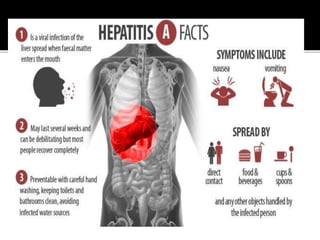
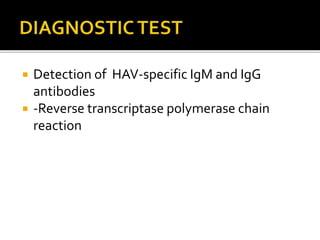
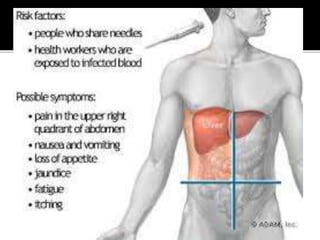
This document discusses hepatitis A and hepatitis C. It notes that hepatitis A is spread through ingestion of food or water contaminated with feces from an infected person and causes flu-like symptoms. It also states that hepatitis C is caused by the hepatitis C virus and can lead to both acute and chronic infection, with 130-150 million people having chronic hepatitis C globally. The document provides details on the symptoms, detection methods, and treatments for both hepatitis A and C.