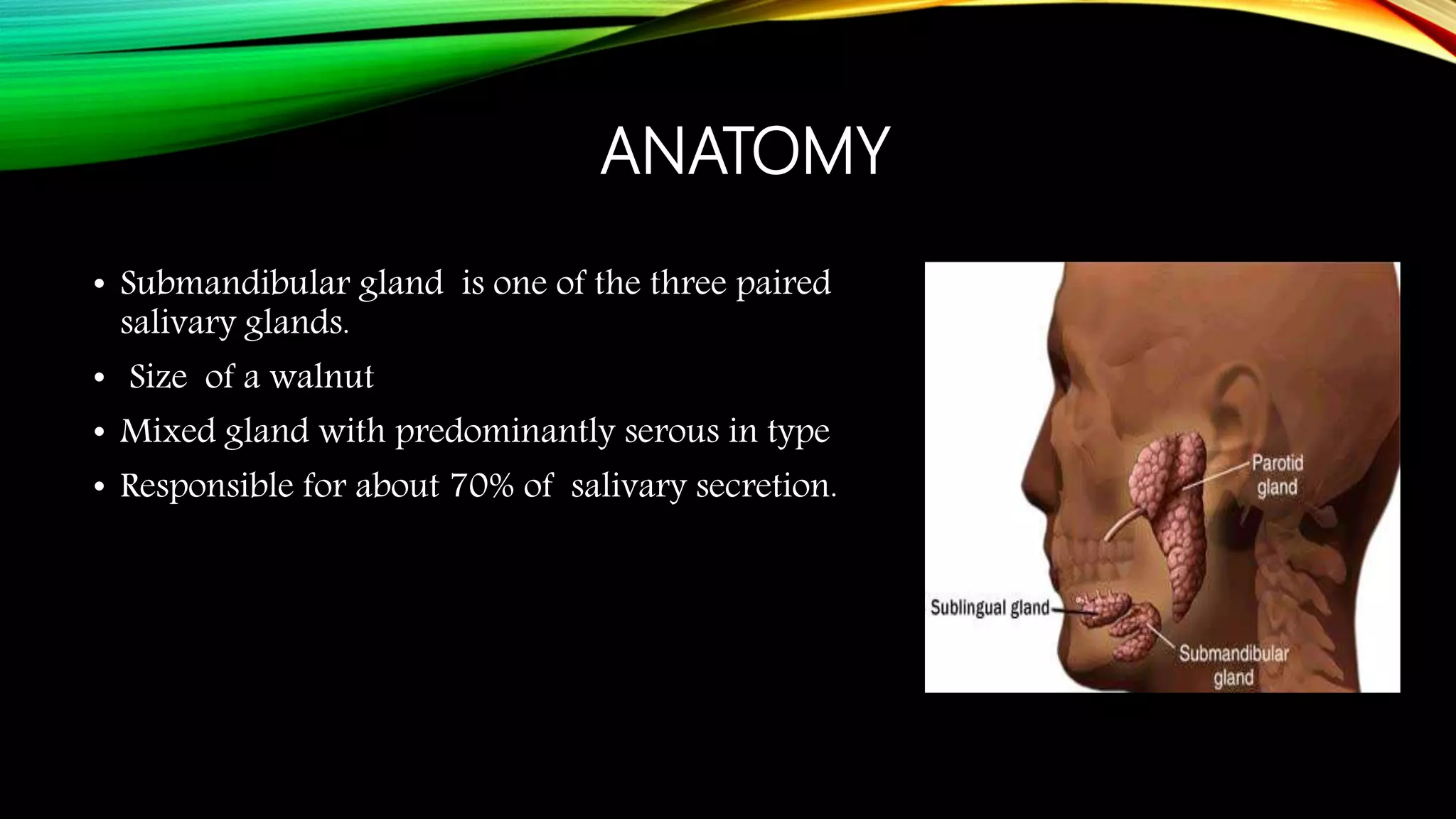
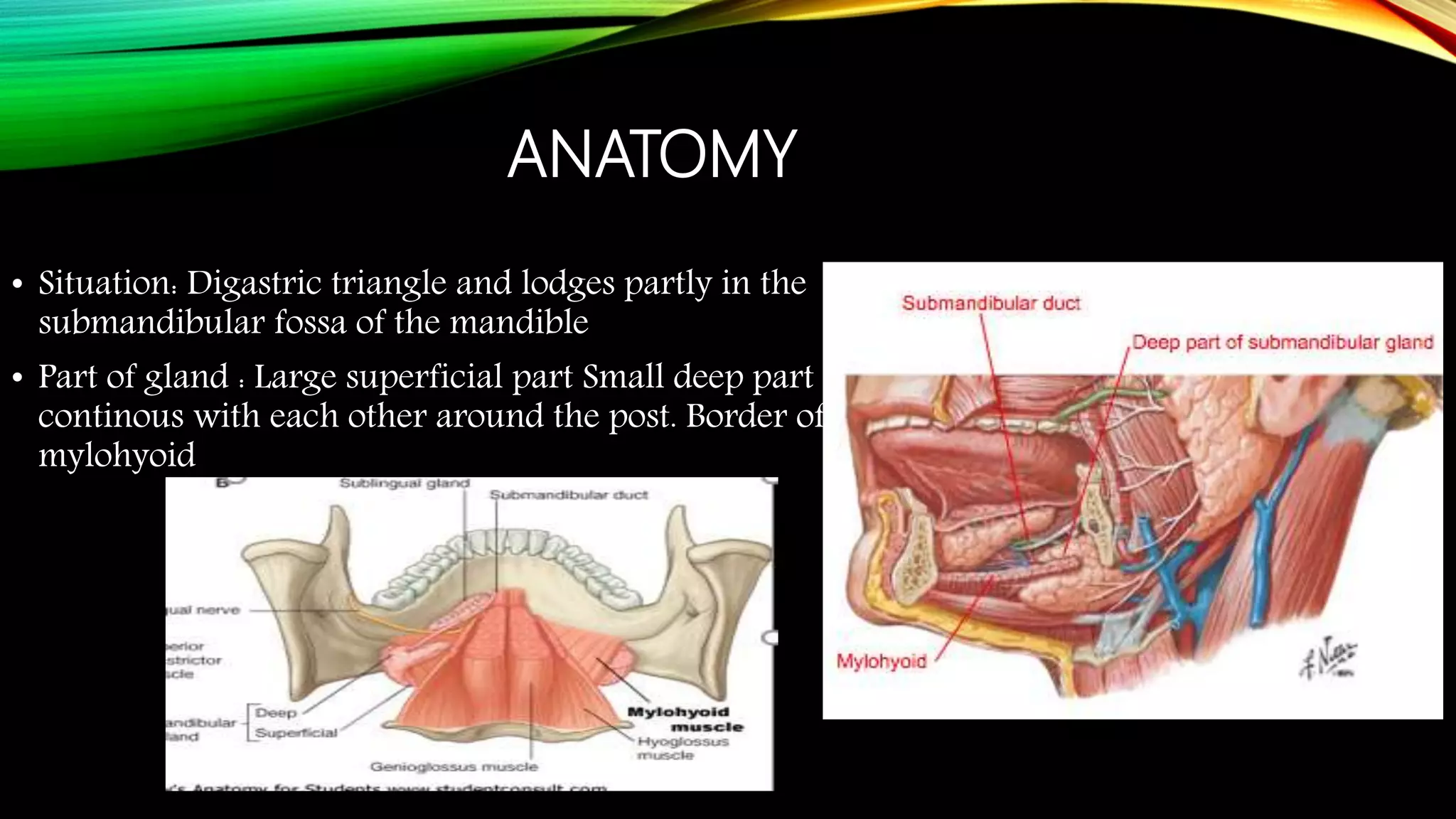
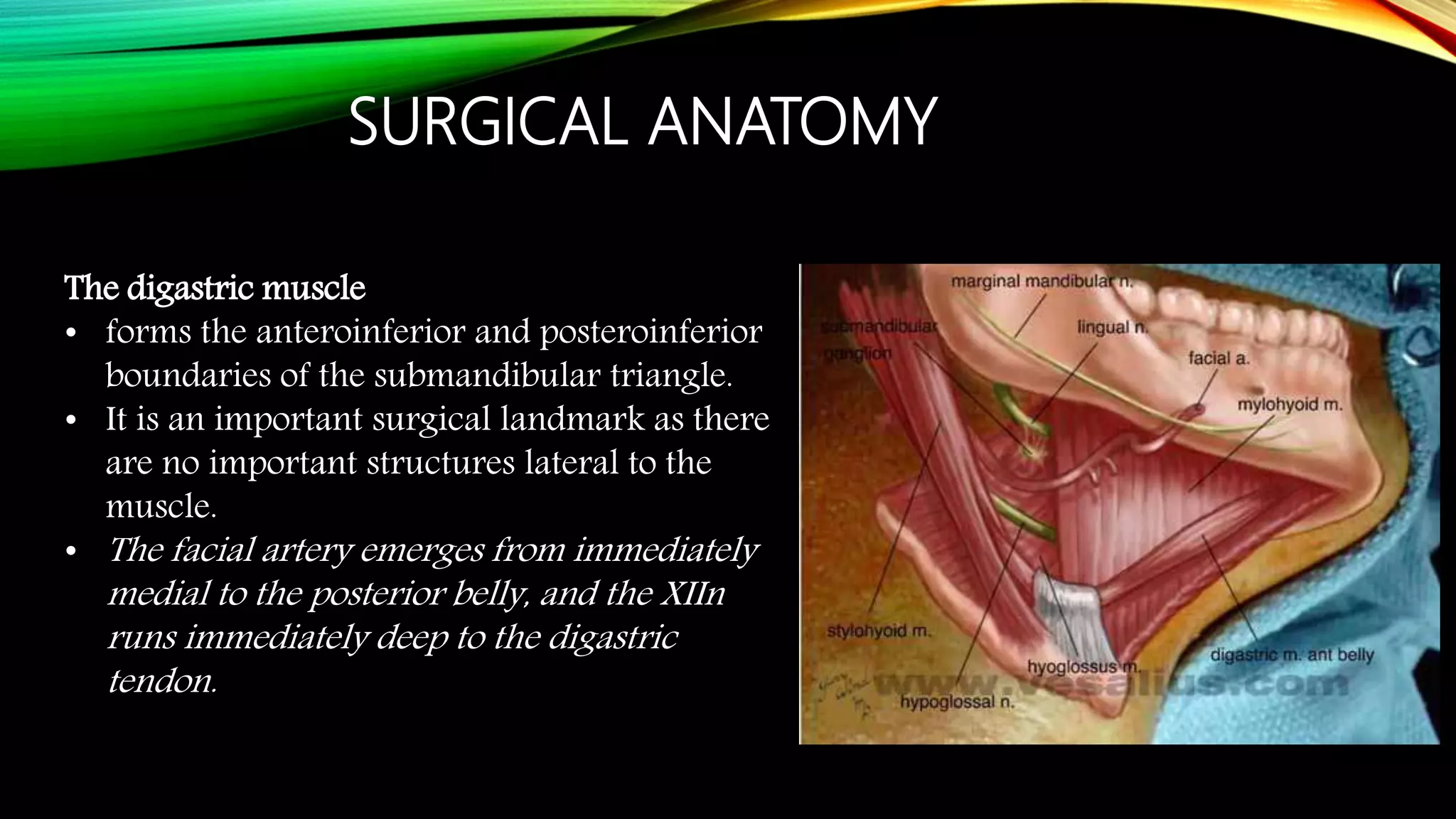
