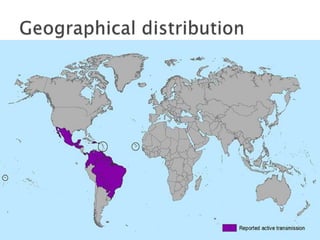
- Zika virus is an emerging mosquito-borne virus first identified in 1947 in Uganda. It spread widely in 2015-2016 throughout South and Central America and the Caribbean.
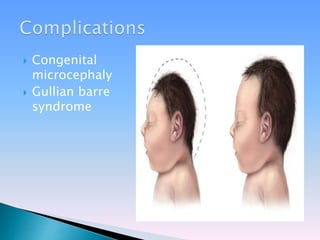
- It is transmitted primarily via the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes. While most cases are asymptomatic, it can cause mild fever and rash. A major concern is its link to microcephaly in babies born to infected mothers.
- There is no vaccine or treatment. Prevention focuses on avoiding mosquito bites through protective clothing and repellents, especially for pregnant women considering travel to outbreak areas.



















![ DEET: (N,N‐diethyl‐m‐toluamide or
N,N‐diethly‐3‐ methyl‐benzamide)
Picaridin: (KBR 3023), 2‐(2‐hydroxyethyl)‐1‐
piperidinecarboxylic acid 1‐methylpropyl
ester )
Oil of Lemon Eucalyptus* or PMD
(para‐Menthane‐3,8‐ diol) the synthesized
version of oil of lemon eucalyptus
IR3535 (Chemical (Chemical Name:
3‐[N‐Butyl‐N‐acetyl] acetyl]‐ aminopropionic
acid, ethyl ester)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/zikavirus-160207110239/85/Zika-virus-24-320.jpg)