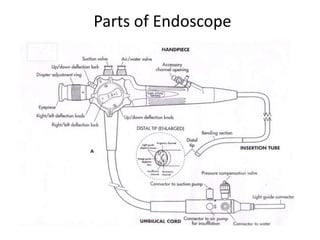
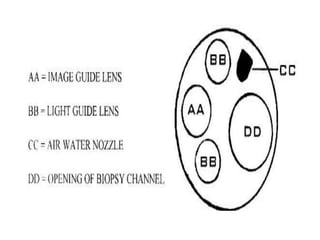
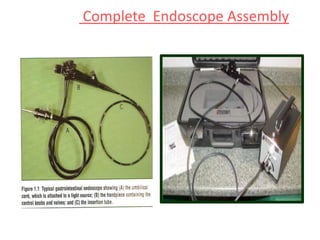
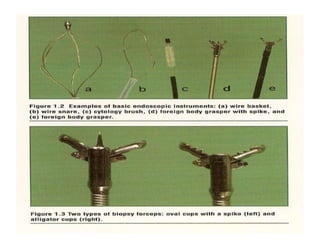
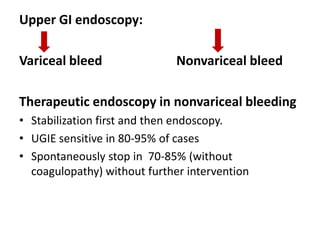
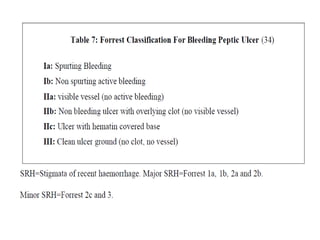
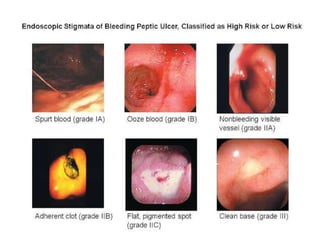
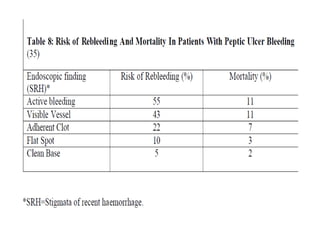
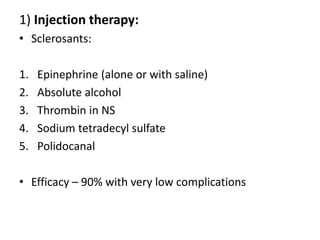
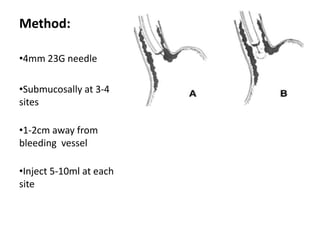
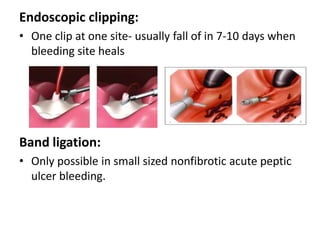
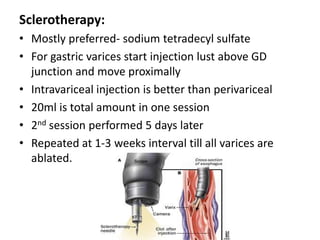
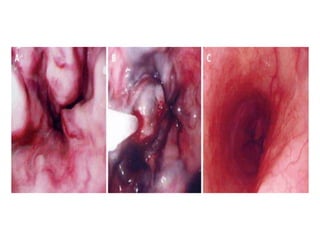
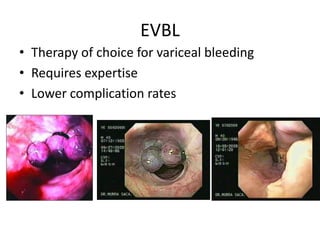
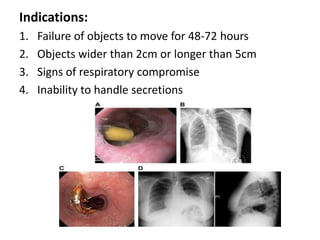
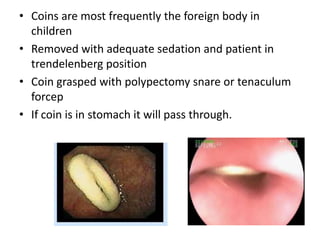
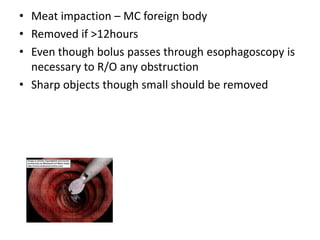
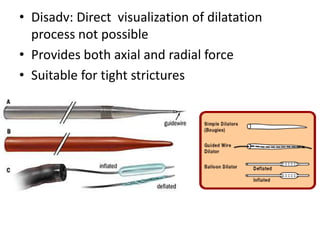
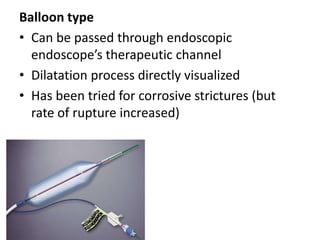
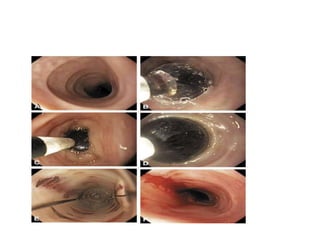
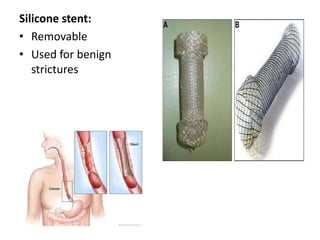
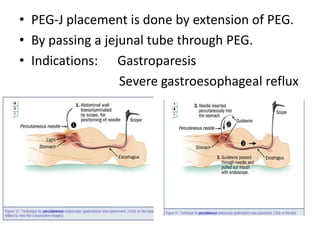
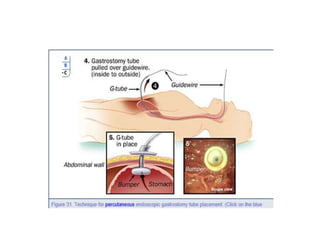
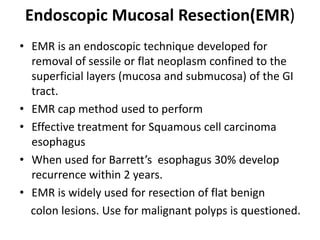
