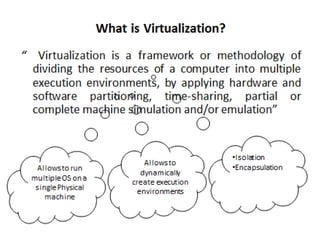
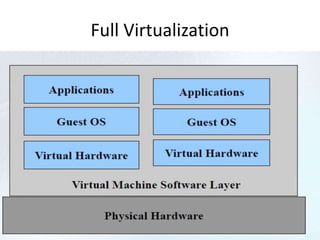
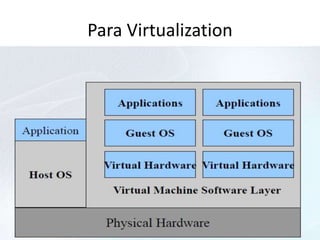
Virtualization allows for the creation of virtual machines that emulate dedicated hardware. A hypervisor software allows multiple virtual machines to run isolated operating systems like Linux and Windows on the same physical host. This improves hardware utilization and lowers costs by reducing physical servers and maintenance. There are two main types of virtual machines - process virtual machines that virtualize individual processes, and system virtual machines that provide a full virtualized environment including OS and processes. Virtualization provides benefits like better hardware usage, isolation, manageability and lower costs.











![Storage virtualization
• Storage virtualization is the process of
completely abstracting logical storage from
physical storage
• Classified into 2 types
– Block [SAN ]
– File
• Technology
– iSCSI ( Internet Small Computer Systems Interface)
– RAID 0,1,5,6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/virtualization-240102235800-95af267a/85/Virtualization-pptx-19-320.jpg)
