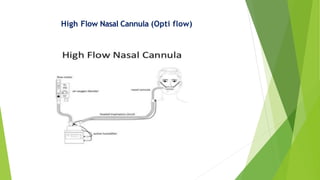
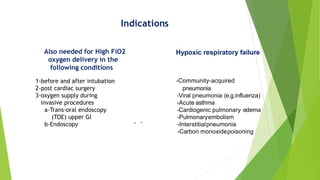
1) High flow nasal cannula (HFNC) delivers humidified oxygen at up to 60 L/min through nasal prongs. It is indicated for hypoxic respiratory failure from conditions like pneumonia.
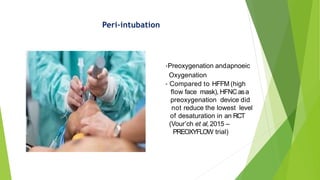
2) Studies show HFNC improves oxygenation and lowers respiratory rate compared to conventional oxygen therapy. It may help prevent intubation and has been used successfully for peri-intubation and post-extubation.
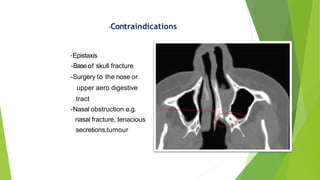
3) However, HFNC is not a reliable form of PEEP and should not delay intubation in severely ill patients. Further research is still needed on its optimal uses.