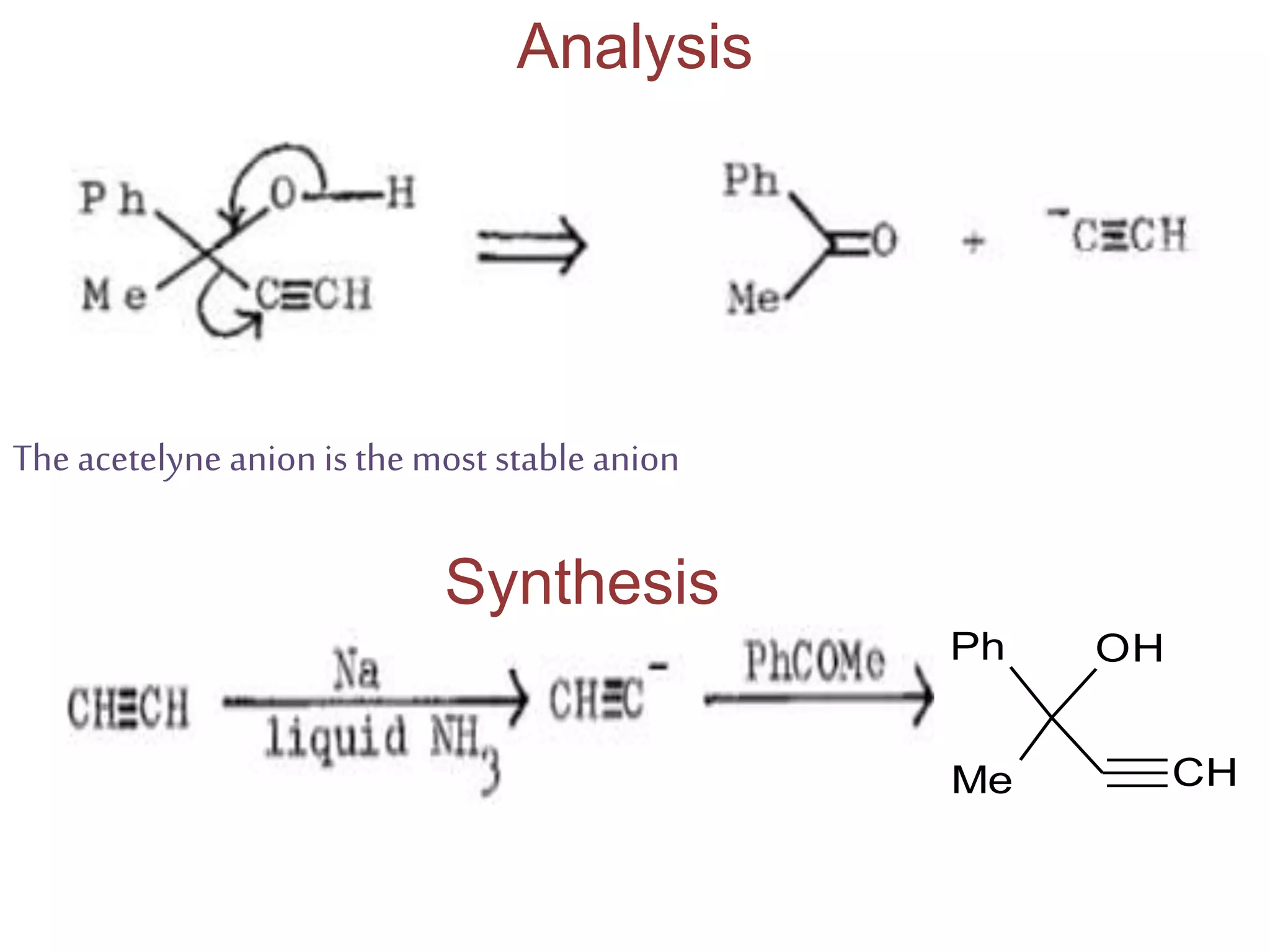
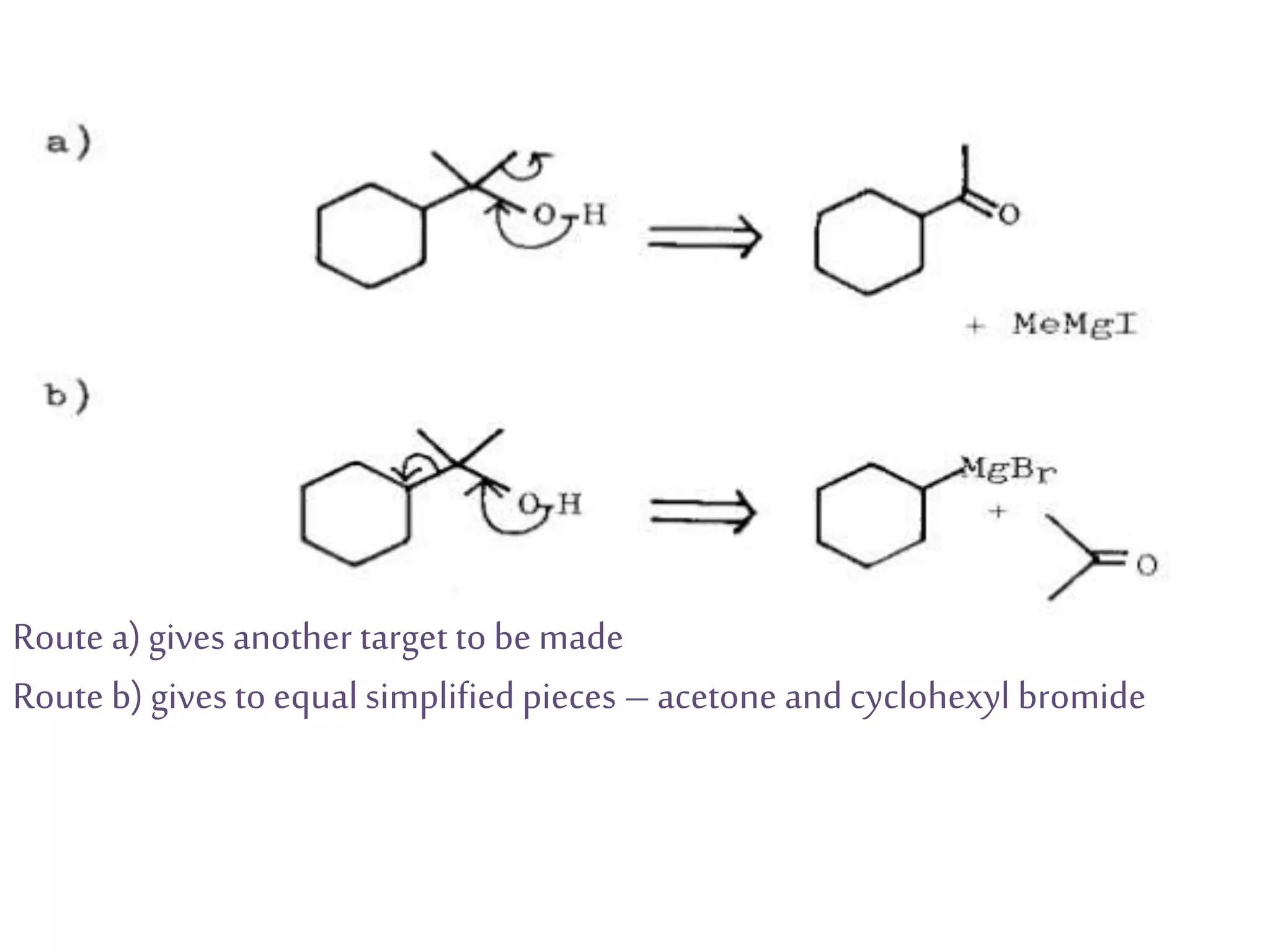
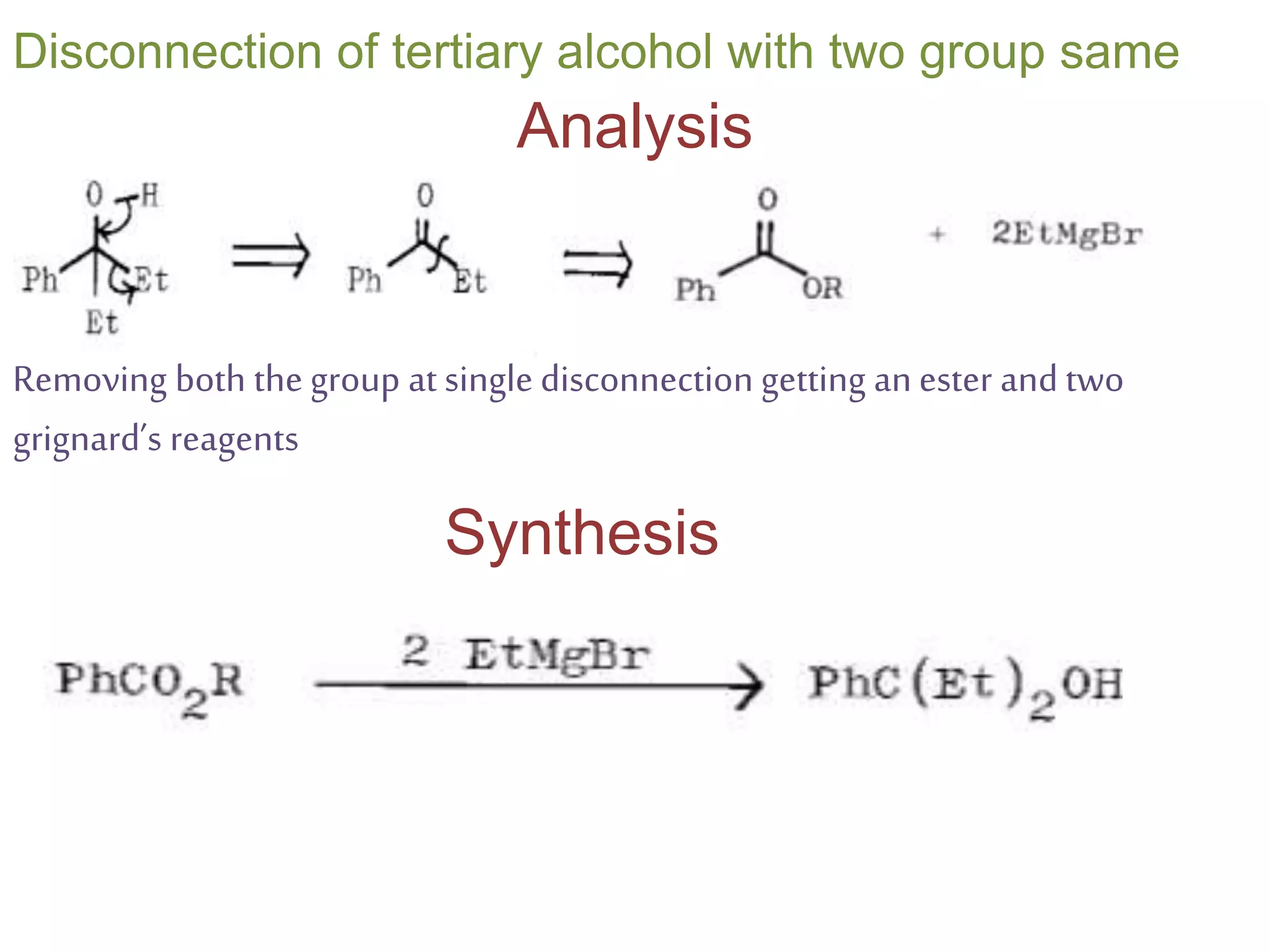
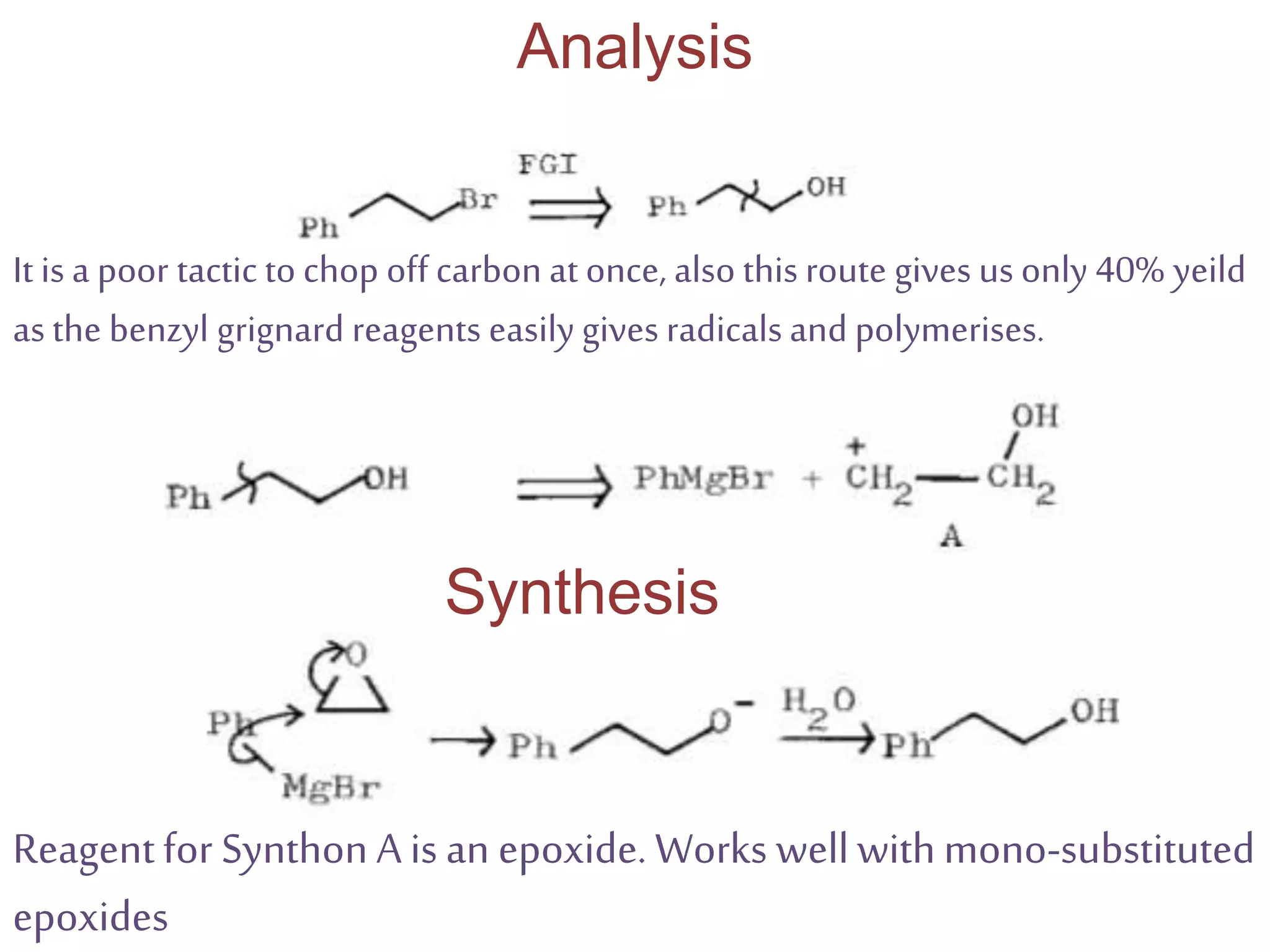