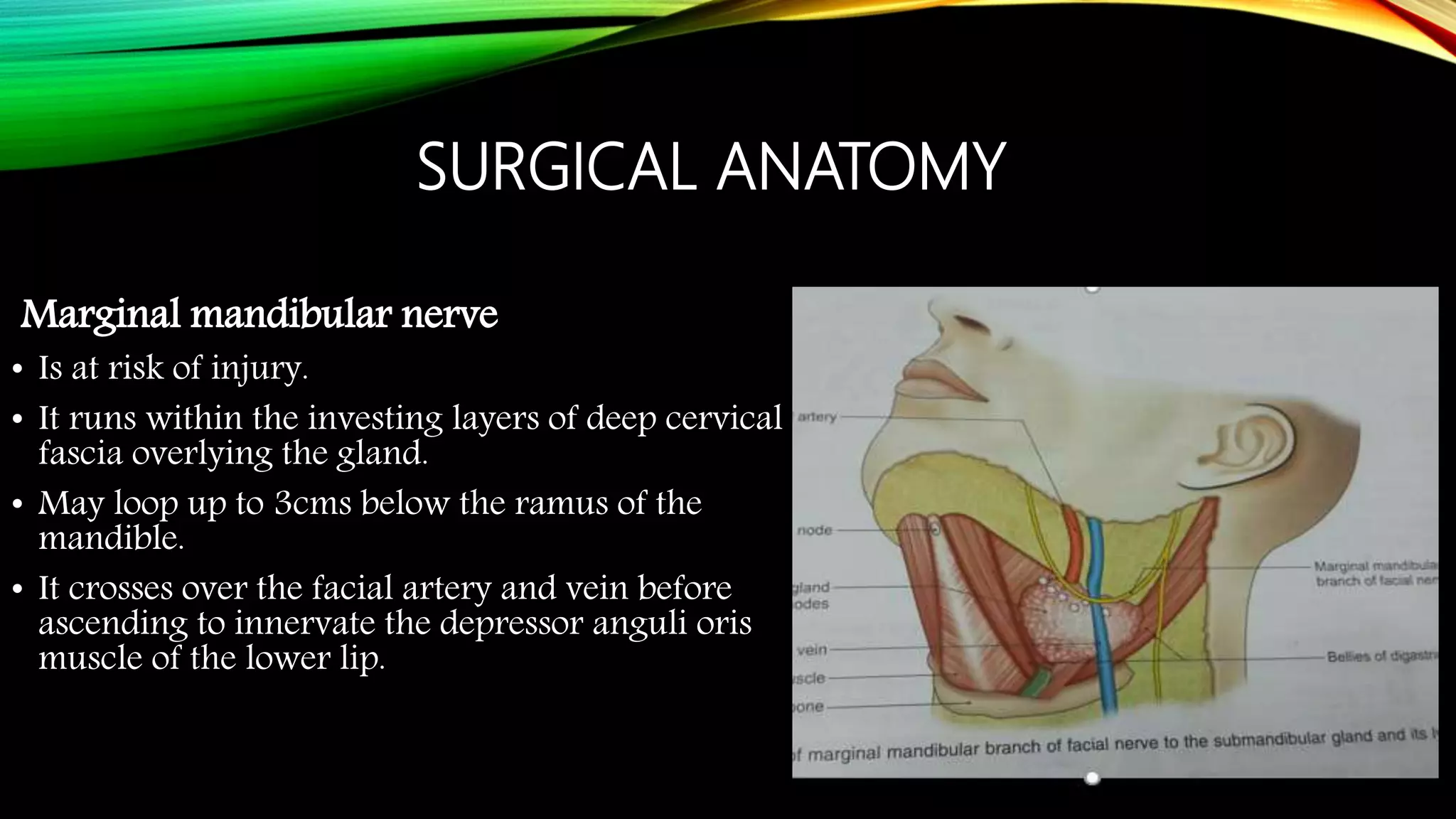
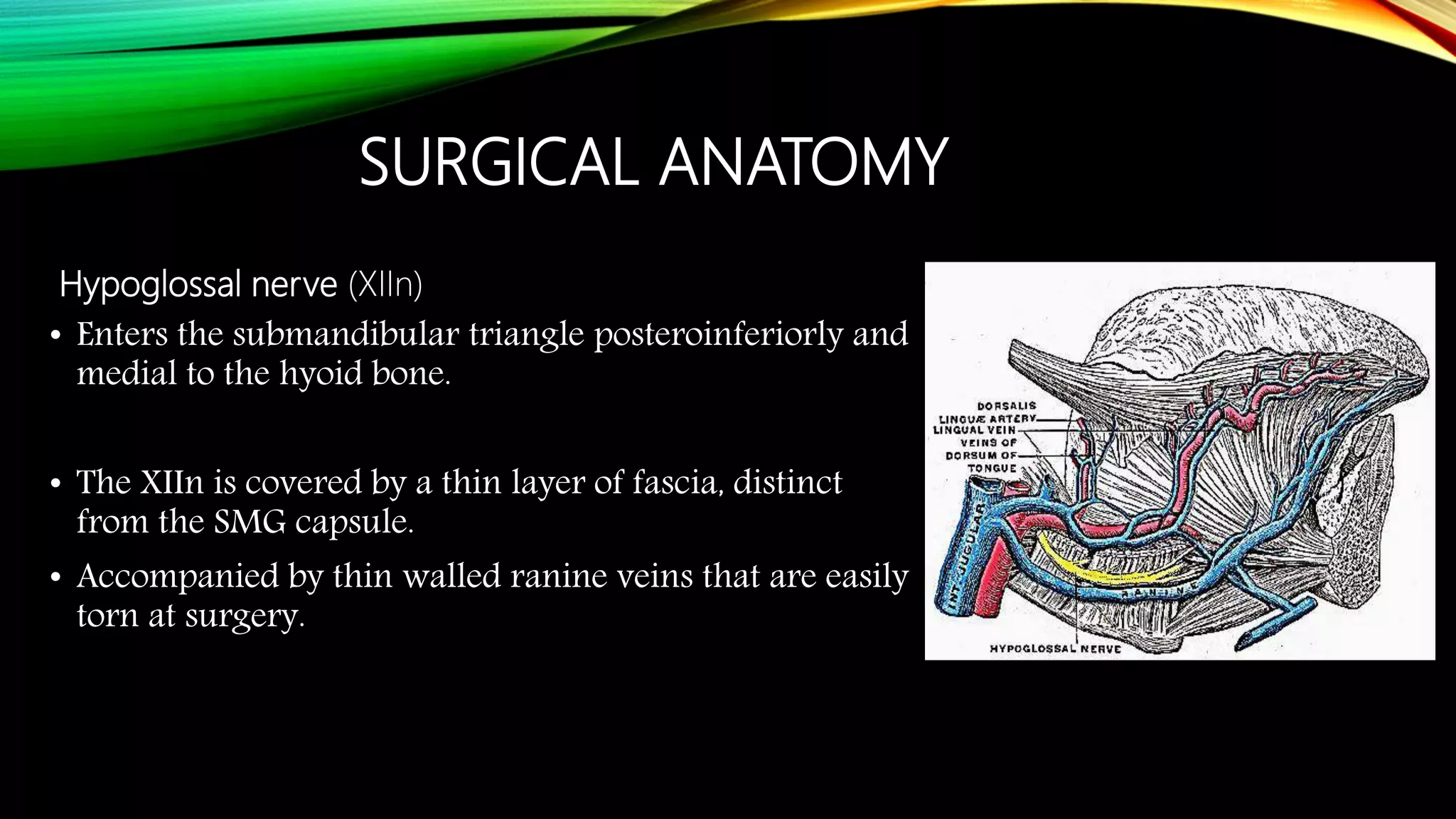
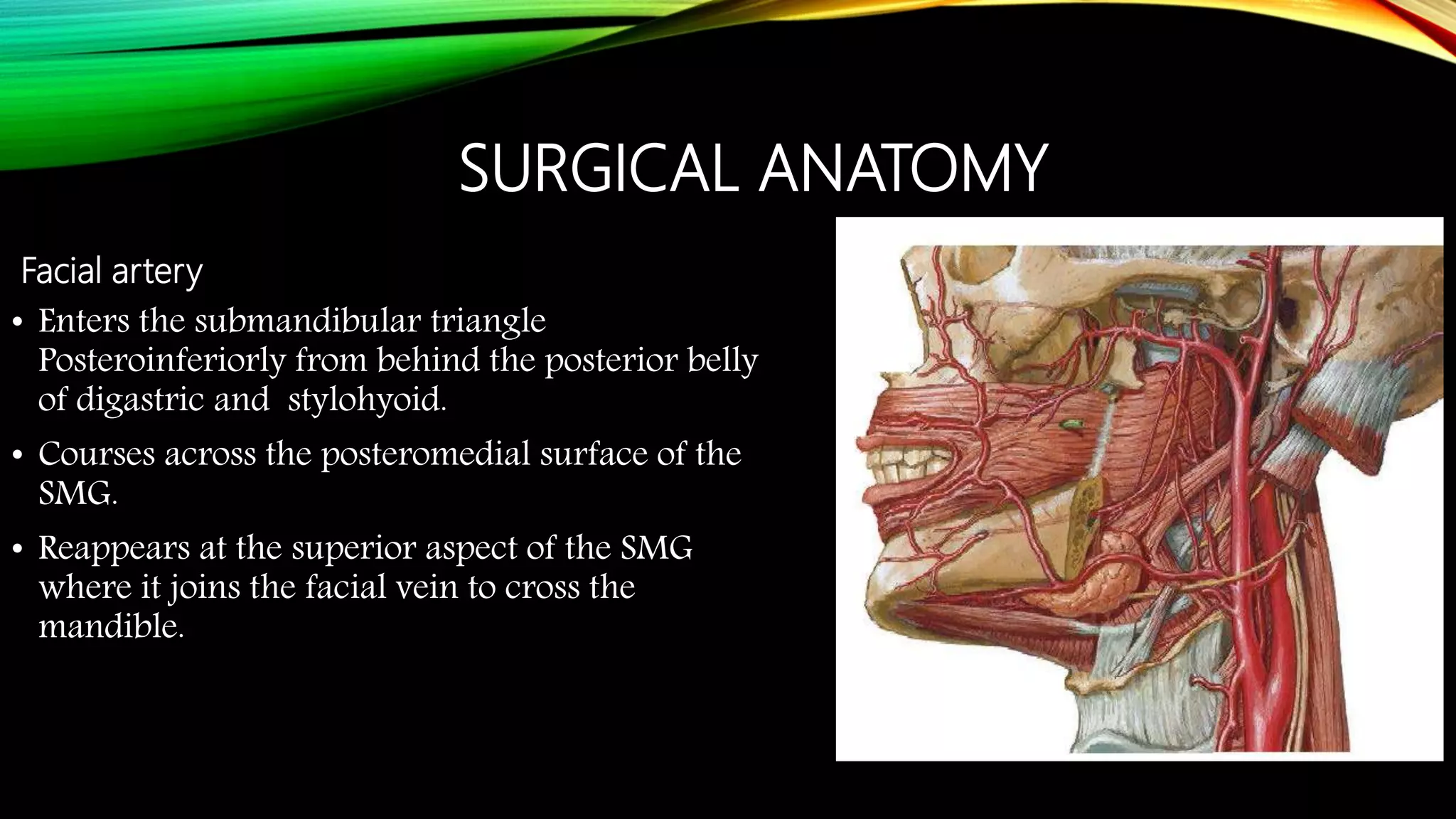
