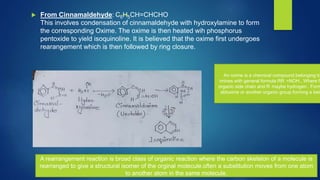
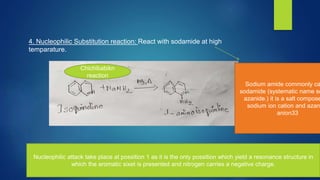
Isoquinoline is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that is a structural isomer of quinoline. It consists of a benzene ring fused to a pyridine ring. Isoquinoline derivatives have many pharmaceutical applications including use as antispasmodics, antitussives, anesthetics, and in the production of morphine and related alkaloids. Isoquinoline can be prepared through the Bischler-Napieralski synthesis which involves the condensation and rearrangement of 2-phenylethylamine or through the reaction of cinnamaldehyde with hydroxylamine. Isoquinoline undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution, oxidation, and reduction reactions.