Embed presentation
Download to read offline



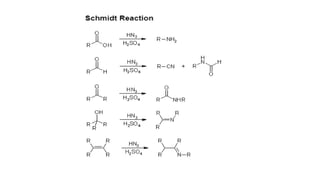




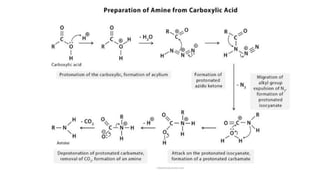
The Schmidt reaction involves reacting hydrazoic acid or alkyl azides with carbonyl compounds, alkenes, or alcohols in the presence of an acid catalyst. This results in a rearrangement that produces amines, imines, or amides along with expelled nitrogen. The Schmidt reaction can be used to synthesize compounds like amino acids, diamines, cyclic amides, and lactams that have various applications such as in drug and cosmetic synthesis.








