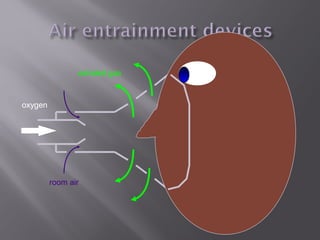
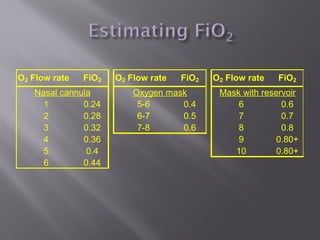
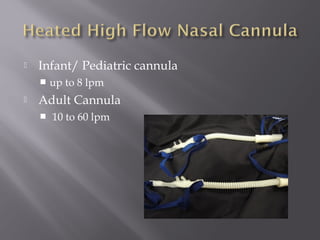
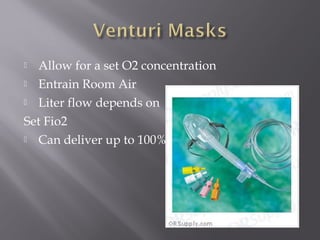
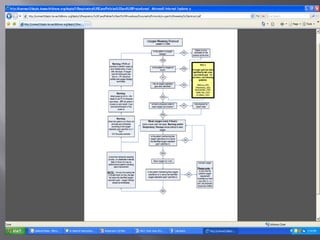
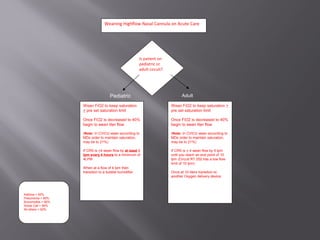
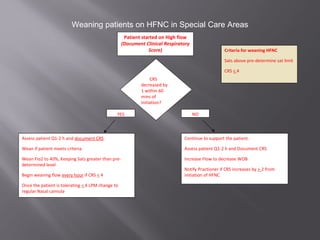
This document provides information on various oxygen delivery devices including their flow rates and fractional inspired oxygen (FiO2) levels. It discusses both high-flow and low-flow devices. High-flow devices discussed include venti-masks, mechanical aerosol systems, non-rebreathing masks, and high flow nasal cannula. Low-flow devices discussed include nasal cannula, simple masks, and partial rebreathing masks. The document provides details on appropriate flow rates and FiO2 levels for different devices. It also provides guidelines for weaning patients from high flow nasal cannula in both pediatric and adult patients. Case examples are presented and recommendations provided.