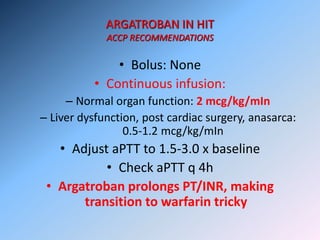
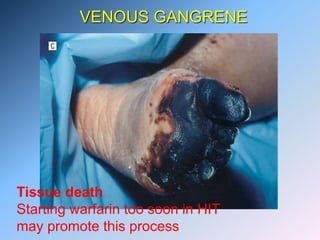
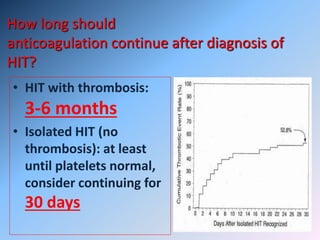
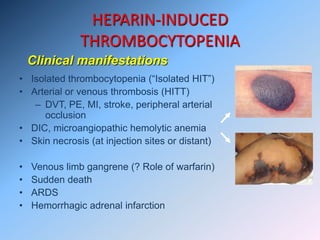
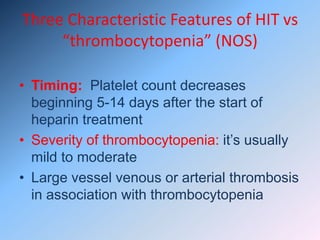
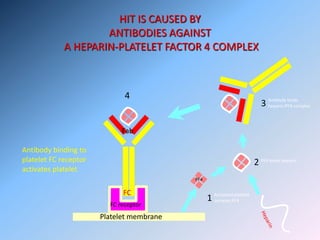
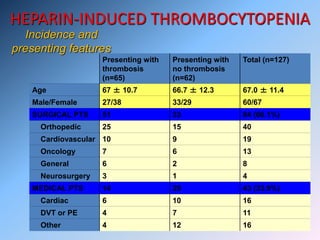
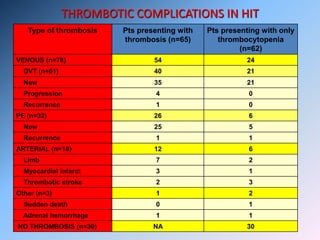
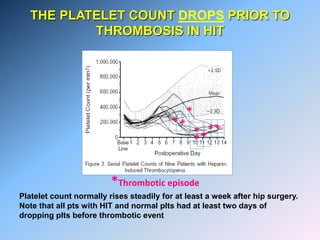
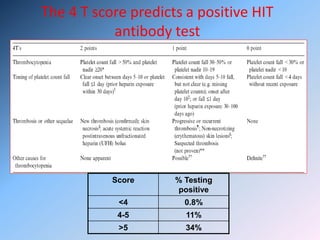
The document discusses Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT). It begins by welcoming readers to a new Facebook group on the topic. HIT is then defined as isolated thrombocytopenia or thrombosis caused by heparin use. The pathogenesis involves antibodies forming against complexes of heparin and platelet factor 4. Diagnosis involves clinical features and lab tests. Treatment requires discontinuing heparin and using alternative anticoagulants like lepirudin or argatroban. Care must be taken to avoid warfarin initially due to risk of venous gangrene.



















![LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF HIT
There are 4 Tests
1. Serotonin release assay (SRA)
2. Heparin-induced platelet aggregation assay (HIPA)
3. Solid phase imunoassay (H-PF4) (Enzyme linked
immunosorbant assay [ELISA])
4. Particle gel immunoassay
HIPA: highly specific but less sensitive than SRA
SRA: Largely restricted to centers studying HIT
C-14-SRA is the “gold standard” assay with sensitivity
and specificity of 90 and nearly 100%, respectively](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heparineinducedthrombocytopenia-150321143626-conversion-gate01/85/Heparine-induced-thrombocytopenia-27-320.jpg)