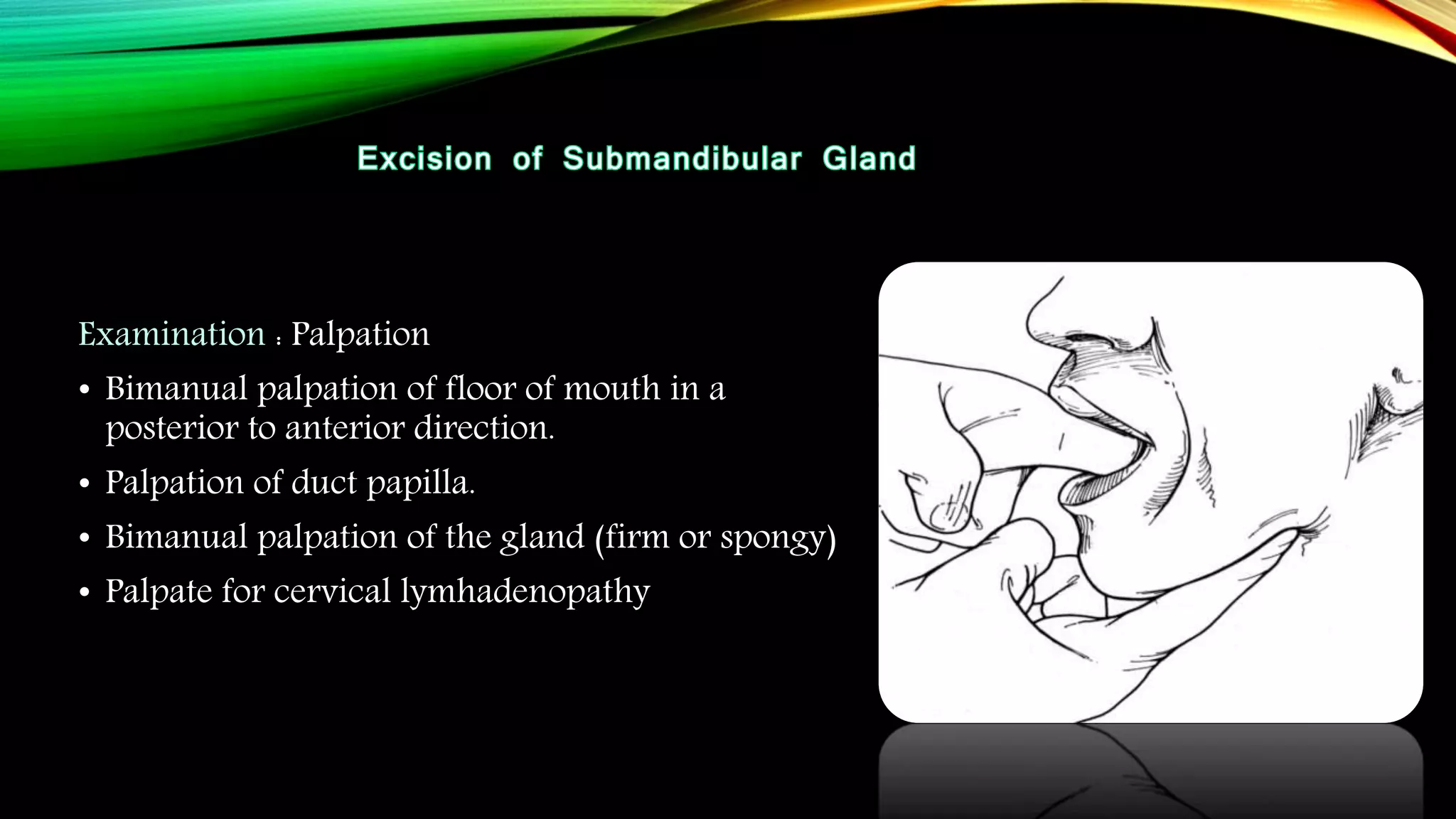
The submandibular gland can be removed through either a transcervical or transoral approach. Key anatomical structures include the marginal mandibular nerve, lingual nerve, hypoglossal nerve, facial artery and vein, and Wharton's duct. The transoral approach has less risk of marginal mandibular nerve injury but a narrower surgical field. Indications for removal include recurrent enlargement, salivary stones, infection, or suspected neoplasm. Care must be taken to identify and preserve nearby nerves and vessels during dissection and removal of the gland.