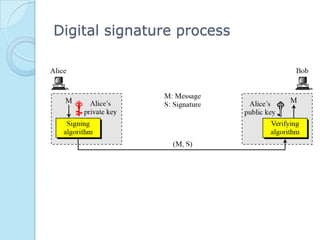
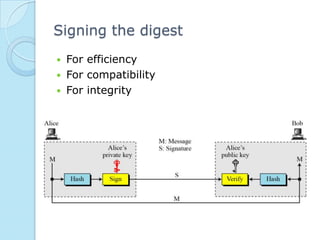
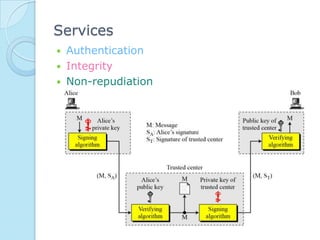
Digital signatures provide authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation for electronic documents by using asymmetric cryptography with a signing key and verification key. The digital signature process involves key generation, signing a message digest with the private key, and verifying the signature with the public key. Digital signatures are used for authentication, integrity, and non-repudiation services and are vulnerable to attacks like key-only attacks and existential or selective forgeries if the private key is compromised.