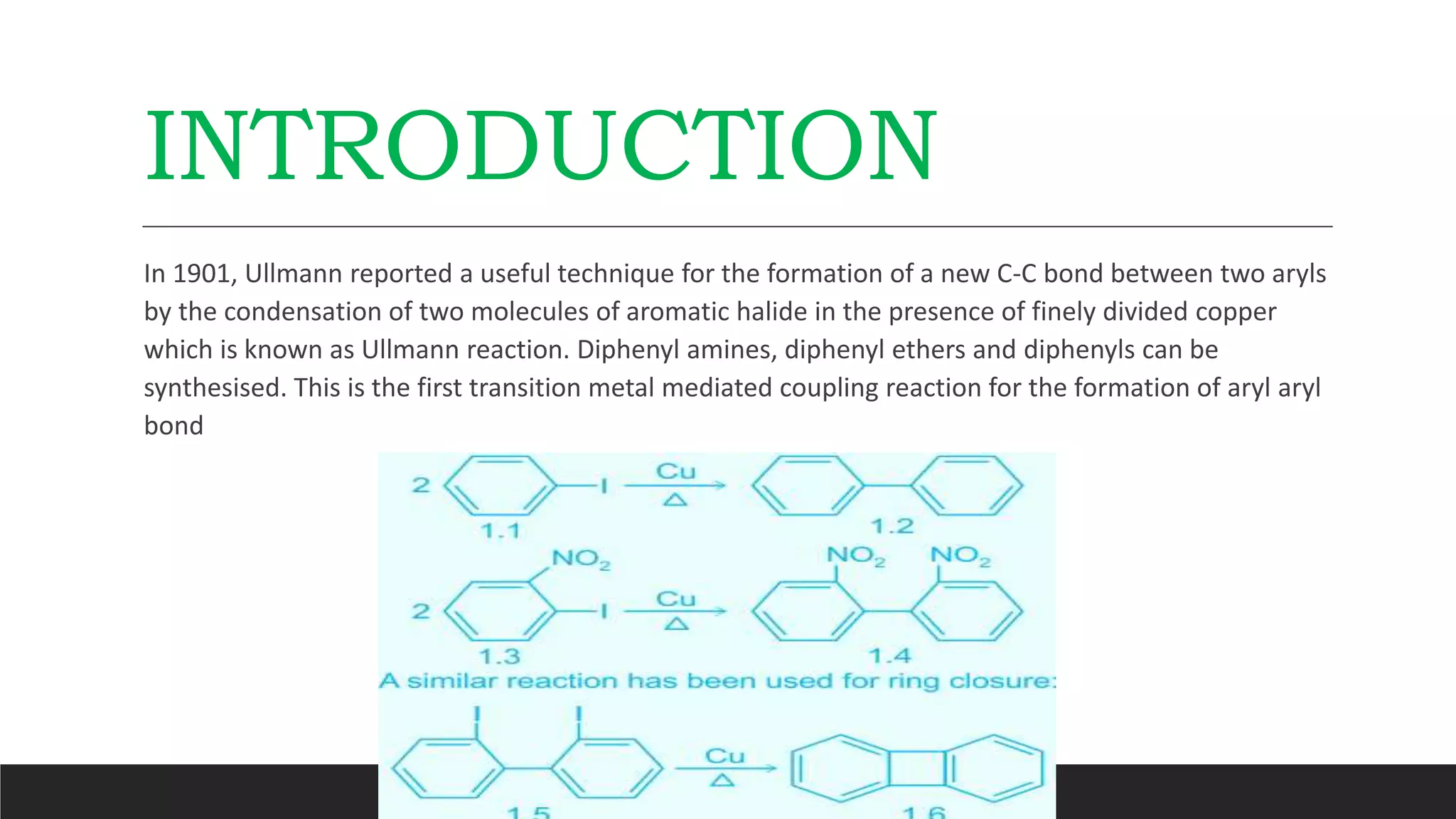
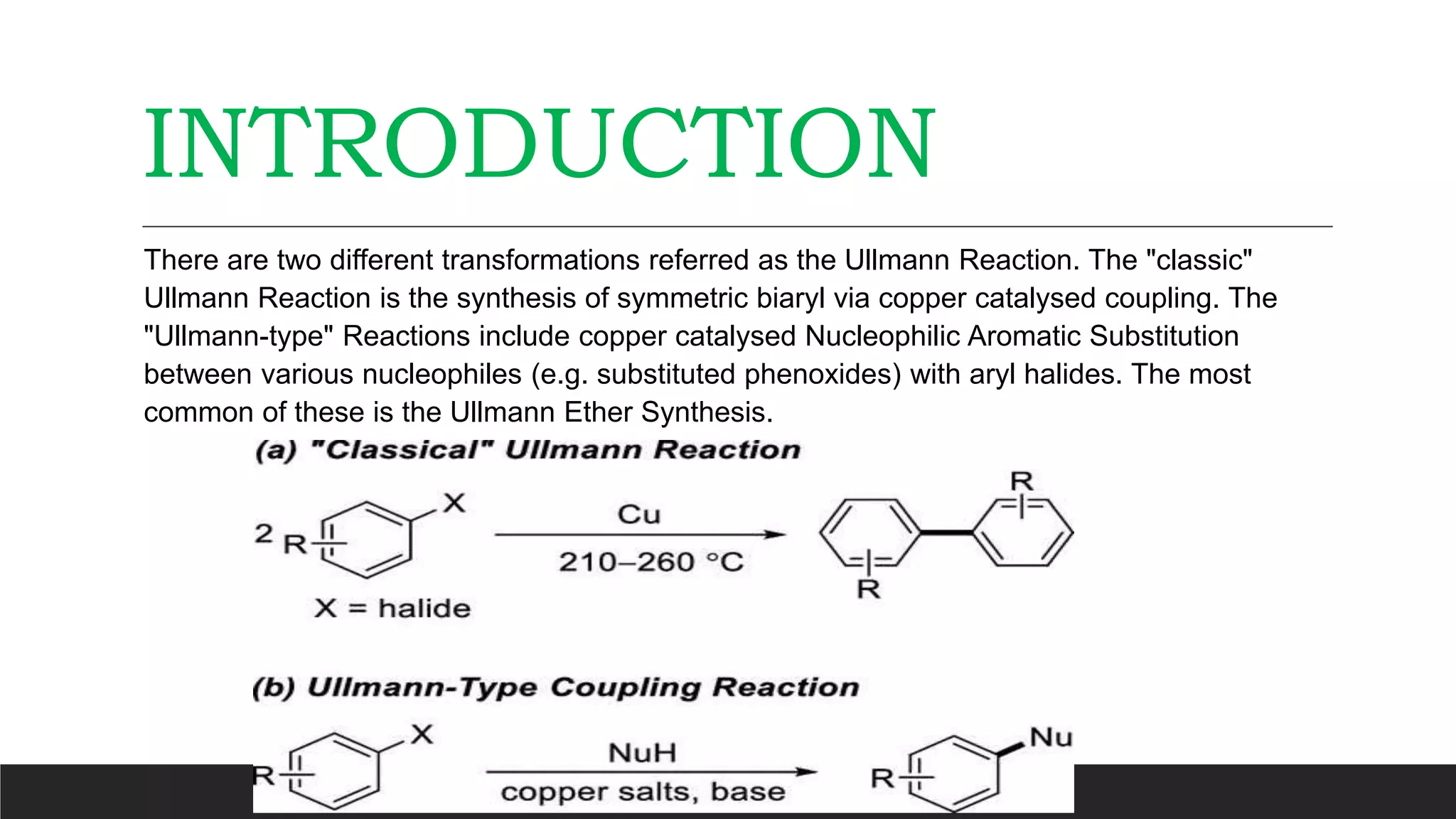
