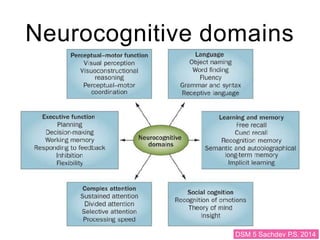
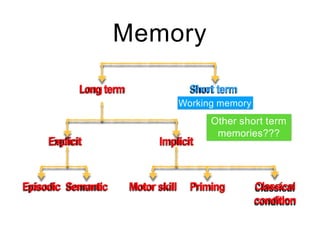
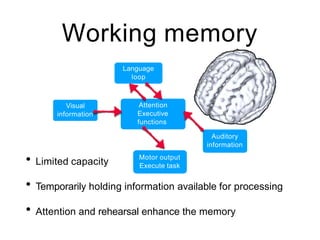
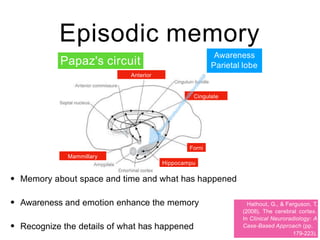
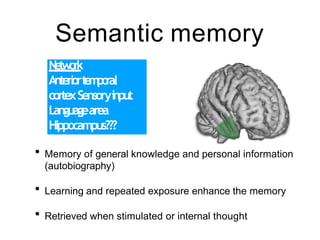
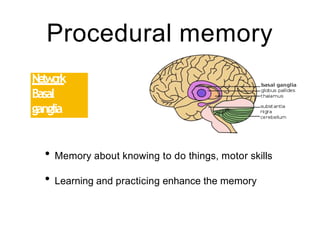
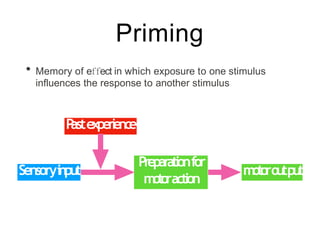
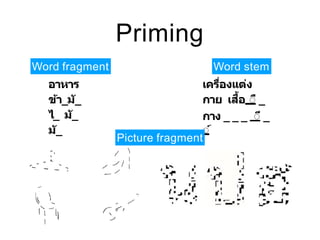
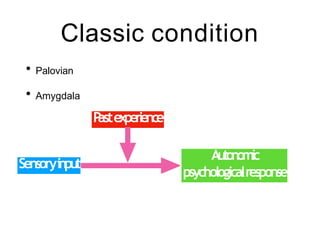
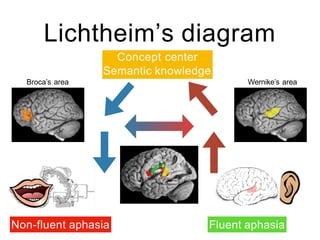
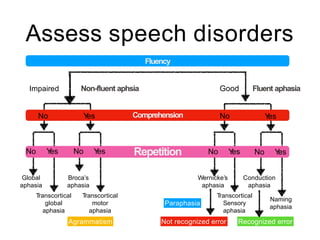
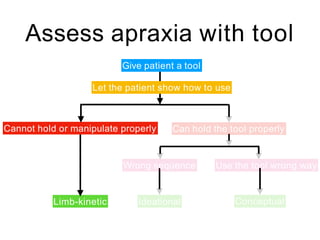
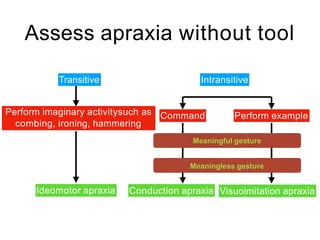
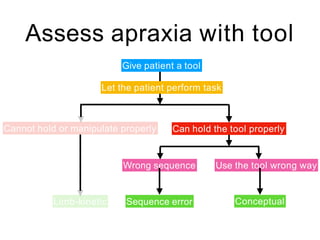
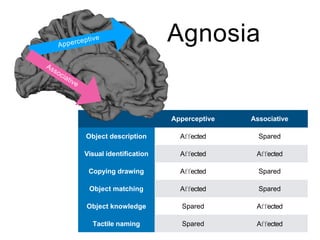
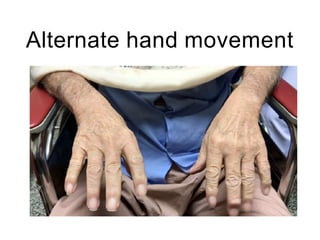
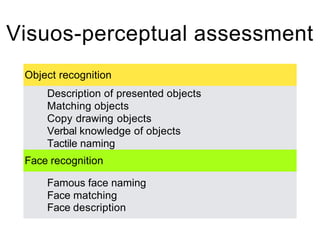
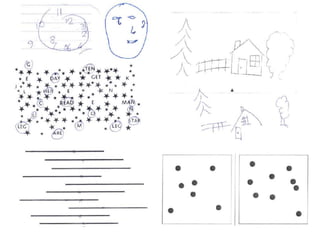
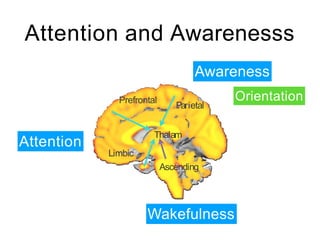
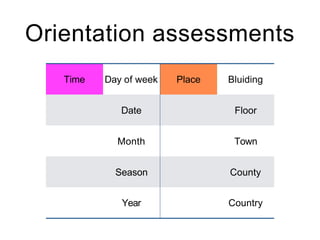
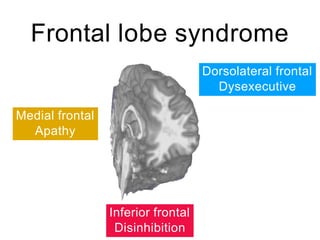
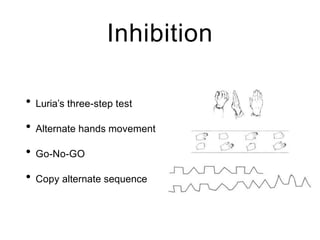
This document discusses various domains of higher cortical functions that can be assessed during a bedside examination, including memory, language, visuospatial abilities, praxis, and executive functions. It provides examples of specific tests that can evaluate each domain, such as recall tests for memory, naming tests for language, and clock drawing for executive function. Neuroanatomical structures associated with each domain are also outlined.