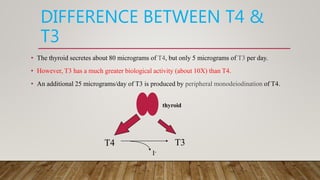
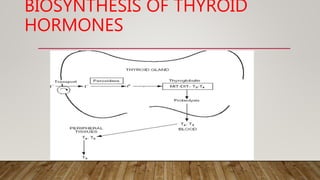
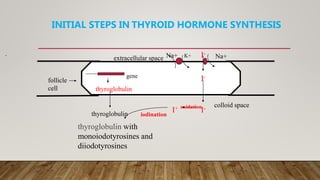
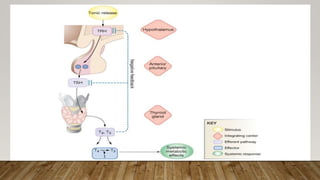
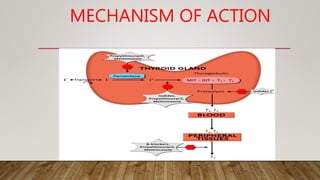
The thyroid gland produces three main hormones: T4, T3, and calcitonin. T4 is produced in larger amounts than T3. Both are produced through a process involving iodine uptake and binding to tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin within the thyroid follicle. T3 has greater biological activity than T4. Hypothyroidism occurs when not enough hormones are produced, while hyperthyroidism is an overproduction. Diseases are treated through antithyroid drugs, radioactive iodine therapy, or thyroid surgery.