, clinical features, and testing procedures for identifying these disorders. Additionally, it categorizes types of apraxia and related testing protocols to assess deficits in tool use, spatial awareness, and constructional abilities.