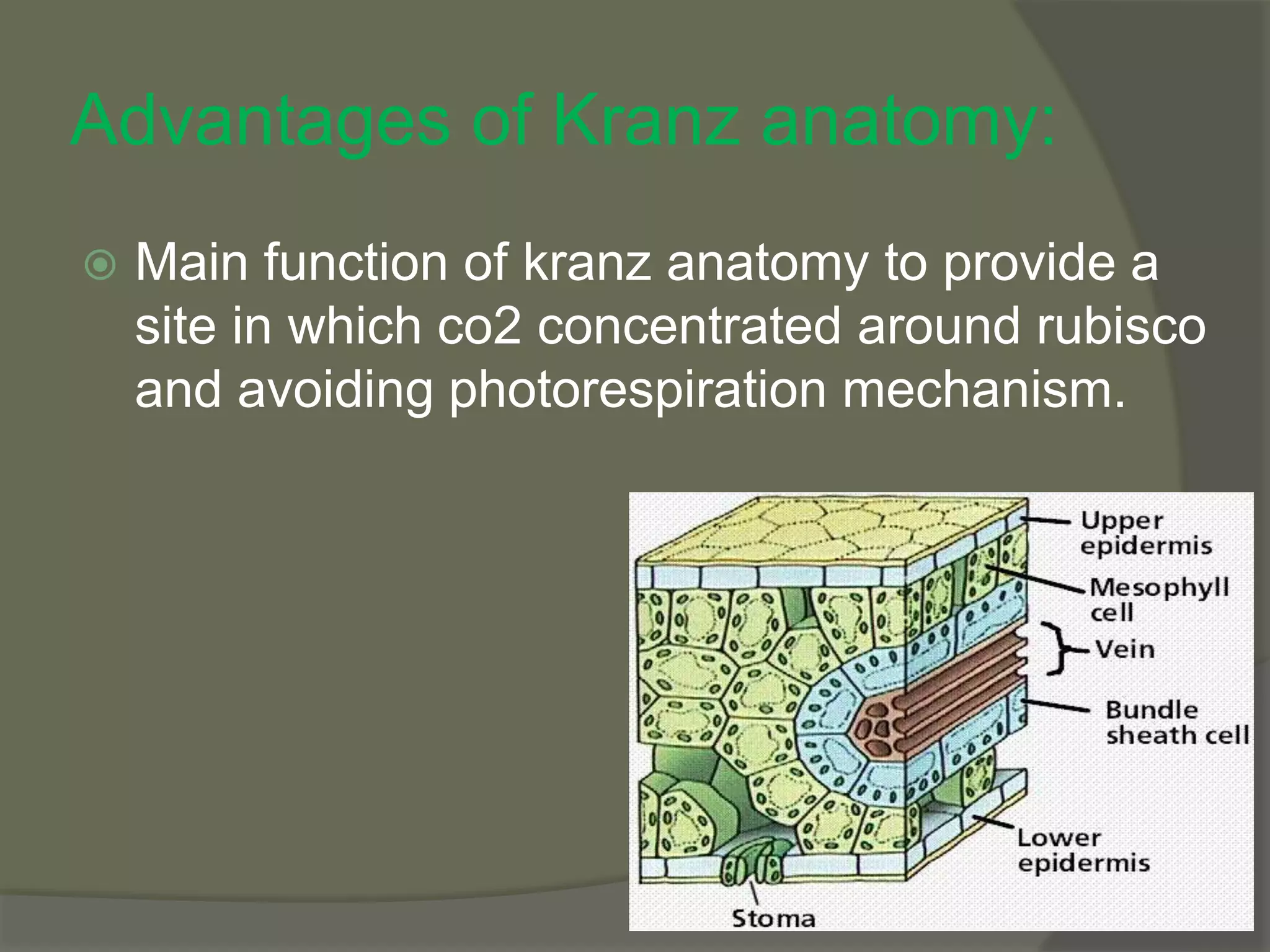
This document discusses C4 plants and their mechanism for carbon fixation. C4 plants have evolved a mechanism to fix carbon more efficiently than C3 plants in conditions like drought, heat, and low CO2/nitrogen levels. They concentrate CO2 around rubisco via a kranz anatomy structure to avoid photorespiration. The C4 mechanism involves converting phosphoenolpyruvate to oxaloacetate, then malate, transporting malate to bundle sheath cells where it is converted back to CO2 and pyruvate, regenerating phosphoenolpyruvate in a cyclic pathway. Major C4 plants include maize, sugarcane, millet, sorghum, and certain