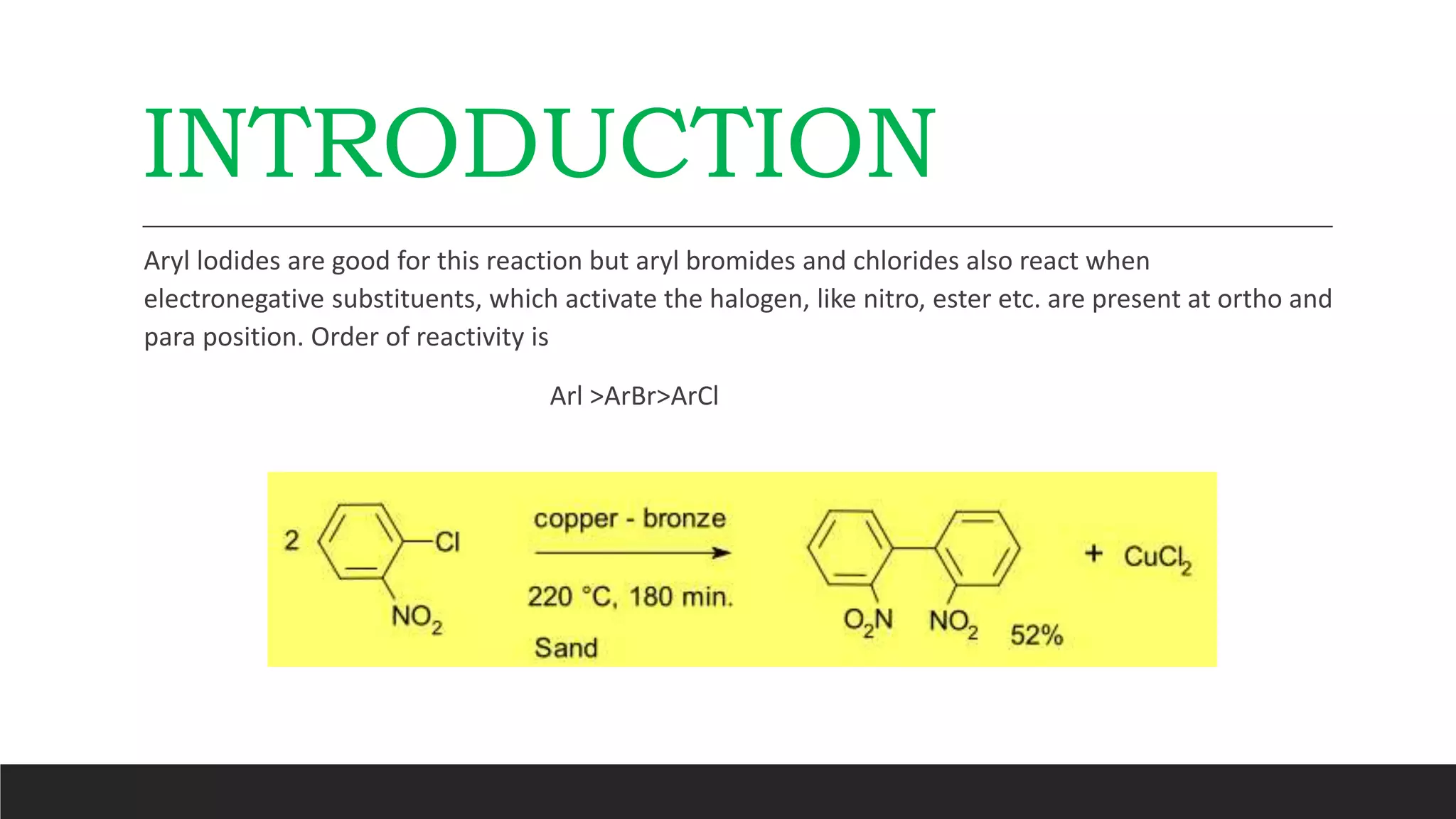
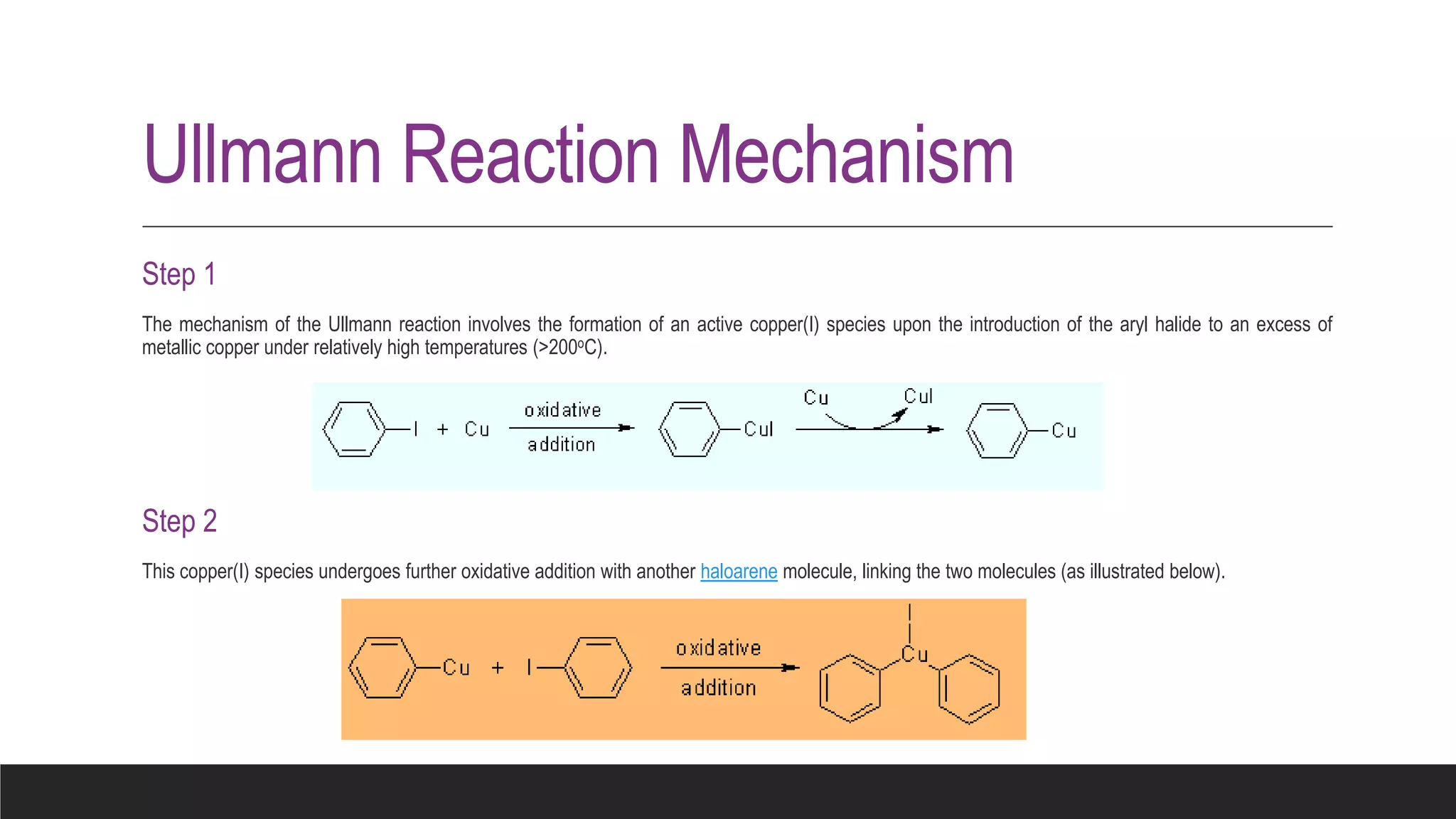
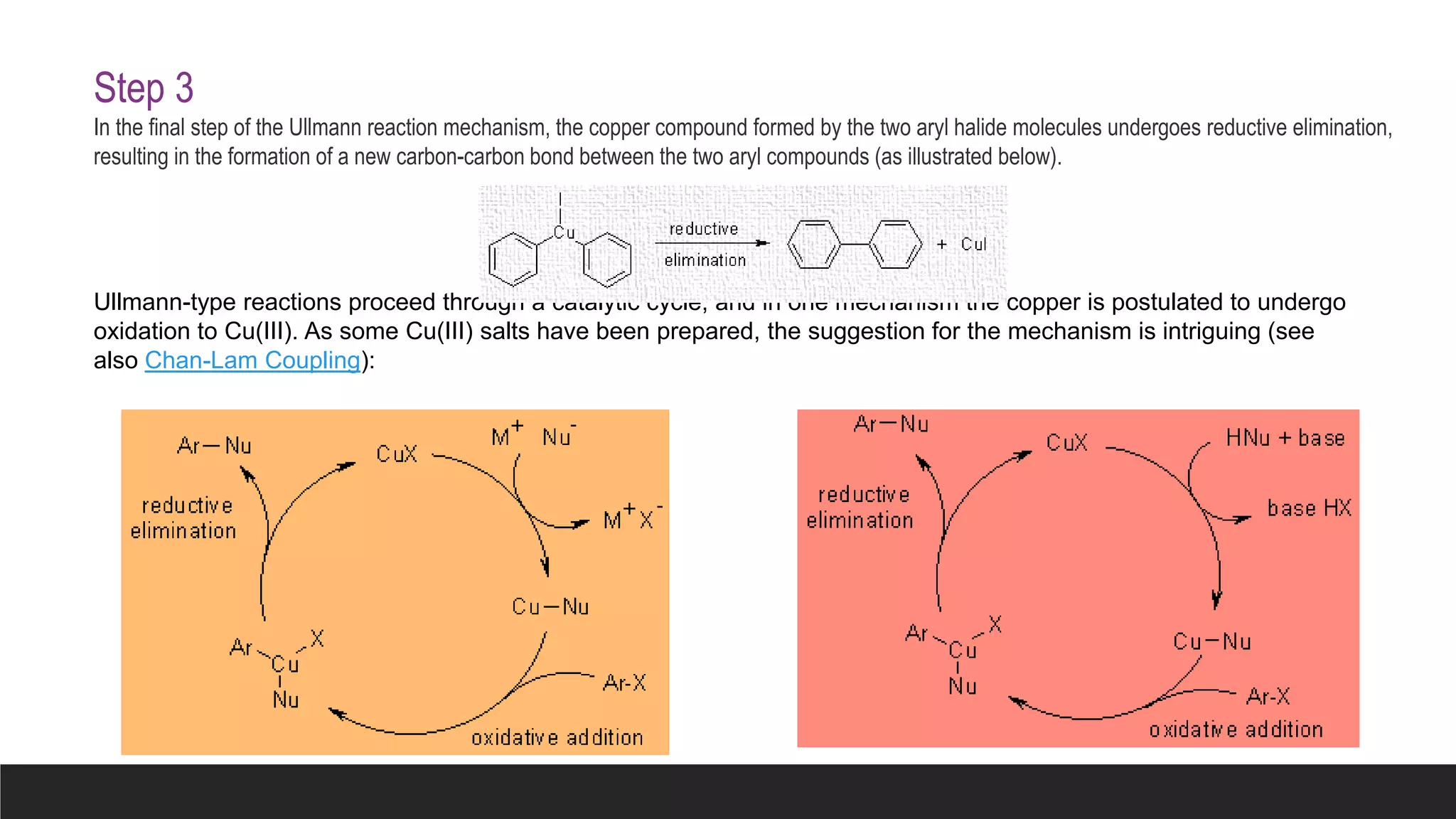
