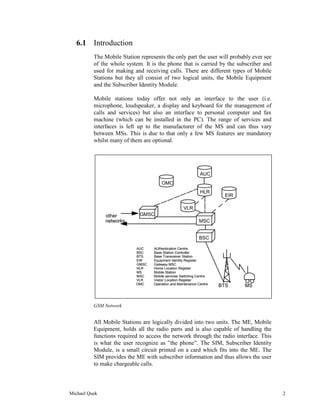
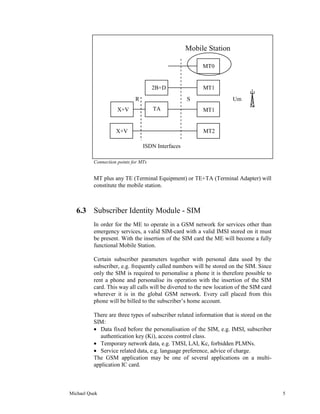
The document describes the key components and features of a mobile station. It discusses the mobile equipment (ME) which contains the radio components and allows network access. It also describes the subscriber identity module (SIM) card which provides subscriber information to allow chargeable calls and personalize the ME. It outlines the basic, supplementary and additional features a mobile station may have such as calling number display, keypad functions and short message capabilities.