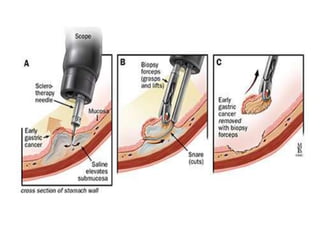
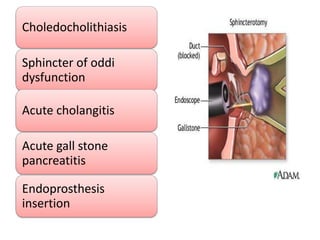
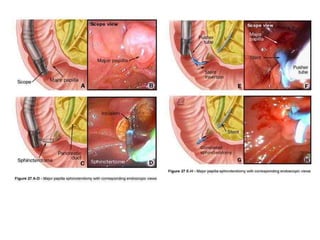
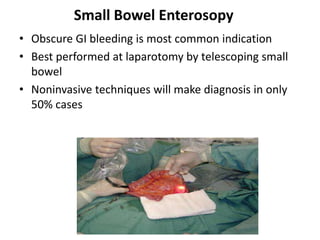
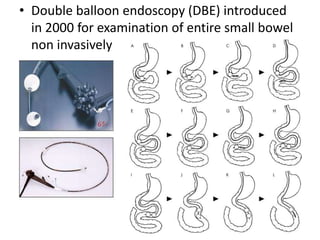
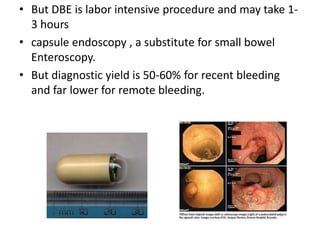
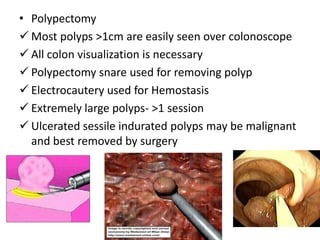
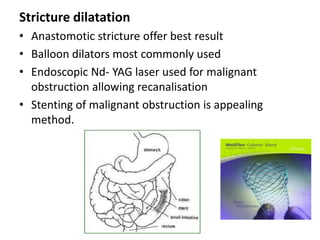
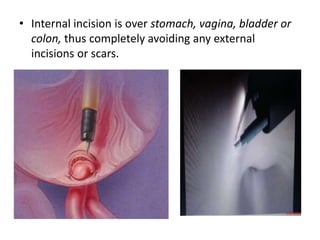
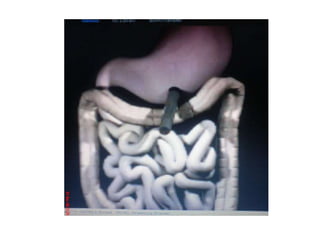
Endoscopy involves examining the interior of hollow organs using an endoscope. It has become an important tool for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in GI surgery. Key developments include the first endoscopes in the early 1800s, and the modern fiberoptic endoscope in the 1950s. Common endoscopic procedures today include upper and lower GI endoscopy, ERCP, EUS, and PEG/PEG-J placement. Endoscopy is used to diagnose and treat conditions like GI bleeding, varices, strictures, cancers, and stones. Procedures include biopsy, polypectomy, dilation, ablation, ligation, and stent/drain placement.