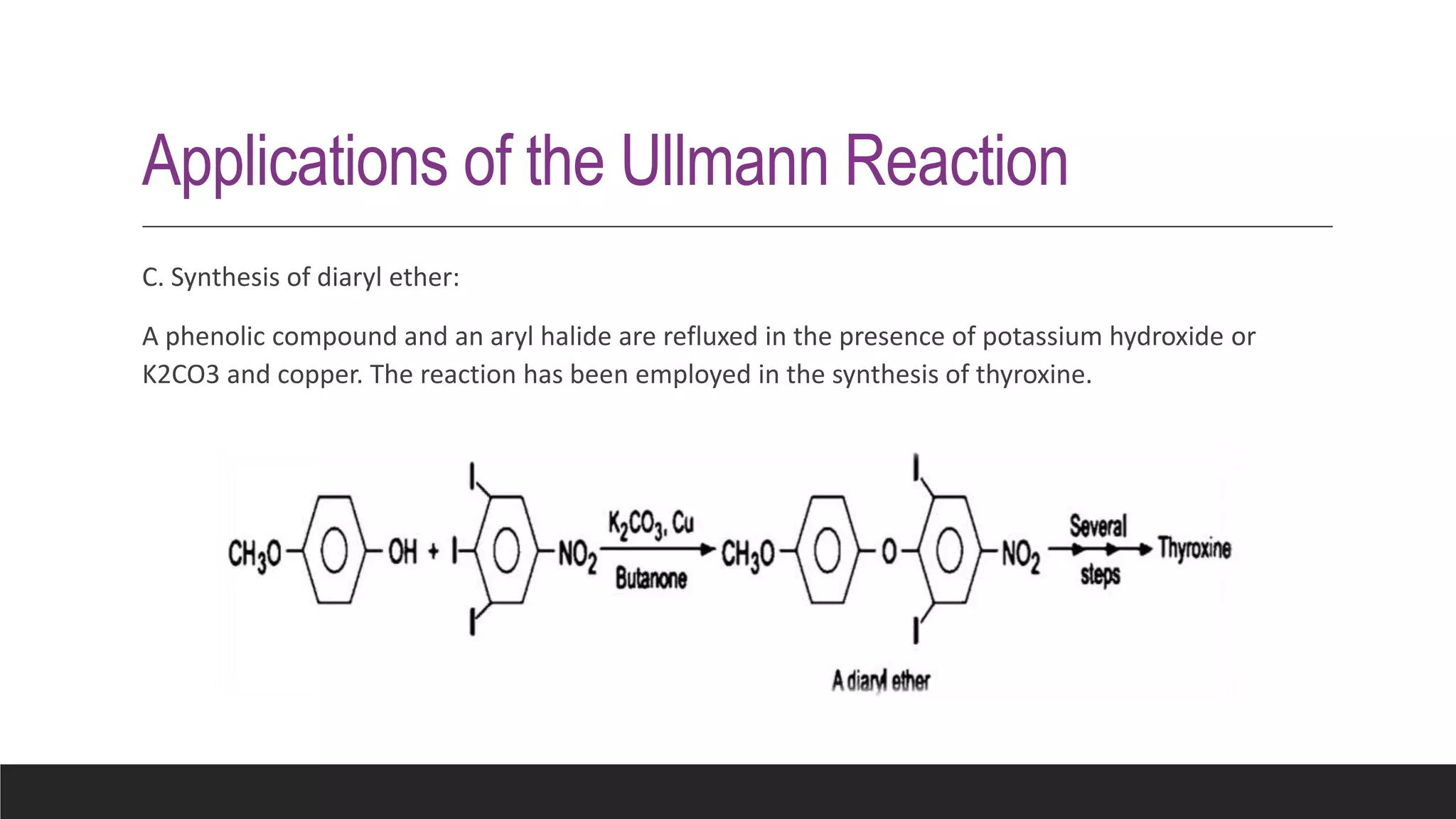
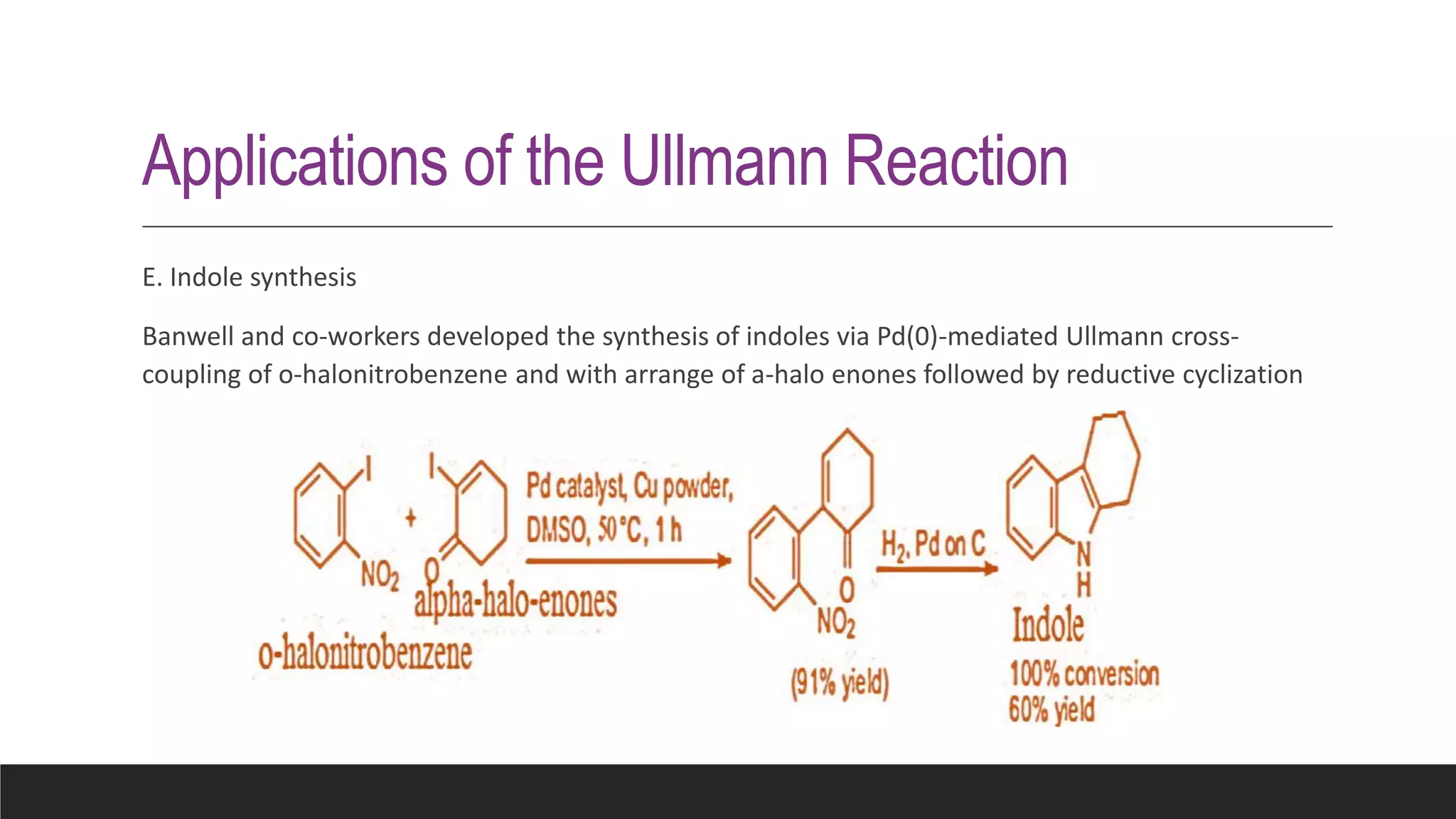
The Ullmann reaction involves the copper-catalyzed formation of a carbon-carbon bond between two aryl halides. It occurs through an oxidative addition of the aryl halide to a copper(I) species, followed by reductive elimination forming the biaryl product. The Ullmann reaction can be used to synthesize symmetrical and unsymmetrical biaryls, diarylamines, diaryl ethers, and has been applied in gossypol and indole syntheses.