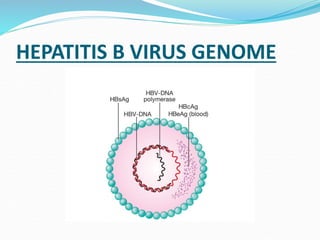
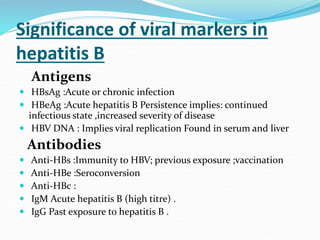
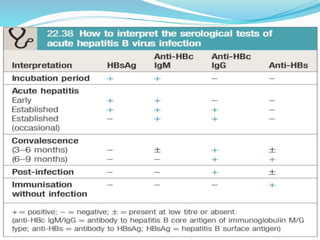
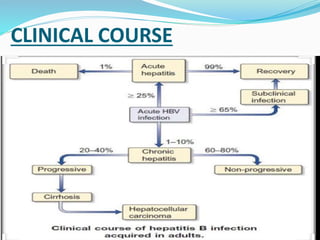
Acute hepatitis can be caused by viruses, toxins, drugs, or autoimmune processes. The most common causes are viral hepatitis A, E, B, C, and D. Hepatitis A and E are usually self-limiting and do not result in chronic liver disease. Hepatitis B, C, and D can become chronic, increasing the risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer. Symptoms of acute hepatitis include fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, and jaundice. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms; vaccination helps prevent hepatitis A and B. Complications can include liver failure, chronic liver disease, or aplastic anemia.