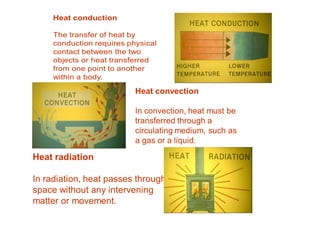
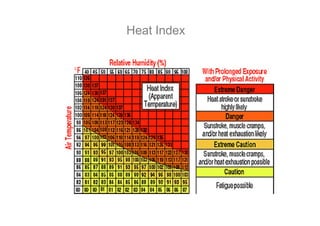
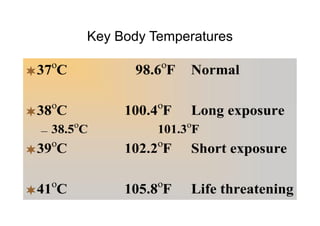
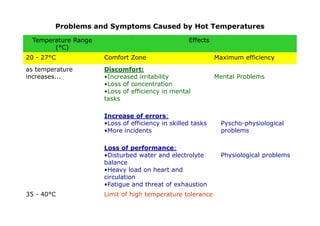
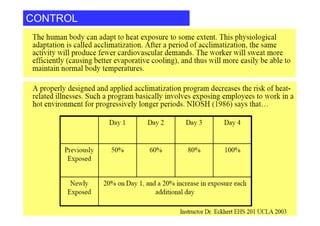
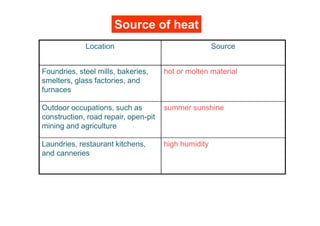
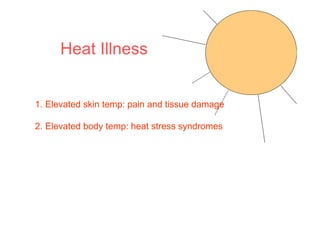
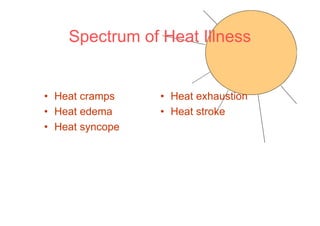
The human body responds to heat stress through various mechanisms controlled by the hypothalamic thermoregulatory center. When core body temperature rises above 37°C, the body initiates heat loss responses like sweating and vasodilation to transfer heat to the skin where it can be dissipated. If skin temperature drops below 37°C, heat production mechanisms like shivering are activated. Prolonged heat exposure can lead to heat illness ranging from mild conditions like heat cramps and heat edema to the life-threatening heat stroke. Acclimatization over 10 days allows the body to better regulate temperature and sweat in hot environments.