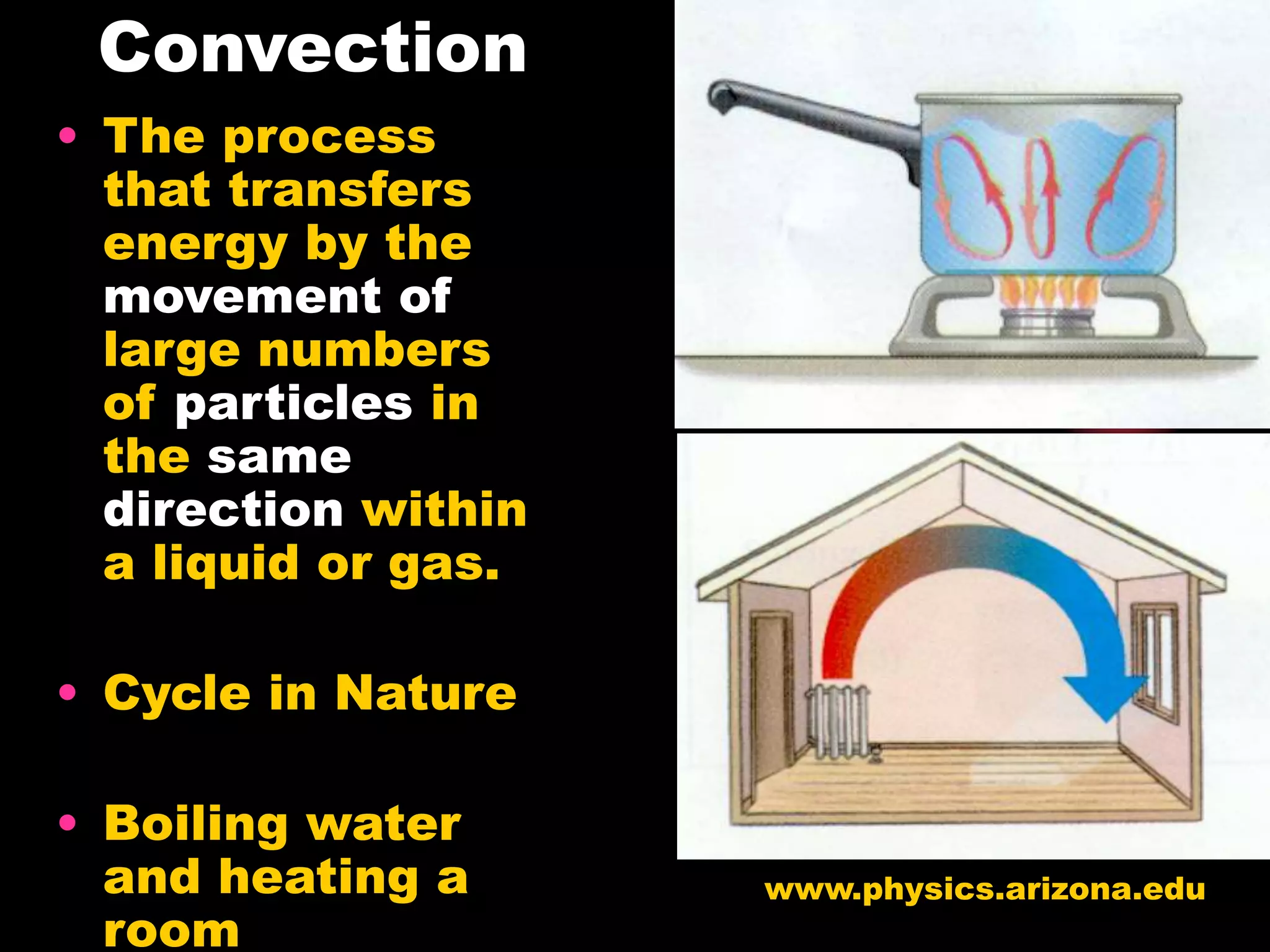
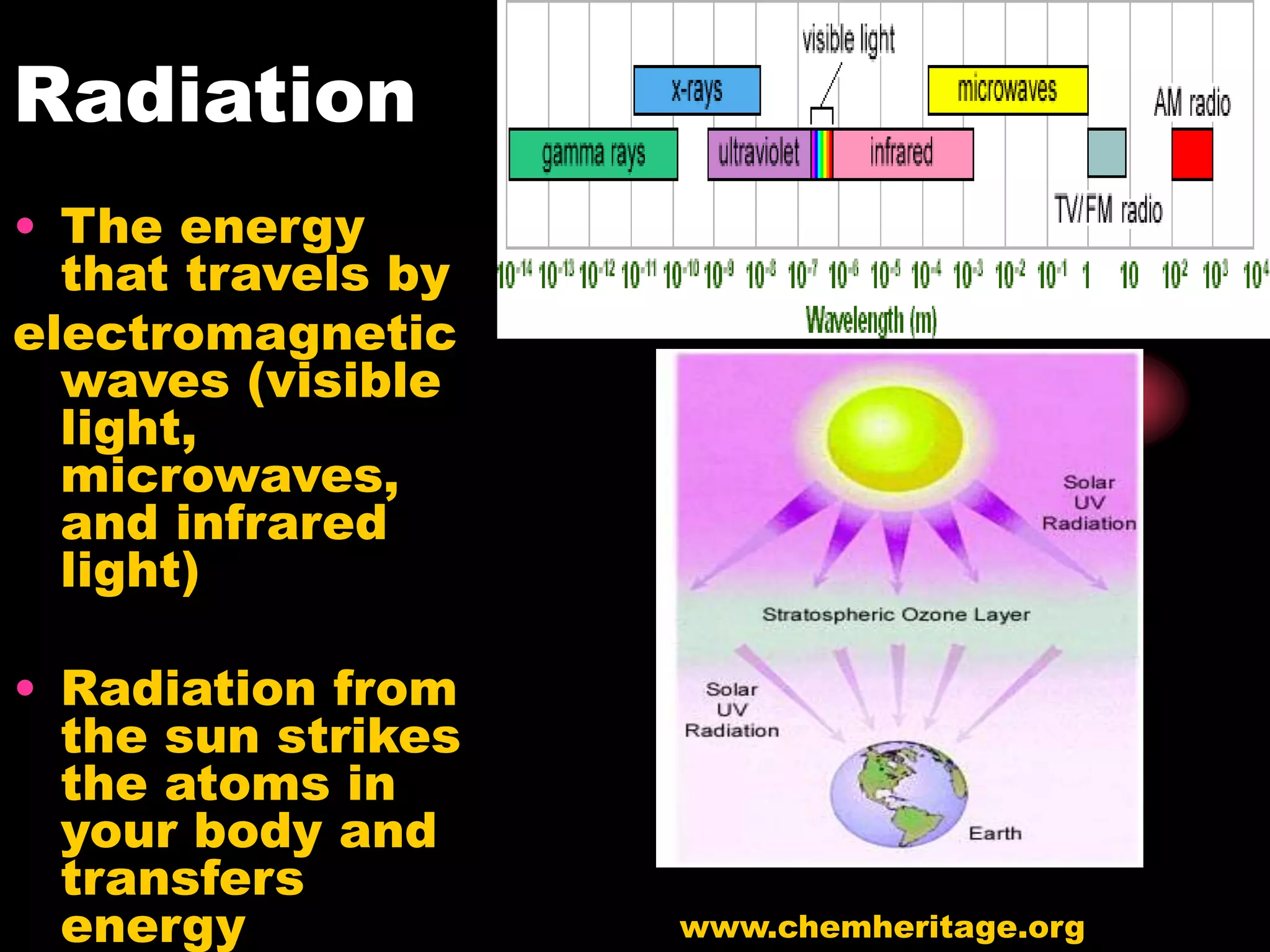
The document discusses key concepts relating to temperature, heat, and the transfer of energy. It explains that heat is the flow of energy from warmer objects to cooler objects due to temperature differences. Temperature is defined as the average kinetic energy of particles in an object, and is measured in units like Celsius and Fahrenheit. Heat is transferred between objects via three methods: conduction (direct contact), convection (movement of particles in fluids and gases), and radiation (electromagnetic waves).