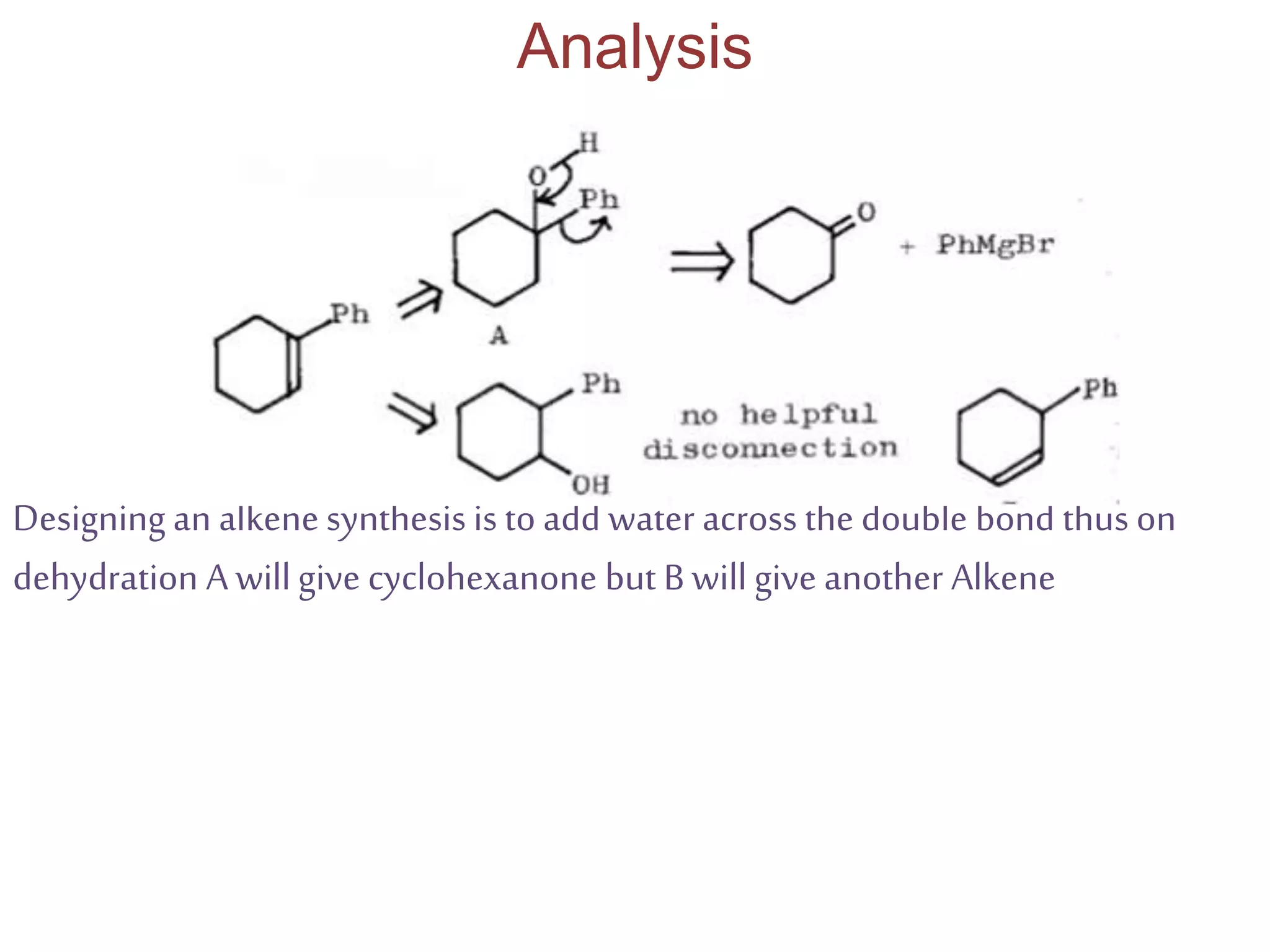
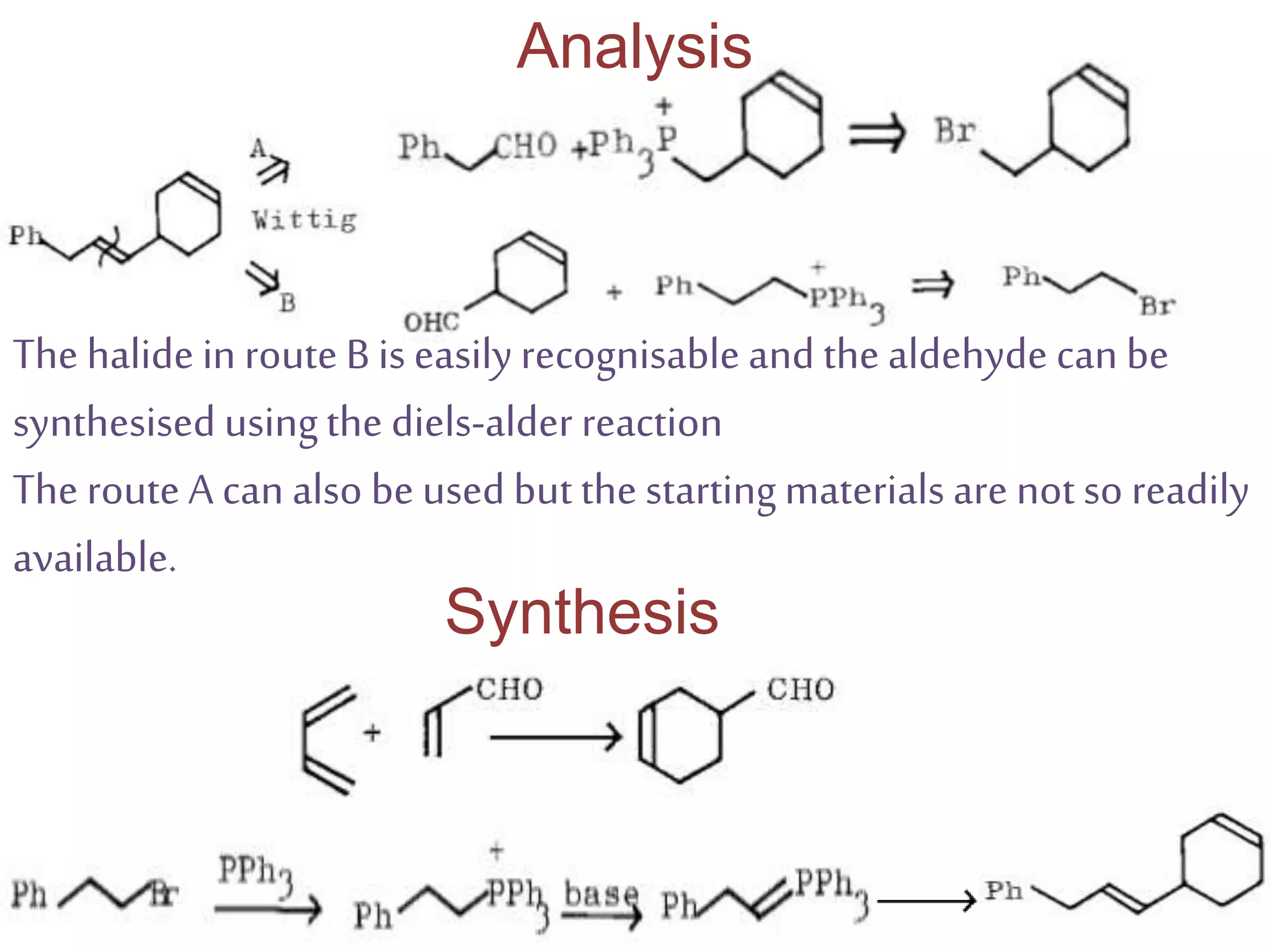
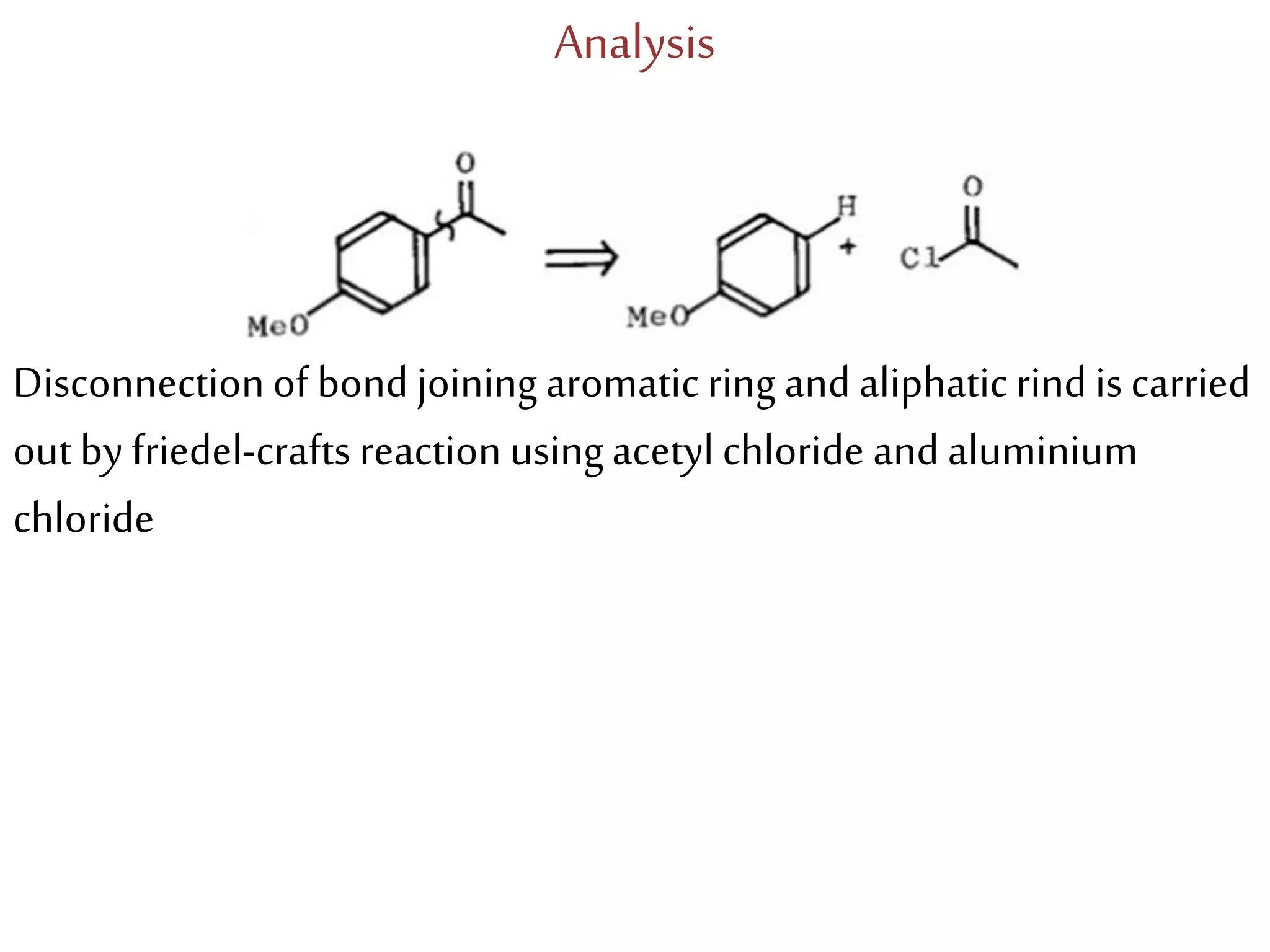
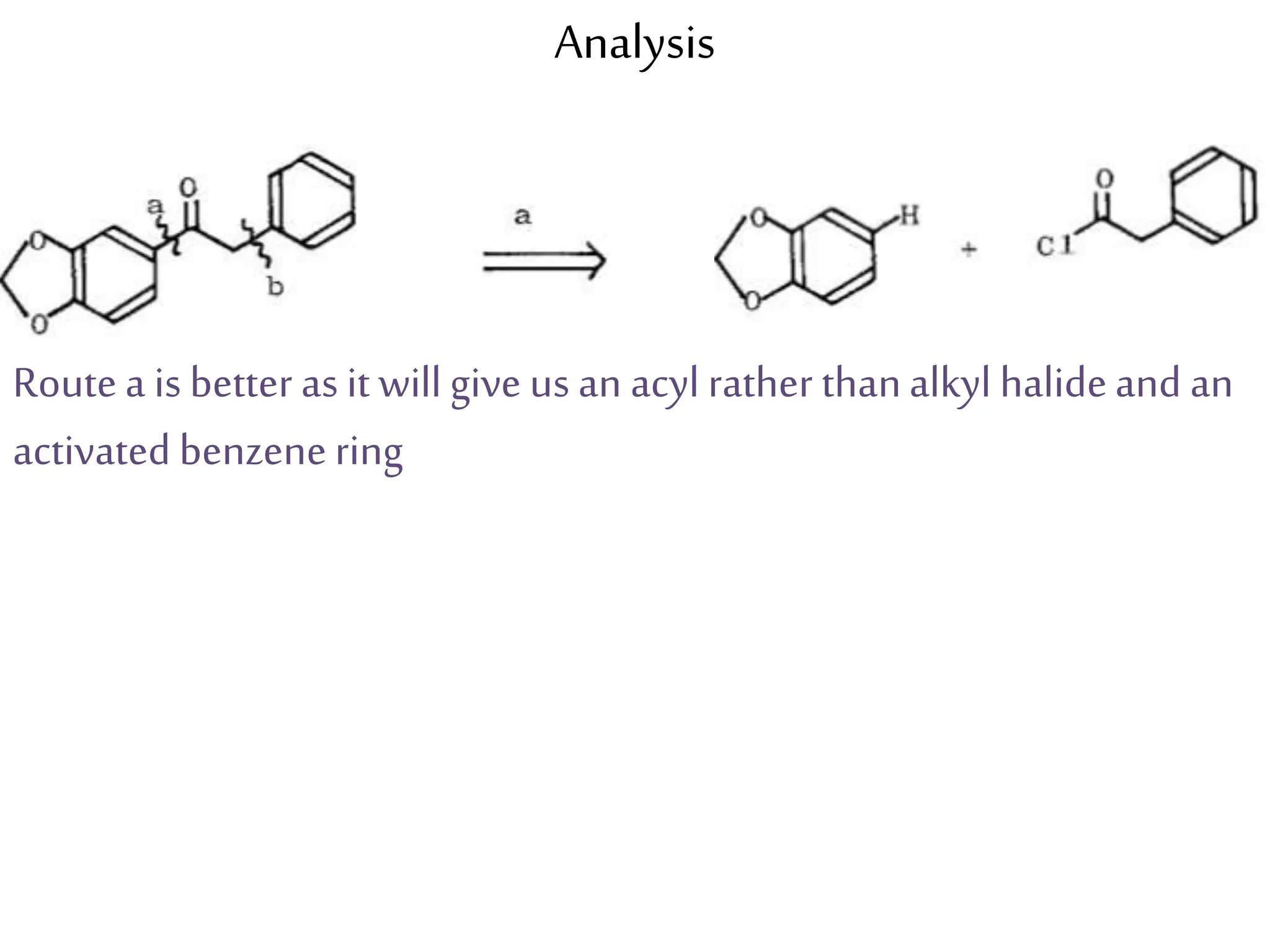
