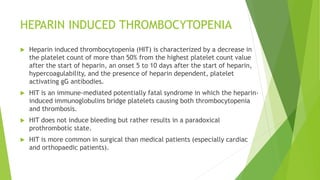
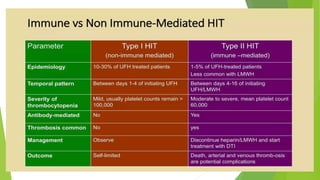
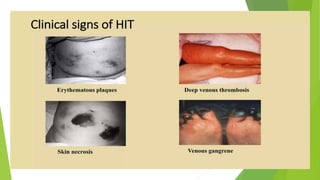
The document discusses alternatives to heparin in the context of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) and includes various anticoagulants such as low molecular weight heparin, danaparoid, and direct thrombin inhibitors. It explains the significance of anticoagulation in extracorporeal circulation and details the classification, causes, and treatment of HIT. Emphasis is placed on the need for prompt recognition and management of HIT to prevent serious thrombotic complications.





![DANAPAROID
Danapariod sodium is a synthetic heparinoid compound prepared from a porcine intestinal
source and consist of heparin sulfate (84%) dermaltan sulfate (12%) and chondroitin sulfate
(4%).
It produce the anticoagulant effect primarily via inhibition of factor Xa.
The incidence of cross reactivity with HIT antibodies is significantly lower with Danapariod.
Elimination dependent on kidney.
No reversal agent for this drug.
Bleeding and transfusion requirement were observed.
Intermittent bolus doses and continuous infusion
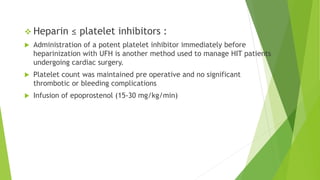
Risk Factors
Inadequate anticoagulation [formation of clot]
Severe postope bleeding
Large quantities of blood transfusion
Low molecular weight with a long half life 118-24 hrs}
Monitoring via anti Xa levels and currently no antidote
It can be useful in the management of HIT after cardiac surgery](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hitppt-240723111307-1116d918/85/Heparin-Thrombocytopenia-Presentationppt-6-320.jpg)



![ Argatroban:
Widely used in pts with HIT who requires percutaneous coronary interventions.
It is a synthetic direct thrombin inhibitor that binds reversibly to the active
site of thrombin molecule.
Primarily metabolized by liver.
Short half life 39-59 mins which is prolonged in pts with moderate
impairment [152 mins]
Disadvantages:
Bleeding / clotting
No monitoring device](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hitppt-240723111307-1116d918/85/Heparin-Thrombocytopenia-Presentationppt-10-320.jpg)