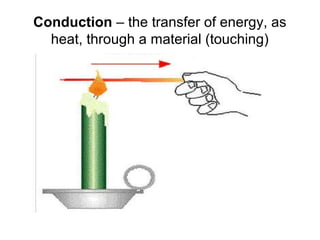
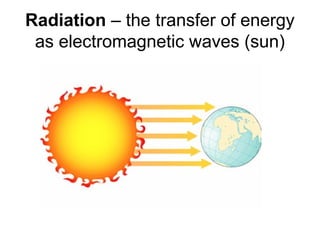
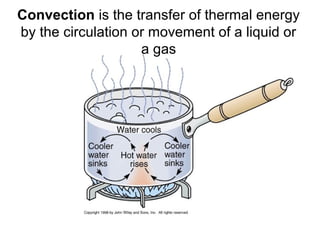
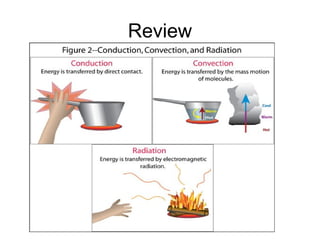
This document discusses key concepts about temperature and heat transfer. It defines temperature as a measure of how fast particles are moving, with higher temperatures indicating faster particle motion. It explains that temperature is measured using thermometers and different scales like Fahrenheit, Celsius and Kelvin. The document also describes the three main methods of heat transfer as conduction (through direct contact), convection (circulation of fluids like gases and liquids), and radiation (transfer of electromagnetic waves). It identifies materials that conduct or insulate heat well and provides formulas for calculating heat transfer.