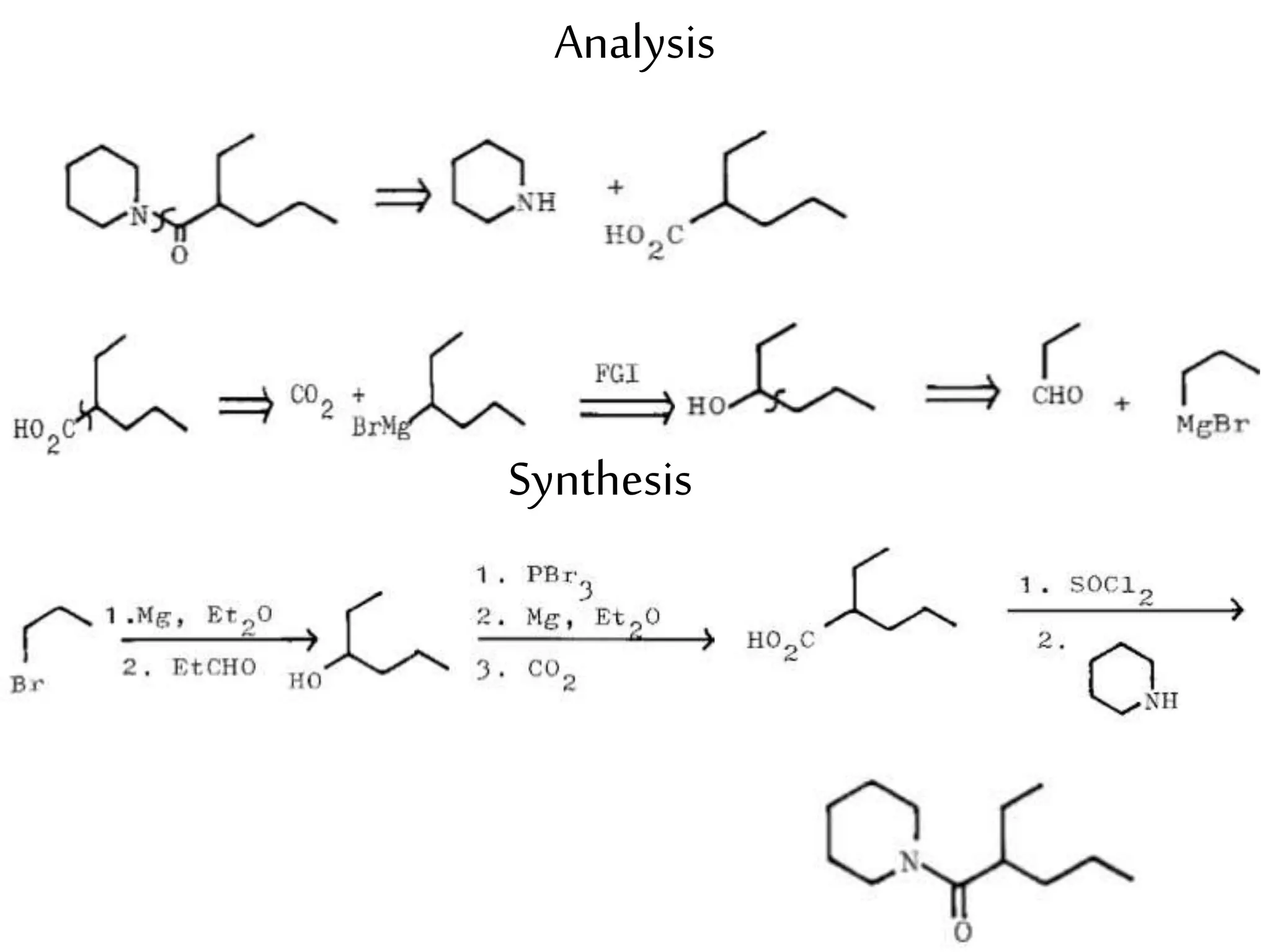
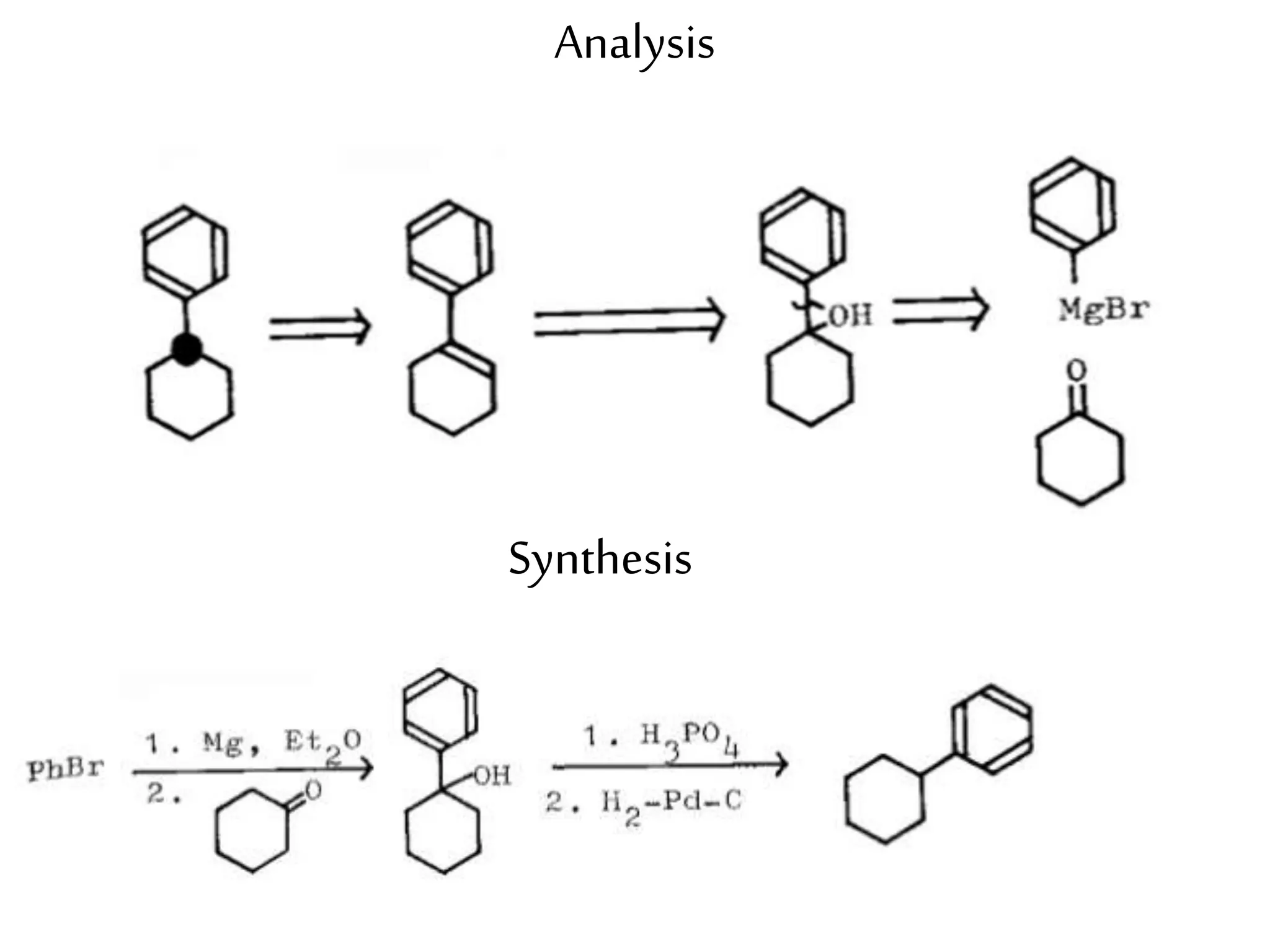
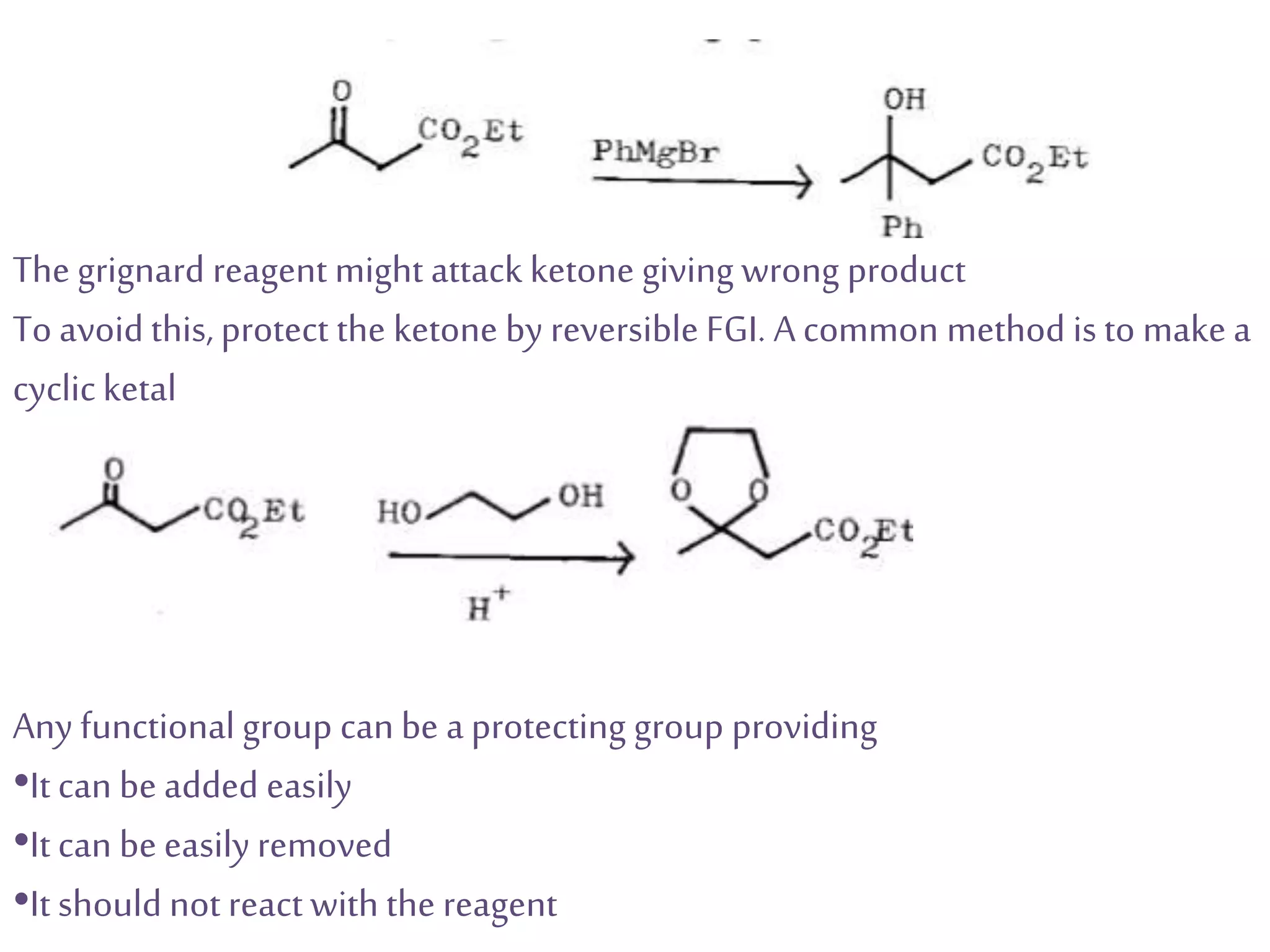
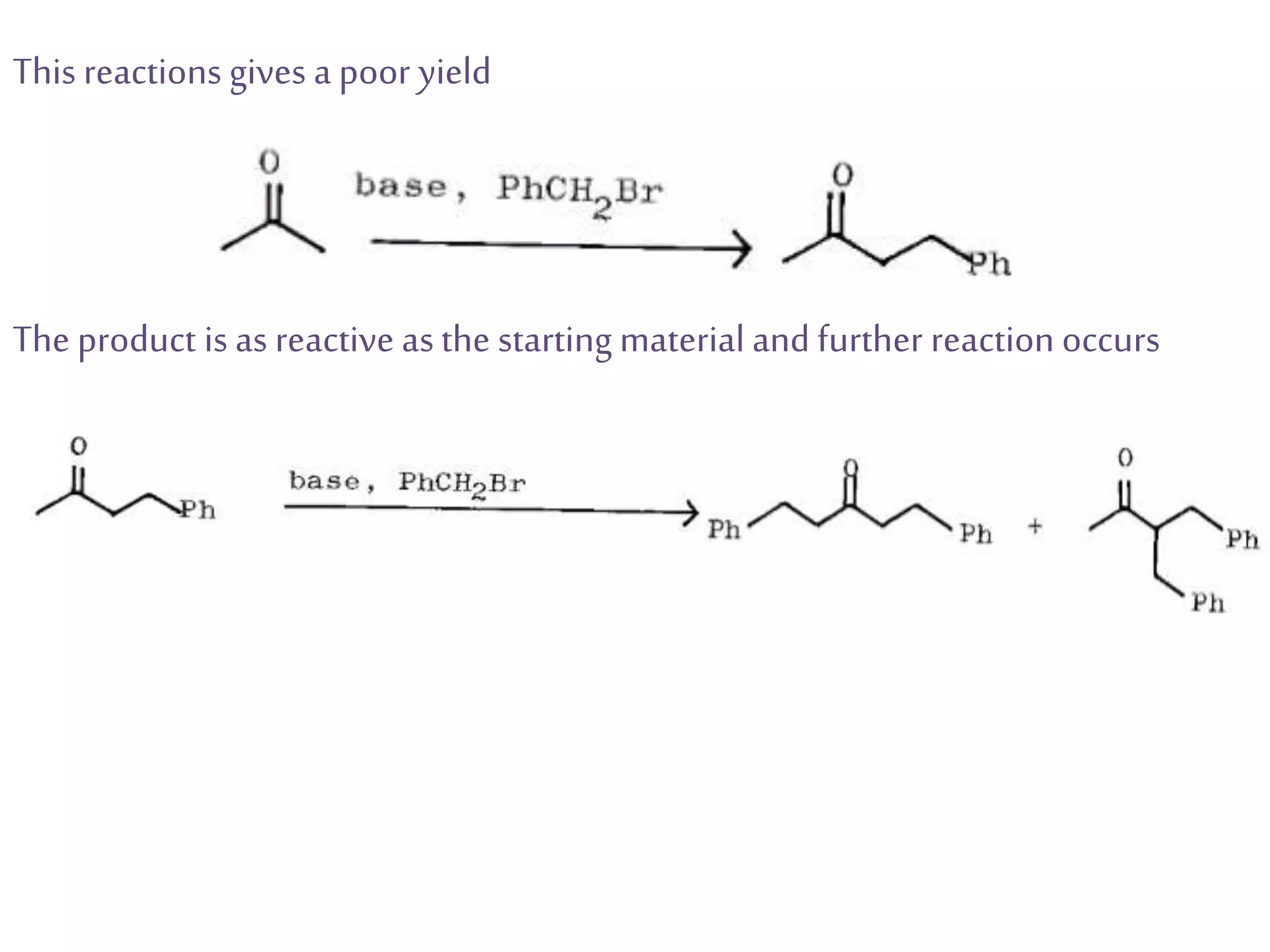
