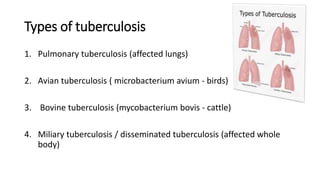
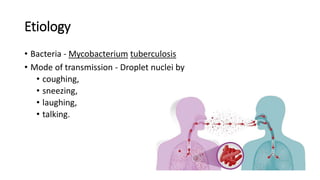
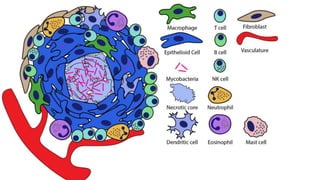
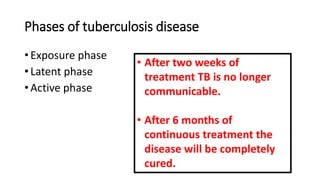
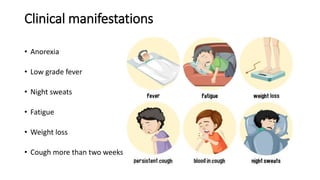
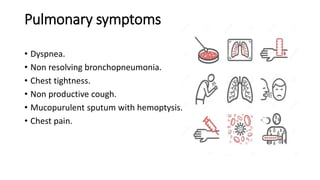
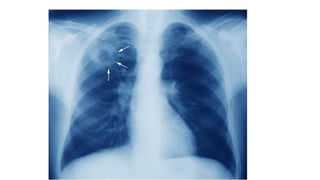
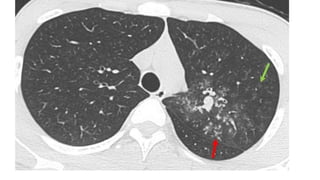
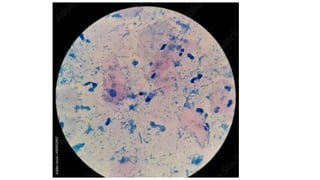
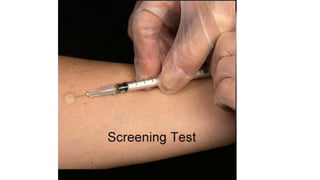
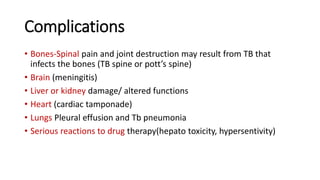
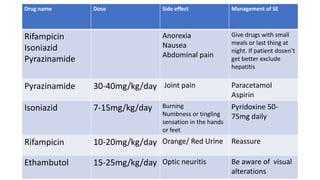
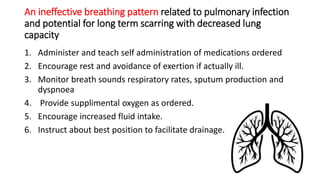
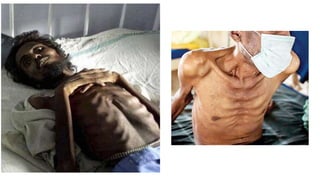
The document provides a comprehensive overview of tuberculosis (TB), a chronic infectious disease caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis, primarily affecting the lungs but can also impact other parts of the body. It details the epidemiology, risk factors, clinical manifestations, diagnostic approaches, treatment options, and nursing care necessary for managing TB patients. Additionally, it addresses drug-resistant TB, the limitations of the BCG vaccine in adults, and highlights the importance of adherence to treatment through directly observed therapy (DOT).