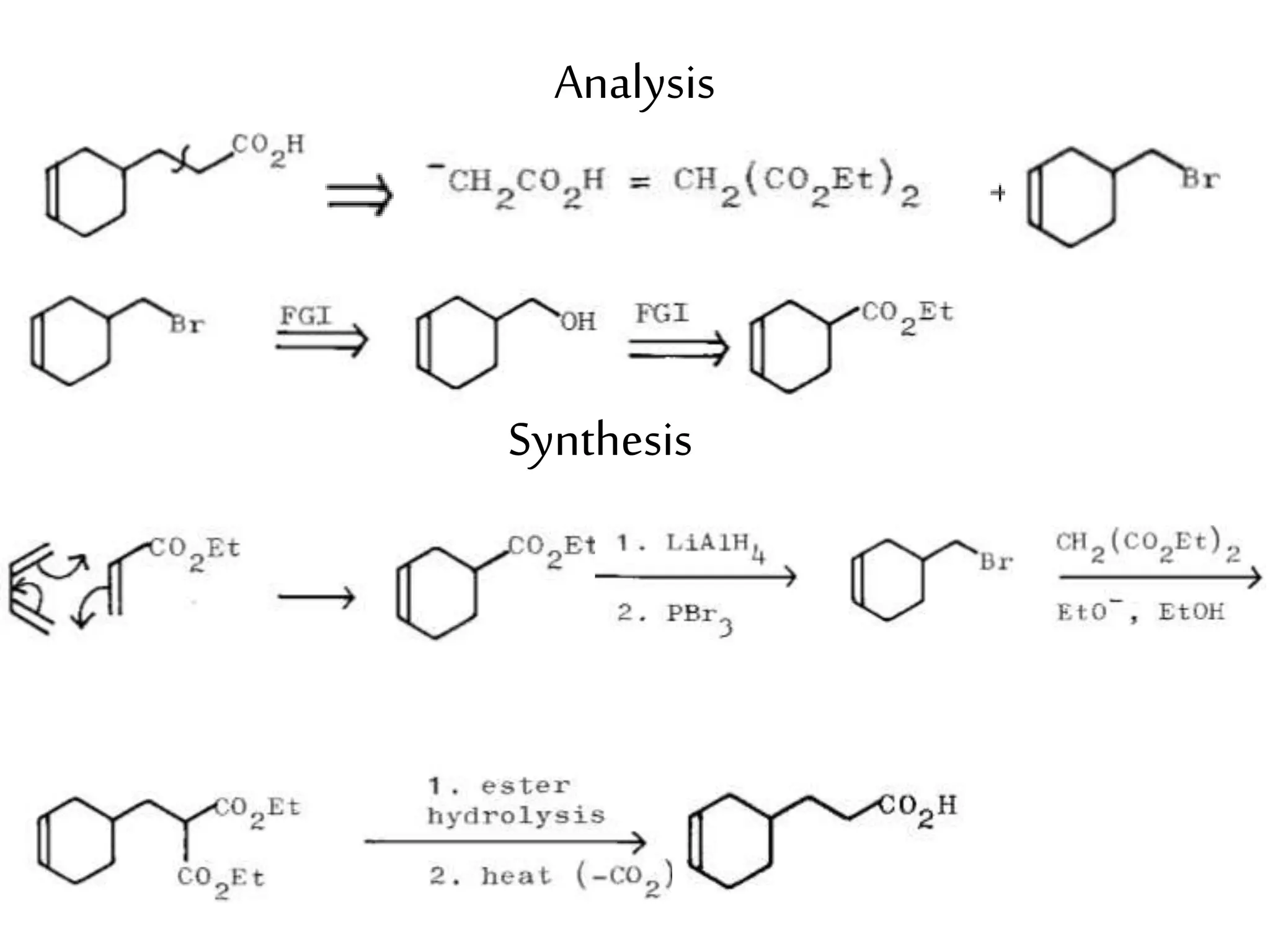
Retrosynthetic analysis is a technique for planning organic syntheses by systematically deconstructing a target molecule into simpler precursor structures through disconnections, with the goal of arriving at commercially available starting materials. Key criteria for good disconnections include a favorable mechanism, maximizing simplification at each step, and producing recognizable starting materials. Common disconnections involve breaking bonds between functional groups like alcohols, alkenes, ketones, acids, and saturated/aromatic hydrocarbons. Protection and activation of reactive groups is sometimes required to control reaction selectivity. Proper application of retrosynthesis allows complex multi-step syntheses to be planned systematically and increases the likelihood of success.